(Press-News.org) (Boston) — African American women born at a low or very low birth weight may be at a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes. The findings, which appear in Diabetes Care, may explain in part the higher occurrence of type 2 diabetes in African American populations, which has a high prevalence of low birth weight.
Researchers from Boston University's Slone Epidemiology Center followed more than 21,000 women enrolled in the Black Women's Health Study over the course of 16 years, analyzing characteristics such as birth weight, current age, family history of diabetes, body mass index, physical activity and socioeconomic status.
The study results indicate that women with low birth weight had a 13 percent higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes than those with normal birth weight, and those with very low birth weight had a 40 percent higher chance of developing the disease. Low birth weight was defined as less than 2.5 kg, and very low birth weight as less than 1.5 kg. It appeared that body size did not play a role in this relationship as there was a clear association between birth weight and diabetes even for women who were not obese.
Although previous studies have shown that birth characteristics such as birth weight can have a major impact on adult health, this is the first large-scale study to demonstrate this effect in an African American population.
"African American women are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and also have higher rates of low birth weight than white women," said Edward Ruiz-Narváez, ScD, assistant professor of epidemiology at Boston University School of Public Health. "Our study shows a clear relationship between birth weight and diabetes that highlights the importance of further research for this at-risk group."
According to the researchers, there are two leading hypotheses for the phenomenon. The first, known as the "thrifty phenotype hypothesis," states that once the newborn body perceives that it lacks nutrition, it reprograms itself to absorb more nutrition, causing an imbalance in metabolism that eventually leads to type 2 diabetes. The second, known as the "fetal insulin hypothesis," states that genes that are responsible for impaired insulin secretion also have a negative effect on birth weight. Some of these genes have been discovered in recent studies, supporting the latter hypothesis.
INFORMATION:
Funding for this study was provided by grants from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, the National Cancer Institute and the American Heart Association.
Low birth weight linked to higher incidence of type 2 diabetes in African American women
2014-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Enabling a new future for cloud computing
2014-08-21
The National Science Foundation (NSF) today announced two $10 million projects to create cloud computing testbeds--to be called "Chameleon" and "CloudLab"--that will enable the academic research community to develop and experiment with novel cloud architectures and pursue new, architecturally-enabled applications of cloud computing.
Cloud computing refers to the practice of using a network of remote servers to store, manage and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer. In recent years, cloud computing has become the dominant method of providing ...
NASA scientists watching, studying Arctic changes this summer
2014-08-21
VIDEO:
In this animation, the Earth rotates slowly as the Arctic sea ice advances over time from March 21, 2014 to August 3, 2014.
Click here for more information.
As we near the final month of summer in the Northern Hemisphere, NASA scientists are watching the annual seasonal melting of the Arctic sea ice cover. The floating, frozen cap that stretches across the Arctic Ocean shrinks throughout summer until beginning to regrow, typically around mid-September.
As of Aug. 19, ...
Extracorporeal support can significantly increase number of organs for transplant
2014-08-21
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Using heart-lung support technology, the University of Michigan's Transplant Center was able to increase the number of kidneys, livers and pancreases available for transplant by about 20 percent.
The results were published in the journal Transplantation and detail the impact of more than 10 years of using Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, or ECMO, to improve the quality and viability of organs donated after circulatory determination of death.
"Organ transplant is limited by the number of donated organs available, so the use of organs that are donated ...
Liberal democracy is possible in Muslim-majority countries
2014-08-21
A new study by University of Toronto and University of Tübingen researchers suggests that Islam is not as much of an impediment to liberal democracy as is often thought.
"One of the key markers for a successful liberal democracy is a high degree of social tolerance," says U of T sociologist Robert Andersen. "We wanted to see the extent to which this existed in countries with a majority of Muslims compared to Western countries."
Andersen, U of T sociologist Robert Brym and Scott Milligan of the University of Tübingen used data from the World Values Survey – a global ...
Canola genome sequence reveals evolutionary 'love triangle'
2014-08-21
Athens, Ga. – An international team of scientists including researchers from the University of Georgia recently published the genome of Brassica napus—commonly known as canola—in the journal Science. Their discovery paves the way for improved versions of the plant, which is used widely in farming and industry.
Canola is grown across much of Canada and its native Europe, but the winter crop is increasingly cultivated in Georgia. Canola oil used for cooking is prized for its naturally low levels of saturated fat and rich supply of omega-3 fatty acids, but the plant is ...
Despite a significant reduction in smog-producing toxins, the Greater Toronto Area still violates Canada's standards for ozone air pollution
2014-08-21
Despite a significant reduction in smog-producing toxins in past decade, GTA still violates Canada's ozone standards
A new study shows that while the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) has significantly reduced some of the toxins that contribute to smog, the city continues to violate the Canada-wide standards for ozone air pollution.
Smog, which can cause or aggravate health problems such as asthma, emphysema and chronic bronchitis, is produced by a set of complex photochemical reactions involving volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides and sunlight, which form ground-level ...
Orgasm rates for single women less predictable than men's, vary by sexual orientation
2014-08-21
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- A new study of American singles found that during sex with a familiar partner, men have the highest orgasm rates. On average, men experience orgasm 85.1 percent of the time, with their sexual orientation making little difference. For women, however, orgasm occurrence is less predictable. On average, women experience orgasm 62.9 percent of the time during sex with a familiar partner -- and this pattern varies with women's sexual orientation, with lesbian women experiencing orgasm more often than heterosexual or bisexual women.
The Indiana University ...
Losing weight lowers health care costs for adults with type 2 diabetes
2014-08-21
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Aug. 21, 2014 – Overweight individuals with diabetes who lose weight by dieting and increasing their physical activity can reduce their health care costs by an average of more than $500 per year, according to a new study.
"Lifestyle interventions promoting weight loss and physical activity are recommended for overweight and obese people with Type 2 diabetes to improve their health," said Mark A. Espeland, professor of public health sciences at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center and lead author of the study. "This is the first study to show that weight ...
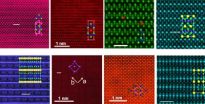
ORNL scientists uncover clues to role of magnetism in iron-based superconductors
2014-08-21
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Aug. 21, 2014—New measurements of atomic-scale magnetic behavior in iron-based superconductors by researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Vanderbilt University are challenging conventional wisdom about superconductivity and magnetism.
The study published in Advanced Materials provides experimental evidence that local magnetic fluctuations can influence the performance of iron-based superconductors, which transmit electric current without resistance at relatively high temperatures.
"In the past, everyone thought ...
When it comes to how pizza looks, cheese matters
2014-08-21
CHICAGO—Most consumers have an idea what they want their pizza slice to look like. Golden cheese with that dark toasted-cheese color scattered in distinct blistery patches across the surface with a bit of oil glistening in the valleys. A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), evaluated the pizza baking performance of different cheeses (mozzarella, cheddar, colby, Edam, Emmental, Gruyere, and provolone) in conjunction with a new quantifiable evaluation technique to see how their composition and functional differences ...