(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
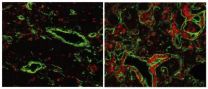
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics (MPI-IE) in Freiburg re-activated expression of an ancient gene, which is not normally expressed in the mammalian immune system, and found that the animals developed a fish-like thymus. To the researchers surprise, while the mammalian thymus is utilized exclusively for T cell maturation, the reset thymus produced not only T cells, but also served as a maturation site for B cells – a property normally seen only in the thymus of fish. Thus the model could provide an explanation of how the immune system had developed in the course of evolution. The study has been published in Cell Reports.
The adaptive immune response is unique to vertebrates. One of its core organs is the thymus, which exists in all vertebrate species. Epithelial cells in the thymus control the maturation of T-cells, which later fight degenerated or infected body cells. The gene FOXN1 is responsible for the development of such T-cells in the mammalian thymus. Scientists led by Thomas Boehm, director at the MPI-IE and head of the department for developmental immunology, activated the evolutionary ancestor of FOXN1, called FOXN4, in the thymic epithelial cells of mice. FOXN4 is present in all vertebrates, but appears to play only a role in the maturation of immune cells of jawed fish, such as cat sharks and zebra fish.
"The simultanuous expression of FOXN4 and FOXN1 in the mouse led to a thymus that showed properties as in fish," said first author Jeremy Swann. Together with earlier results this suggests that the development and function of thymic tissue was originally intitiated by FOXN4. Due to an evolutionary gene duplication, which led to FOXN1, transiently both genes, and finally only FOXN1 were active in the thymus.
To the researchers surprise not only T-cells developed in the thymus of the mice, but also B-cells. Mature B-cells are responsible for antibody production. In mammals, they normally do not mature in the thymus, but in other organs, such as the bone marrow. "Our studies suggest a plausible scenario for the transition of a bipotent lymphopoietic tissue to a lymphoid organ supporting primarily T cell development," said Boehm. Since B- and T-cell progenitors can not yet be distinguished, it remains unclear whether the B-cell development is based on the migration of dedicated B-cell precursors to the thymus, or to maturation from a shared T/B progenitor in the thymus itself. Comparative studies often suggest that the origin of a particular evolutionary innovation must have occurred in an extinct species. "Here, the re-creation and functional analysis of presumed ancestral stages could provide essential insights into the course of such developments," explained Boehm the study approach.
INFORMATION:
500 million year reset for the immune system
A single factor can reset the immune system of mice to a state likely similar to what it was 500 million years ago, when the first vertebrates emerged
2014-08-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GW researchers develop model to study impact of faculty development programs
2014-08-18
WASHINGTON (Aug. 18, 2014) — Methods used to demonstrate the impact of faculty development programs have long been lacking. A research report from the George Washington University (GW) introduces a new model to demonstrate how faculty development programming can affect institutional behaviors, beyond the individual participant.
"Faculty development is essential for helping medical education faculty meet the demands of their roles as teachers, scholars, administrators, and leaders," said co-author Ellen Goldman, MBA, Ed.D., associate professor of clinical research and ...
Electric vehicle consumers better off with electric range under 100 miles: INFORMS study
2014-08-18
Until battery cost is cut down to $100 per kilowatt hour, the majority of U.S. consumers for battery electric vehicles (BEV) will be better off by choosing an electric vehicle with a range below 100 miles, according to a new study in the Articles in Advance section of Transportation Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS).
The research suggests reconsideration of the R&D goal that battery electric vehicles should have a driving range similar to that of conventional vehicles. It also implies that the focus of policy ...
Free fatty acids may be as effective as antibiotics in treating catheter infections
2014-08-18
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – Researchers at Rhode Island Hospital, Veterans Affair Medical Center in Providence and University of Rhode Island have found that a free fatty acid, made up of compounds similar to those naturally made in the body, may be as effective at fighting certain infections as antibiotics. The study is published online in advance of print in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
"More and more bacteria are developing resistance to commonly used antibiotics," said Leonard Mermel, D.O., medical director of the department of epidemiology and infection control ...
Did an exceptional iceberg sink the Titanic?
2014-08-18
While the sinking of the Titanic in 1912 is typically blamed on human, design and construction errors, a new Significance paper points to 2 other unfavorable factors outside human control: there were a greater number of icebergs than normal that year, and weather conditions had driven them further south, and earlier in the year, than was usual.
The paper also notes that iceberg discharge from glaciers is increasing, with more heavy iceberg years since the 1980s than before, and increasing global warming will likely cause this trend to continue.
"As use of the Arctic ...
Butterflies' evolutionary responses to warmer temperatures may compromise their ability to adapt to future climate change
2014-08-18
Members of the brown argus butterfly species that moved north in response to recent climate change have evolved a narrower diet dependent on wild Geranium plants, UK researchers report. However, butterflies that did not move north have more diverse diets, including plants such as Rockrose that are abundant in southern parts of the UK.
So although rapid evolutionary changes have allowed the brown argus to move north and track the warming climate, they have led to a more restricted diet. This increased specialization may limit this butterfly's continued spread north, ...
Invasion of the Americas by mosquito-borne virus likely
2014-08-18
While media attention has been focused recently on coronavirus cases in the Arabian peninsula and the Ebola outbreak in West Africa, experts note that another threat lies in the spread of Chikungunya fever, an illness that is transmitted by mosquitoes and can cause fever, joint and muscle pain, headaches, and rashes. While it does not often cause death, the symptoms can be severe and disabling, with no treatment available.
The potential for worldwide spread of Chikungunya virus is much higher than the risk of dissemination of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus ...
Study suggests hatha yoga boosts brain function in older adults
2014-08-18
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Practicing hatha yoga three times a week for eight weeks improved sedentary older adults' performance on cognitive tasks that are relevant to everyday life, researchers report.
The findings involved 108 adults between the ages of 55 and 79 years of age, 61 of whom attended hatha yoga classes. The others met for the same number and length of sessions and engaged in stretching and toning exercises instead of yoga.
At the end of the eight weeks, the yoga group was speedier and more accurate on tests of information recall, mental flexibility and task-switching ...
The double threat of climate and land use change enhances risks to biodiversity
2014-08-18
Researchers from Aarhus University, Denmark, and the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, have developed a new approach to measure the combined exposure of species to both climate and land use change. This new metric was used to assess the risk to species in the face of combined rates of climate and land use for the US from 2001 to 2051.
Their results, which have just been published in Nature Climate Change, highlight areas expected to be most vulnerable to losses in biodiversity and ecosystem function due to the individual or combined effects of climate and land use ...
BGRF announces OncoFinder algorithm for reducing errors in transcriptome analysis
2014-08-18
Scientists from the Biogerontology Research Foundation (BGRF), a UK-based charity founded to support ageing research and address the challenges of a rapidly ageing population, propose a new concept for signalome-wide analysis of changes in intracellular pathways, called OncoFinder, which allows for accurate and robust cross-platform analysis of gene expression data. This new technique will allow scientists to derive useful information from and compare the hundreds of thousands of data sets obtained using legacy equipment as well as data sets obtained from biological samples ...
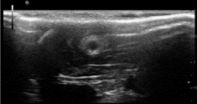
Ultrasound imaging of chitosan nerve conduits that bridge sciatic nerve defects in rats
2014-08-18
New simple and effective methods are needed to better evaluate the outcomes of repair using nerve conduits in vivo. Ultrasound is a common noninvasive clinical detection modality that has been used in many fields. However, ultrasound has only rarely been used to observe implanted nerve conduits in vivo. Hongkui Wang and co-workers from Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University report the first use of ultrasound to noninvasively observe the changes in chitosan nerve conduits implanted in rats over time. The ultrasound imaging clearly showed whether there are unsatisfactory ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] 500 million year reset for the immune systemA single factor can reset the immune system of mice to a state likely similar to what it was 500 million years ago, when the first vertebrates emerged