New research finds working memory is the key to early academic achievement
Finding the roots of illiteracy
2014-07-08
(Press-News.org) Working memory in children is linked strongly to reading and academic achievement, a new study from the University of Luxembourg and partner Universities from Brazil* has shown. Moreover, this finding holds true regardless of socio-economic status. This suggests that children with learning difficulties might benefit from teaching methods that prevent working memory overload. The study was published recently in the scientific journal "Frontiers in Psychology".
The study was conducted in Brazil on 106 children between 6 and 8 from a range of social backgrounds, with half living under the official poverty line. Similar studies have been conducted in the English-speaking world, so it was interesting to see that the results were similar in this highly-unequal, Portuguese-speaking society.
The study sought to identify the cognitive skills underpinning learning success. Children were tested for IQ and so-called "executive functions", a set of cognitive processes that we use to control our thoughts and actions, including how we remember information, control our emotions, pay attention and shift between thoughts. These results were compared to attainment in reading, spelling, mathematics, language and science. The results show that a child's working memory skills - their ability to hold and work with information in mind - predicted success in all aspects of learning, regardless of IQ. Moreover, most children identified by their teachers as "poor readers" struggle with their working memory.
"Our findings suggest the importance of early screening and intervention, especially in the context of poverty. At present, poor working memory is rarely identified by teachers," said project leader Dr. Pascale Engel de Abreu, Associate Professor at the University of Luxembourg "Poor literacy, low academic achievement and living in poverty create a mutually reinforcing cycle. There is a chance to break this by early identification of children with working memory problems and by helping them to acquire the mental tools which will enable them to learn," she added.
INFORMATION:
* Universidade Federal da Bahia (UFBA), Universidade Federal de São Paulo (UNIFESP), Universidade de São Paulo (USP)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sandalwood scent facilitates wound healing and skin regeneration
2014-07-08
Skin cells possess an olfactory receptor for sandalwood scent, as researchers at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum have discovered. Their data indicate that the cell proliferation increases and wound healing improves if those receptors are activated. This mechanism constitutes a possible starting point for new drugs and cosmetics. The team headed by Dr Daniela Busse and Prof Dr Dr Dr med habil Hanns Hatt from the Department for Cellphysiology published their report in the "Journal of Investigative Dermatology".
The nose is not the only place where olfactory receptors occur
Humans ...
Treatment-resistant hypertension requires proper diagnosis
2014-07-08
High blood pressure—also known as hypertension—is widespread, but treatment often fails. One in five people with hypertension does not respond to therapy. This is frequently due to inadequate diagnosis, as Franz Weber and Manfred Anlauf point out in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2014; 111: 425–31).
If a patient's blood pressure is not controlled by treatment, this can be due to a number of reasons. Often it is the medication the patient is on. Some patients may be taking other medicines – in addition to their antihypertensive ...
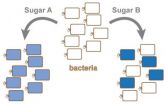
When faced with some sugars, bacteria can be picky eaters
2014-07-08
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of Minnesota have found for the first time that genetically identical strains of bacteria can respond very differently to the presence of sugars and other organic molecules in the environment, with some individual bacteria devouring the sugars and others ignoring it.
"This highlights the complexity of bacterial behaviors and their response to environmental conditions, and how much we still need to learn," says Dr. Chase Beisel, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State ...
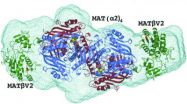
A possible pathway for inhibiting liver and colon cancer is found
2014-07-08
A group of scientists from Spain, the UK and the United States has revealed the structure of a protein complex involved in liver and colon cancers. Both of these types of cancer are of significant social and clinical relevance as in 2012 alone, liver cancer was responsible for the second highest mortality rate worldwide, with colon cancer appearing third in the list.
The international team from CIC bioGUNE, the University of Liverpool and the US research centre USC-UCLA has successfully unravelled the mechanism by which two proteins, MATα2 and MATβ, bind to ...
KAIST develops TransWall, a transparent touchable display wall
2014-07-08
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, July 8, 2014 – At a busy shopping mall, shoppers walk by store windows to find attractive items to purchase. Through the windows, shoppers can see the products displayed, but may have a hard time imagining doing something beyond just looking, such as touching the displayed items or communicating with sales assistants inside the store. With TransWall, however, window shopping could become more fun and real than ever before.
Woohun Lee, a professor of Industrial Design at KAIST, and his research team have recently developed TransWall, a two-sided, ...
Travel campaign fuels $1B rise in hospitality industry
2014-07-08
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- The Obama administration's controversial travel-promotion program has generated a roughly $1 billion increase in the value of the hospitality industry and stands to benefit the U.S. economy in the long run.
So finds the first scientific evidence, from a Michigan State University-led study, showing a positive economic impact of the Travel Promotion Act. Congress is currently reviewing whether to extend the law, which went into effect in March 2010.
"We found positive stock market reactions related to the passage of the act and therefore agree ...
Low doses of arsenic cause cancer in male mice
2014-07-08
Mice exposed to low doses of arsenic in drinking water, similar to what some people might consume, developed lung cancer, researchers at the National Institutes of Health have found.
Arsenic levels in public drinking water cannot exceed 10 parts per billion (ppb), which is the standard set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. However, there are no established standards for private wells, from which millions of people get their drinking water.
In this study, the concentrations given to the mice in their drinking water were 50 parts per billion (ppb), 500 ppb, ...
Recalled yogurt contained highly pathogenic mold
2014-07-08
DURHAM, N.C. -- Samples isolated from Chobani yogurt that was voluntarily recalled in September 2013 have been found to contain the most virulent form of a fungus called Mucor circinelloides, which is associated with infections in immune-compromised people.
The study by Duke University scientists shows that this strain of the fungus can survive in a mouse and be found in its feces as many as 10 days after ingestion.
In August and September 2013, more than 200 consumers of contaminated Chobani Greek Yogurt became ill with vomiting, nausea and diarrhea. The U.S. Food ...
Shining light on the 100-year mystery of birds sensing spring for offspring
2014-07-08
Nagoya, Japan – Professor Takashi Yoshimura and colleagues of the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM) of Nagoya University have finally found the missing piece in how birds sense light by identifying a deep brain photoreceptor in Japanese quails, in which the receptor directly responds to light and controls seasonal breeding activity. Although it has been known for over 100 years that vertebrates apart from mammals detect light deep inside their brains, the true nature of the key photoreceptor has remained to be a mystery up until now. This study led by ...
A healthy lifestyle adds years to life
2014-07-08
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), cancer, diabetes and chronic respiratory disorders - the incidence of these non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is constantly rising in industrialised countries. The Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is, therefore, in the process of developing a national prevention strategy with a view to improving the population's health competence and encouraging healthier behaviour. Attention is focusing, amongst other things, on the main risk factors for these diseases which are linked to personal behaviour – i.e. tobacco smoking, an unhealthy diet, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] New research finds working memory is the key to early academic achievementFinding the roots of illiteracy