(Press-News.org) Adolescents who behave aggressively are more likely to drink alcohol and in larger quantities than their peers, according to a recent study completed in Finland. Depression and anxiety, on the other hand, were not linked to increased alcohol use. The study investigated the association between psychosocial problems and alcohol use among 4074 Finnish 13- to 18-year-old adolescents. The results were published in Journal of Adolescence.
The results indicate that smoking and attention problems also increase the probability of alcohol use. Furthermore, among girls, early menarche and parental divorce are also associated with alcohol use. The study found aggressive behaviour to be more common in girls than in boys, which is a novel result.
"The findings raise questions about a possible change in the behaviour of adolescent girls and their vulnerability during adolescent social and emotional development," says Eila Laukkanen, Professor and Chief Physician of Adolescent Psychiatry at the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital.
Out of all the study participants, 60% reported to use alcohol. Already among 15-year-olds, more than 50% reported to use alcohol. No significant differences between the alcohol use of boys and girls were found. The proportion of adolescents who use alcohol has not grown in comparison to earlier studies; however, many adolescents consume high amounts of alcohol - and even amounts that exceed the risk levels. Alcohol use that begins early in adolescence can increase the probability of mental health problems and alcohol dependence, and be detrimental to brain development.
INFORMATION:
The study was carried out in cooperation between the University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio University Hospital, the University of Tampere, and Päijät-Häme Central Hospital.
For further information, please contact:
Petri Kivimäki, MB, University of Eastern Finland, School of Medicine, pkivimak(at)student.uef.fi , +358504131469
Professor, Chief Physician Eila Laukkanen, University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital, eila.laukkanen(at)kuh.fi +358447172994
Research article:
Petri Kivimäki, Virve Kekkonen, Hannu Valtonen, Tommi Tolmunen, Kirsi Honkalampi, Ulrich Tacke, Jukka Hintikka, Soili M. Lehto, Eila Laukkanen. Alcohol use among adolescents, aggressive behaviour, and internalizing problems. Journal of Adolescence. Volume 37, Issue 6, August 2014, 945-951.
Aggressive behaviour increases adolescent drinking, depression doesn't
2014-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A synopsis of the carabid beetle tribe Lachnophorini reveals remarkable 24 new species
2014-08-06
An extensive study by Smithsonian scientists presents a synopsis of the carabid beetle tribe Lachnophorini. The research contains a new genus and the remarkable 24 new species added to the tribe. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
Beetles from the family Carabidae, commonly known as ground beetles are a large, cosmopolitan group, with more than 40,000 species worldwide, Carabid beetles range in size from 0.6 mm to 90.2 mm and occur in nature in several fractal universes influencing life therein as predators, ectoparasitoids, seed eaters, and even ...
Study: arctic mammals can metabolize some pesticides, limits human exposure
2014-08-06
Fortunately, you are not always what you eat – at least in Canada's Arctic.
New research from the University of Guelph reveals that arctic mammals such as caribou can metabolize some current-use pesticides (CUPs) ingested in vegetation.
This limits exposures in animals that consume the caribou – including humans.
"This is good news for the wildlife and people of the Arctic who survive by hunting caribou and other animals," said Adam Morris, a PhD student in the School of Environmental Sciences and lead author of the study published recently in Environmental Toxicology ...
New material structures bend like microscopic hair
2014-08-06
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT engineers have fabricated a new elastic material coated with microscopic, hairlike structures that tilt in response to a magnetic field. Depending on the field's orientation, the microhairs can tilt to form a path through which fluid can flow; the material can even direct water upward, against gravity.
Each microhair, made of nickel, is about 70 microns high and 25 microns wide — about one-fourth the diameter of a human hair. The researchers fabricated an array of the microhairs onto an elastic, transparent layer of silicone.
In experiments, the ...
Coping skills help women overcome the mental anguish of unwanted body evaluation and sexual advances
2014-08-06
Some young women simply have more resilience and better coping skills and can shrug off the effect of unwanted cat calls, demeaning looks and sexual advances. Women with low resilience struggle and could develop psychological problems when they internalize such behavior, because they think they are to blame. So say Dawn Szymanski and Chandra Feltman of the University of Tennessee in the US, in Springer's journal Sex Roles, after studying how female college students handle the sexually objectifying behavior of men.
According to the popular feminist Objectification Theory, ...
Curing arthritis in mice
2014-08-06
Rheumatoid arthritis is a condition that causes painful inflammation of several joints in the body. The joint capsule becomes swollen, and the disease can also destroy cartilage and bone as it progresses. Rheumatoid arthritis affects 0.5% to 1% of the world's population. Up to this point, doctors have used various drugs to slow or stop the progression of the disease. But now, ETH Zurich researchers have developed a therapy that takes the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in mice to a new level: after receiving the medication, researchers consider the animals to be fully ...
Job insecurity in academia harms the mental wellbeing of non-tenure track faculty
2014-08-06
Non-tenure-track academics experience stress, anxiety, and depression due to their insecure job situation, according to the first survey of its kind published in the open-access journal Frontiers in Psychology.
There were 1.4 contingent faculty workers in the USA, according to a report by the American Association of University Professors. These faculty members, such as research adjunct faculty, lecturers and instructors, are off the so-called "tenure track". They work under short-term contracts with limited health and retirement benefits, often part-time and at different ...
Preparing for a changing climate: Ecologists unwrap the science in the National Climate Change Assessment
2014-08-06
Two Ignite sessions focusing on findings in the United States National Climate Assesment5 (NCA) will take place on Monday, August 11th during the Ecological Society of America's 99th Annual Meeting, held this year in Sacramento, California.
The first session, Ignite 1: From Plains to Oceans to Islands: Regional Findings from the Third National Climate Assessment will highlight major findings from the report about the regional effects of climate change, discuss impacts to the ecosystems of the region, and explore how changes in those ecosystems can moderate or exacerbate ...
Triangulum galaxy snapped by VST
2014-08-06
Messier 33, otherwise known as NGC 598, is located about three million light-years away in the small northern constellation of Triangulum (The Triangle). Often known as the Triangulum Galaxy it was observed by the French comet hunter Charles Messier in August 1764, who listed it as number 33 in his famous list of prominent nebulae and star clusters. However, he was not the first to record the spiral galaxy; it was probably first documented by the Sicilian astronomer Giovanni Battista Hodierna around 100 years earlier.
Although the Triangulum Galaxy lies in the northern ...
Study: Many cancer survivors smoke years after diagnosis
2014-08-06
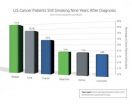
ATLANTA – August 6, 2014–Nearly one in ten cancer survivors reports smoking many years after a diagnosis, according to a new study by American Cancer Society researchers. Further, among ten cancer sites included in the analysis, the highest rates of smoking were in bladder and lung cancers, two sites strongly associated with smoking. The study appears early online in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
Cigarette smoking decreases the effectiveness of cancer treatments, increases the probability of recurrence, and reduces survival time. Nonetheless, some studies ...
Nearly 10 percent of patients with cancer still smoke
2014-08-06
PHILADELPHIA — Nine years after diagnosis, 9.3 percent of U.S. cancer survivors were current smokers and 83 percent of these individuals were daily smokers who averaged 14.7 cigarettes per day, according to a report in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
"We need to follow up with cancer survivors long after their diagnoses to see whether they are still smoking and offer appropriate counseling, interventions, and possible medications to help them quit," said Lee Westmaas, PhD, director of tobacco ...