(Press-News.org) A recent study illustrated that the mode conversion of the ultrasonic guided waves can quantitatively reflect the fracture degree of long cortical bone, which may provide new method for long bone fracture evaluation and healing monitoring.
This scientific paper (Quantitative evaluation of long bone fractures by ultrasonic guided waves) is published on SCIENCE CHINA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica (in Chinese), 2014, 44(7). Professor TA De-an from school of information science and technology, Fudan university leads this study. The impacts of fracture width and depth on the amplitude of guided waves are quantitatively analyzed.
Bone fracture is a medical condition in which bone discontinuity is created by stresses higher than the bone can bear. Statistical studies show that 5-10% of the fractured patients are suffering the healing obstacles. Fracture healing is a proliferative process and full recovery can take 3-5 years. The diseases in the healing process are easily neglected, leading to severe bone loss and secondary damage, impacting the physical condition of the patients. Thus, early diagnosis of the healing obstacle is crucial to ensure the healing process. The accurate diagnosis and dynamic monitoring are fundamental for the prompt treatment.
With the advantages of quantitative ultrasound (QUS), such as low-expense, portability, and non-ionizing radiation, ultrasonic guided waves can also detect the geometry of long cortical bone, (e.g. thickness, profile and section) and measure the material parameters, (e.g. BMD, porosity and Young's modulus), which has attracted increasing attentions. However, due to the immature understanding to the ultrasound propagation in long cortical bones, ultrasonic guided waves method has not been widely applied to the clinical practice of the long bone fracture evaluation.
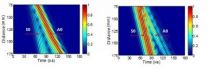
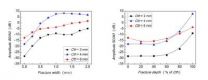
Numerical simulations are carried out to analyze the guided waves propagation in the fractured long bone. The innovation of this study is the use of narrowband low-frequency ultrasound to avoid the multimode overlap. Only two fundamental guided modes, symmetric S0 and asymmetric A0, are excited, which simplifies the mode separation and quantitative determination. Fig. 1a and Fig. 1b depict the guided signals in the intact and fractured long bones, respectively. The impacts of fracture width and depth on the amplitudes of each guided modes are quantitatively discussed. It is demonstrated that the amplitude of the A0 mode is very sensitive to the width and depth variation. The ratio between the amplitudes of S0 and A0 is further proposed to evaluate the fracture degree (Fig. 2).
It indicates that the mode conversion of the ultrasonic guided waves can characterize the changes in the fracture depth and fracture width and provide quantitative parameters for fracture evaluation. The study may also be helpful to the ultrasound monitoring of long bone healing.
INFORMATION:
See the article:
Liu D, Xu K L, Li D W, et al. Quantitative evaluation of long bone fractures by ultrasonic guided waves (in Chinese). Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 2014, 44(7):682-690.
Science China Press Co., Ltd. (SCP) is a scientific journal publishing company of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). For 60 years, SCP takes its mission to present to the world the best achievements by Chinese scientists on various fields of natural sciences researches.
http://www.scichina.com/
New progress in long bone fracture evaluation using ultrasound
2014-08-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Flexible tapes from the nanoworld
2014-08-13
Porphyrin molecules are essential to many biological processes, such as photosynthesis and respiration. Dr. Wilhelm Auwärter's group is investigating these all-round talents at TU München.
Normally, hydrogen attaches to the outer edges of the porphyrin core – named porphine, but other chemical entities can take the place of hydrogen, thereby changing the properties of the molecules.
Alissa Wiengarten, PhD student at the TUM Department of Physics, heats a porphine powder in a vacuum chamber. In the process, individual porphine molecules leave the collective and adhere ...
Teachers play key role in program to fight childhood obesity
2014-08-13
An innovative physical activities guide developed at the Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute (FPG) is helping North Carolina fight childhood obesity. New research shows that when teachers direct these physical activities, young children become more active and less sedentary.
"In the past twenty years, childhood obesity rates have skyrocketed," said FPG investigator Allison De Marco. "And for the first time in over a century, children's life expectancies are declining because of increased numbers of overweight kids."
De Marco said these statistics are especially ...
Researchers uncover clues about how the most important TB drug attacks its target
2014-08-13
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health say they have discovered a new clue to understanding how the most important medication for tuberculosis (TB) works to attack dormant TB bacteria in order to shorten treatment.
The antibiotic Pyrazinamide (PZA) has been used to treat TB since the 1950s, but its mechanisms are the least understood of all TB drugs. The PZA findings may help researchers identify new and more effective drugs not only for TB – which can require six months or more of treatment – but other persistent bacterial infections. A report ...
Hurricane Julio and 2 tropical lows 'bookend' Hawaii
2014-08-13
Infrared satellite imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite shows three tropical system s in the Central Pacific Ocean that appears like bookends with Hawaii in-between.
In an infrared image from the GOES-West satellite taken August 13 at 1200 UTC (8 a.m. EDT/2 a.m. HST), Hurricane Julio lies to the north of Hawaii, while two low pressure areas lie to the southeast of the island state. The image was created by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
On August 13 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT/11 p.m. HST on Aug.12) the center of ...
How useful is economics -- how is economics useful?
2014-08-13
What insights do the models, experiments and econometric regressions of scientific research provide about the economy – and why and under what conditions are they useful in dealing with real-world problems? This question will be overarching the discussions among 17 Nobel Laureates in Economic Sciences and approximately 450 aspiring young economists from more than 80 countries in Lindau, Germany, next week. The 5th Lindau Meeting on Economic Sciences will bring them together for a unique dialogue across generations, cultures and scientific backgrounds. The meeting will open ...
Many older emergency department patients are malnourished
2014-08-13
More than half of emergency department patients age 65 and older who were seen at UNC Hospitals during an 8-week period were either malnourished or at risk for malnutrition.
In addition, more than half of the malnourished patients had not previously been diagnosed, according to a new study by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. The study was published online August 13 by the journal Annals of Emergency Medicine.
"Malnutrition is known to be a common problem among older adults. What is surprising in our study is that most of the malnourished ...
Reduction of tau protein improves symptoms in model of severe childhood epilepsy
2014-08-13
Researchers at the Gladstone Institutes have shown that reducing brain levels of the protein tau effectively blocks the development of disease in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome, a severe intractable form of childhood epilepsy. This therapeutic strategy not only suppressed seizure activity and premature death, but also improved cognitive and behavioral abnormalities that can accompany this syndrome.
Previous studies from this group have shown that lowering tau levels reduces abnormal brain activity in models of Alzheimer's disease, but this is the first demonstration ...
'Shape-shifting' material could help reconstruct faces
2014-08-13
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 13, 2014 — Injuries, birth defects (such as cleft palates) or surgery to remove a tumor can create gaps in bone that are too large to heal naturally. And when they occur in the head, face or jaw, these bone defects can dramatically alter a person's appearance. Researchers will report today that they have developed a "self-fitting" material that expands with warm salt water to precisely fill bone defects, and also acts as a scaffold for new bone growth.
The team will describe their approach in one of nearly 12,000 presentations at the 248th National ...
Dust -- and the microbes hitching rides on it -- influences rain, climate
2014-08-13
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 13, 2014 — Dusty air blowing across the Pacific from Asia and Africa plays a critical role in precipitation patterns throughout the drought-stricken western U.S. Today, a scientist will present new research suggesting that the exact chemical make-up of that dust, including microbes found in it, is the key to how much rain and snow falls from clouds throughout the region. This information could help better predict rain events, as well as explain how air pollution from a variety of sources influences regional climate in general.
She will present a talk ...
Rooting out skin creams that contain toxic mercury
2014-08-13
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 13, 2014 — As countries try to rid themselves of toxic mercury pollution, some people are slathering and even injecting creams containing the metal onto or under their skin to lighten it, putting themselves and others at risk for serious health problems. To find those most at risk, scientists are reporting today that they can now identify these creams and intervene much faster than before. They're speaking at the 248th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
The meeting, organized by the world's largest scientific society, ...