(Press-News.org) HOUSTON – (July 29, 2014) – Tough, ultralight foam of atom-thick sheets can be made to any size and shape through a chemical process invented at Rice University.
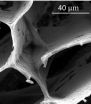
In microscopic images, the foam dubbed "GO-0.5BN" looks like a nanoscale building, with floors and walls that reinforce each other. The structure consists of a pair of two-dimensional materials: floors and walls of graphene oxide that self-assemble with the assistance of hexagonal boron nitride platelets.
The researchers say the foam could find use in structural components, as supercapacitor and battery electrodes and for gas absorption, among other applications.
The research by an international collaboration led by the Rice lab of materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan is detailed today in the online journal Nature Communications.
Graphene oxide (GO) is a variant of graphene, the hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms known for its superior strength and conductivity. It can be produced in bulk by chemically exfoliating oxidized graphite. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) looks like GO, with the same "chicken wire" array of atoms. An insulator known as "white graphene," h-BN has an ability to form seamless interfaces with graphene that has led to the creation of interesting hybrid materials at Rice and elsewhere.
Soumya Vinod, the Rice graduate student who co-led the project, said she and her colleagues expected adding h-BN to graphene oxide would toughen the resulting foam, but "the ordered, layered structure was not entirely expected."
"Once we observed the structure, we knew it was very different from the other nanoengineered foams reported and could lead to very interesting properties," she said.
Those properties include the ability to handle a great deal of strain and still bounce back to its native form. This is remarkable, Vinod said, for a material so light that a stray breath in the lab would send the small samples flying.
Both components of the new material start as cheap, plentiful powders. Atom-thick layers of graphene oxide and h-BN are chemically exfoliated from the powders, mixed in the proper proportion with a few chemical catalysts and freeze-dried. The resulting foam takes the shape of the container and is 400 times less dense than graphite.
For testing, Vinod and her colleagues made foams of pure graphene oxide and foams with h-BN at 25 and 50 percent by weight. The 50 percent h-BN version was found to be the most mechanically stable, though she expects to optimize the mix -- and increase the size -- with further experimentation. "We found that more concentration of h-BN leads to low structural integrity, but we've yet to optimize the right amount," she said.
A close-up look at the foam revealed the floors as self-assembled sheets of overlapping GO flakes. Cross-linking platelets of h-BN were uniformly distributed throughout the material and held the sheets together.
Samples the size of a pencil's eraser were compressed with one or two pennies to see how well they would bounce back.
The h-BN platelets connect to graphene oxide and absorb stress from compression and stretching, preventing the GO floors from crumbling and significantly enhancing the material's thermal stability, Vinod said. The platelets also prevented the propagation of cracks that destroyed samples with less or no h-BN.
INFORMATION:
Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, a graduate student at the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, with a complimentary appointment at Rice, is co-lead author of the paper. Co-authors include Pedro Alves da Silva Autreto, a researcher at the State University of Campinas, São Paulo, with a complimentary appointment at Rice; Rice alumnus Jaime Taha-Tijerina, a researcher at Carbon Sponge Solutions in Houston and at Viakable Technology and Research Center in Monterrey, Mexico; Rice graduate students Sehmus Ozden and Alin Cristian Chipara; Rice senior faculty fellow Robert Vajtai; Douglas Galvao, a professor at the University of Campinas; and Rice alumnus Tharangattu Narayanan, a scientist at the Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi, India. Ajayan is Rice's Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering, professor of materials science and nanoengineering and of chemistry, and chair of the Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering.
The U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research through a Multidisciplinary University Research Grant, the National Science Foundation (NSF) through the Early Concept Grants for Exploratory Research competition and the Indo-U.S. Science and Technology Forum supported the research. The researchers utilized the NSF-supported Data Analysis and Visualization Cyberinfrastructure (DAVinCI) supercomputer and the BlueBioU supercomputer, both administered by Rice's Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology.
Read the abstract at http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2014/140729/ncomms5541/full/ncomms5541.html
This news release can be found online at http://news.rice.edu/2014/07/29/tough-foam-from-tiny-sheets/
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
Related Materials:
Ajayan Research Group: http://ajayan.rice.edu
Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering: http://msne.rice.edu
Images for download:
http://news.rice.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/0804_FOAM-4-WEB.jpg
An electron microscope image of foam created at Rice University shows layers of graphene oxide stacked to form a three-dimensional structure with the help of hexagonal boron nitride linkers. (Credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University)
http://news.rice.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/0804_FOAM-5-WEB.jpg
An electron microscope image shows a connecting link in foam made of graphene oxide and hexagonal boron nitride. The tough, ultralight foam was created by materials scientists at Rice University. (Credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University)
http://news.rice.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/0804_FOAM-3-WEB.jpg
An illustration shows sheets of graphene oxide that self-assemble into the floors and walls of structured foam with help from platelets of hexagonal boron nitride that bind the sheets together. The tough, ultralight foam was created by materials scientists at Rice University. (Credit: Illustration by Pedro Alves da Silva Autreto/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just over 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go here.
Tough foam from tiny sheets
Rice University lab uses atom-thick materials to make ultralight foam
2014-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research may explain how foremost anticancer 'guardian' protein learned to switch sides
2014-07-29
Cold Spring Harbor, NY -- Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have discovered a new function of the body's most important tumor-suppressing protein. Called p53, this protein has been called "the guardian of the genome." It normally comes to the fore when healthy cells sense damage to their DNA caused by stress, such as exposure to toxic chemicals or intense exposure to the sun's UV rays. If the damage is severe, p53 can cause a cell to commit preprogrammed cell-death, or apoptosis. Mutant versions of p53 that no longer perform this vital function, on the ...
Study: Pediatric preventive care guidelines need retooling for computerized format
2014-07-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- With the increasing use of electronic medical records and health information exchange, there is a growing demand for a computerized version of the preventive care guidelines pediatricians use across the United States. In a new study, researchers from the Indiana University School of Medicine and the Regenstrief Institute report that substantial work lies ahead to convert the American Academy of Pediatrics' Bright Future's guidelines into computerized prompts for physicians, but the payoff has the potential to significantly benefit patients from birth to ...
Menu secrets that can make you slim by design
2014-07-29
If you've ever ordered the wrong food at a restaurant, don't blame yourself; blame the menu. What you order may have less to do with what you want and more to do with a menu's layout and descriptions.
After analyzing 217 menus and the selections of over 300 diners, the Cornell study published this month in the International Journal of Hospitality Management showed that when it comes to what you order for dinner, two things matter most: what you see on the menu and how you imagine it will taste.
First, any food item that attracts attention (with bold, hightlighted or ...
From 'Finding Nemo' to minerals -- what riches lie in the deep sea?
2014-07-29
As fishing and the harvesting of metals, gas and oil have expanded deeper and deeper into the ocean, scientists are drawing attention to the services provided by the deep sea, the world's largest environment. "This is the time to discuss deep-sea stewardship before exploitation is too much farther underway," says lead-author Andrew Thurber. In a review published today in Biogeosciences, a journal of the European Geosciences Union (EGU), Thurber and colleagues summarise what this habitat provides to humans, and emphasise the need to protect it.
"The deep sea realm is so ...
Genomic analysis of prostate cancer indicates best course of action after surgery
2014-07-29
(PHILADELPHIA) – There is controversy over how best to treat patients after they've undergone surgery for prostate cancer. Does one wait until the cancer comes back or provide men with additional radiation therapy to prevent cancer recurrence? Now, a new study from Thomas Jefferson University shows that a genomic tool can help doctors and patients make a more informed decision.
"We are moving away from treating everyone the same," says first author Robert Den, M.D., Assistant Professor of Radiation Oncology and Cancer Biology at Thomas Jefferson University. "Genomic ...
Optimum inertial self-propulsion design for snowman-like nanorobot
2014-07-29
Scale plays a major role in locomotion. Swimming microorganisms, such as bacteria and spermatozoa, are subjected to relatively small inertial forces compared to the viscous forces exerted by the surrounding fluid. Such low-level inertia makes self-propulsion a major challenge. Now, scientists have found that the direction of propulsion made possible by such inertia is opposite to that induced by a viscoelastic fluid. These findings have been published in EPJ E by François Nadal from the Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), in Le Barp, France, and colleagues. ...
Team studies the social origins of intelligence in the brain
2014-07-29
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — By studying the injuries and aptitudes of Vietnam War veterans who suffered penetrating head wounds during the war, scientists are tackling -- and beginning to answer -- longstanding questions about how the brain works.
The researchers found that brain regions that contribute to optimal social functioning also are vital to general intelligence and to emotional intelligence. This finding bolsters the view that general intelligence emerges from the emotional and social context of one's life.
The findings are reported in the journal Brain.
"We are ...
NOAA: Alaska fisheries and communities at risk from ocean acidification
2014-07-29
Ocean acidification is driving changes in waters vital to Alaska's valuable commercial fisheries and subsistence way of life, according to new NOAA-led research that will be published online in Progress in Oceanography.
Many of Alaska's nutritionally and economically valuable marine fisheries are located in waters that are already experiencing ocean acidification, and will see more in the near future, the study shows. Communities in southeast and southwest Alaska face the highest risk from ocean acidification because they rely heavily on fisheries that are expected to ...
Preterm children's brains can catch up years later
2014-07-29
There's some good news for parents of preterm babies – latest research from the University of Adelaide shows that by the time they become teenagers, the brains of many preterm children can perform almost as well as those born at term.
A study conducted by the University's Robinson Research Institute has found that as long as the preterm child experiences no brain injury in early life, their cognitive abilities as a teenager can potentially be as good as their term-born peers.
However, the results of the study, published in this month's issue of The Journal of Pediatrics, ...
New anesthesia technique helps show cause of obstruction in sleep apnea
2014-07-29
July 29, 2014 – A simplified anesthesia procedure may enable more widespread use of preoperative testing to demonstrate the cause of airway obstruction in patients with severe sleep apnea, suggests a study in Anesthesia & Analgesia.
Dr. Joshua H. Atkins and Dr. Jeff E. Mandel of the University of Pennsylvania and their colleagues have developed a new "ramp control" anesthetic technique for putting patients to sleep briefly-just enough to show the "obstructive anatomy" responsible for sleep apnea. The simplified technique requires no special expertise and limits drops ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
[Press-News.org] Tough foam from tiny sheetsRice University lab uses atom-thick materials to make ultralight foam