(Press-News.org) A Swiss research study conducted last year showed that the full moon affects sleep. The findings demonstrated that people average 20 minutes less sleep, take five minutes longer to fall asleep and experience 30 minutes more of REM sleep, during which most dreaming is believed to occur.
Different outcome
Numerous studies through the years have attempted to prove or disprove the hypothesis that lunar phases affect human sleep. But results have been hard to repeat. A group of researchers at the famed Max Planck Institute and elsewhere analyzed data from more than 1,000 people and 26,000 nights of sleep, only to find no correlation.
International researchers are being urged to publish their results in hopes of getting to the bottom of the question. Michael Smith and his co-researchers at Sahlgrenska Academy have analyzed data generated by a previous sleep study and compared them with the lunar cycle.
20 minutes less sleep
Based on a study of 47 healthy 18-30 year-olds and published in Current Biology, the results support the theory that a correlation exists.
"Our study generated findings similar to the Swiss project," Michael Smith says. "Subjects slept an average of 20 minutes less and had more trouble falling asleep during the full moon phase. However, the greatest impact on REM sleep appeared to be during the new moon."
More susceptible brain
The retrospective study by the Gothenburg researchers suggests that the brain is more susceptible to external disturbances when the moon is full.
"The purpose of our original study was to examine the way that noise disturbs sleep," Mr. Smith continues. "Re-analysis of our data showed that sensitivity, measured as reactivity of the cerebral cortex, is greatest during the full moon."
Greater cortical reactivity was found in both women and men, whereas only men had more trouble falling asleep and slept less when the moon was full. Skeptics warn that both age and gender differences may be a source of error, not to mention more subtle factors such as physical condition and exposure to light during the day.
Need for more studies
Though fully aware of the issues, Mr. Smith is not prepared to dismiss the results of the Gothenburg study.
"The rooms in our sleep laboratories do not have any windows," he says. "So the effect we found cannot be attributable to increased nocturnal light during full moon. Thus, there may be a built-in biological clock that is affected by the moon, similar to the one that regulates the circadian rhythm. But all this is mere speculation – additionally, more highly controlled studies that target these mechanisms are needed before more definitive conclusions can be drawn."
INFORMATION:
The article Human sleep and cortical reactivity are influenced by lunar phase is published in Current Biology.
Contradictory findings about the effect of the full moon on sleep
2014-07-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Collisions with robots -- without risk of injury
2014-07-08
Everybody has experienced this: You aren't careful for just one moment and suddenly you run into the edge of a table. At first, it hurts. A little later, a bruise starts to appear. What falls into the category of "nothing bad, but aggravating" in the case of a table, takes on a new dimension when the colliding partner is a robot, because such a collision can injure humans seriously. That is why these mechanical assistants usually still work behind protective barriers. Since some applications require humans and robots to work hand-in-hand, though, their cooperation has become ...
Preterm babies more likely to survive in larger newborn care units
2014-07-08
Premature newborns are 32% less likely to die if they are admitted to high volume neonatal units rather than low volume, according to new research.
The study, led by the University of Warwick and published in BMJ Open, analysed data from 165 neonatal units across the UK. It found babies born at less than 33 weeks gestation were 32% less likely to die if they were admitted to high volume units, compared to low volume.
For babies born at less than 27 weeks the effect was greater, with the odds of dying almost halved when they were admitted to high volume units, compared ...
New research finds working memory is the key to early academic achievement
2014-07-08
Working memory in children is linked strongly to reading and academic achievement, a new study from the University of Luxembourg and partner Universities from Brazil* has shown. Moreover, this finding holds true regardless of socio-economic status. This suggests that children with learning difficulties might benefit from teaching methods that prevent working memory overload. The study was published recently in the scientific journal "Frontiers in Psychology".
The study was conducted in Brazil on 106 children between 6 and 8 from a range of social backgrounds, with half ...
Sandalwood scent facilitates wound healing and skin regeneration
2014-07-08
Skin cells possess an olfactory receptor for sandalwood scent, as researchers at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum have discovered. Their data indicate that the cell proliferation increases and wound healing improves if those receptors are activated. This mechanism constitutes a possible starting point for new drugs and cosmetics. The team headed by Dr Daniela Busse and Prof Dr Dr Dr med habil Hanns Hatt from the Department for Cellphysiology published their report in the "Journal of Investigative Dermatology".
The nose is not the only place where olfactory receptors occur
Humans ...
Treatment-resistant hypertension requires proper diagnosis
2014-07-08
High blood pressure—also known as hypertension—is widespread, but treatment often fails. One in five people with hypertension does not respond to therapy. This is frequently due to inadequate diagnosis, as Franz Weber and Manfred Anlauf point out in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2014; 111: 425–31).
If a patient's blood pressure is not controlled by treatment, this can be due to a number of reasons. Often it is the medication the patient is on. Some patients may be taking other medicines – in addition to their antihypertensive ...
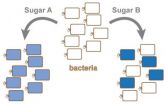
When faced with some sugars, bacteria can be picky eaters
2014-07-08
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of Minnesota have found for the first time that genetically identical strains of bacteria can respond very differently to the presence of sugars and other organic molecules in the environment, with some individual bacteria devouring the sugars and others ignoring it.
"This highlights the complexity of bacterial behaviors and their response to environmental conditions, and how much we still need to learn," says Dr. Chase Beisel, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State ...
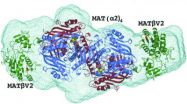
A possible pathway for inhibiting liver and colon cancer is found
2014-07-08
A group of scientists from Spain, the UK and the United States has revealed the structure of a protein complex involved in liver and colon cancers. Both of these types of cancer are of significant social and clinical relevance as in 2012 alone, liver cancer was responsible for the second highest mortality rate worldwide, with colon cancer appearing third in the list.
The international team from CIC bioGUNE, the University of Liverpool and the US research centre USC-UCLA has successfully unravelled the mechanism by which two proteins, MATα2 and MATβ, bind to ...
KAIST develops TransWall, a transparent touchable display wall
2014-07-08
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, July 8, 2014 – At a busy shopping mall, shoppers walk by store windows to find attractive items to purchase. Through the windows, shoppers can see the products displayed, but may have a hard time imagining doing something beyond just looking, such as touching the displayed items or communicating with sales assistants inside the store. With TransWall, however, window shopping could become more fun and real than ever before.
Woohun Lee, a professor of Industrial Design at KAIST, and his research team have recently developed TransWall, a two-sided, ...
Travel campaign fuels $1B rise in hospitality industry
2014-07-08
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- The Obama administration's controversial travel-promotion program has generated a roughly $1 billion increase in the value of the hospitality industry and stands to benefit the U.S. economy in the long run.
So finds the first scientific evidence, from a Michigan State University-led study, showing a positive economic impact of the Travel Promotion Act. Congress is currently reviewing whether to extend the law, which went into effect in March 2010.
"We found positive stock market reactions related to the passage of the act and therefore agree ...
Low doses of arsenic cause cancer in male mice
2014-07-08
Mice exposed to low doses of arsenic in drinking water, similar to what some people might consume, developed lung cancer, researchers at the National Institutes of Health have found.
Arsenic levels in public drinking water cannot exceed 10 parts per billion (ppb), which is the standard set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. However, there are no established standards for private wells, from which millions of people get their drinking water.
In this study, the concentrations given to the mice in their drinking water were 50 parts per billion (ppb), 500 ppb, ...