(Press-News.org) In a research paper published this week in Science, the collaboration led by MIT's theory professor Leonid Levitov and Manchester's Nobel laureate Sir Andre Geim report a material in which electrons move at a controllable angle to applied fields, similar to sailboats driven diagonally to the wind.
The material is graphene – one atom-thick chicken wire made from carbon – but with a difference. It is transformed to a new so-called superlattice state by placing it on top of boron nitride, also known as `white graphite', and then aligning the crystal lattices of the two materials. In contrast to metallic graphene, a graphene superlattice behaves as a semiconductor.
In original graphene, charge carriers behave like massless neutrinos moving at the speed of light and having the electron charge. Although an excellent conductor, graphene does not allow for easy switching on and off of current, which is at the heart of what a transistor does.
Electrons in graphene superlattices are different and behave as neutrinos that acquired a notable mass. This results in a new, relativistic behaviour so that electrons can now skew at large angles to applied fields. The effect is huge, as found in the Manchester-MIT experiments.
The reported relativistic effect has no known analogue in particle physics and extends our understanding of how the universe works.
Beyond the discovery, the observed phenomenon may also help enhance the performance of graphene electronics, making it a worthy companion to silicon.
The research suggests that transistors made from graphene superlattices should consume less energy than conventional semiconductor transistors because charge carriers drift perpendicular to the electric field, which results in little energy dissipation.
The Manchester-MIT researchers demonstrate the first such transistor, which opens a venue for less power hungry computers.
Professor Geim comments 'It is quite a fascinating effect, and it hits a very soft spot in our understanding of complex, so-called topological materials. It is extremely rare to come across with a phenomenon that bridges materials science, particle physics, relativity and topology.'
Professor Levitov adds 'It is widely believed than unconventional approaches to information processing are key for the future of IT hardware. This belief has been the driving force behind a number of important recent developments, in particular the development of spintronics. The demonstrated transistor highlights the promise of graphene-based systems for alternative ways of information processing. '
INFORMATION:
New species of electrons can lead to better computing
2014-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Hot Jupiters' provoke their own host suns to wobble
2014-09-11
Blame the "hot Jupiters."
These large, gaseous exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) can make their suns wobble when they wend their way through their own solar systems to snuggle up against their suns, according to new Cornell University research to be published in Science, Sept. 11.
Images: https://cornell.box.com/lai
"Although the planet's mass is only one-thousandth of the mass of the sun, the stars in these other solar systems are being affected by these planets and making the stars themselves act in a crazy way," said Dong Lai, Cornell professor of ...
Diversified farming practices might preserve evolutionary diversity of wildlife
2014-09-11
As humans transform the planet to meet our needs, all sorts of wildlife continue to be pushed aside, including many species that play key roles in Earth's life-support systems. In particular, the transformation of forests into agricultural lands has dramatically reduced biodiversity around the world.
A new study by scientists at Stanford and the University of California, Berkeley, in this week's issue of Science shows that evolutionarily distinct species suffer most heavily in intensively farmed areas. They also found, however, that an extraordinary amount of evolutionary ...
You can classify words in your sleep
2014-09-11
When people practice simple word classification tasks before nodding off—knowing that a "cat" is an animal or that "flipu" isn't found in the dictionary, for example—their brains will unconsciously continue to make those classifications even in sleep. The findings, reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 11, show that some parts of the brain behave similarly whether we are asleep or awake and pave the way for further studies on the processing capacity of our sleeping brains, the researchers say.
"We show that the sleeping brain can be far more ...
Gut microbes determine how well the flu vaccine works
2014-09-11
Annual flu epidemics cause millions of cases of severe illness and up to half a million deaths every year around the world, despite widespread vaccination programs. A study published by Cell Press on September 11th in Immunity reveals that gut microbes play an important role in stimulating protective immune responses to the seasonal flu vaccine in mice, suggesting that differences in the composition of gut microbes in different populations may impact vaccine immunity. The study paves the way for global public health strategies to improve the effectiveness of the flu vaccine. ...
Stem cells help researchers understand how schizophrenic brains function
2014-09-11
Using human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs), researchers have gained new insight into what may cause schizophrenia by revealing the altered patterns of neuronal signaling associated with this disease. They did so by exposing neurons derived from the hiPSCs of healthy individuals and of patients with schizophrenia to potassium chloride, which triggered these stem cells to release neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, that are crucial for brain function and are linked to various disorders. By discovering a simple method for stimulating hiPSCs to release neurotransmitters, ...
Intestinal bacteria needed for strong flu vaccine responses in mice
2014-09-11
Mice treated with antibiotics to remove most of their intestinal bacteria or raised under sterile conditions have impaired antibody responses to seasonal influenza vaccination, researchers have found.
The findings suggest that antibiotic treatment before or during vaccination may impair responses to certain vaccines in humans. The results may also help to explain why immunity induced by some vaccines varies in different parts of the world.
In a study to be published in Immunity, Bali Pulendran, PhD, and colleagues at Emory University demonstrate a dependency on gut ...
Our microbes are a rich source of drugs, UCSF researchers discover
2014-09-11
Bacteria that normally live in and upon us have genetic blueprints that enable them to make thousands of molecules that act like drugs, and some of these molecules might serve as the basis for new human therapeutics, according to UC San Francisco researchers who report their new discoveries in the September 11, 2014 issue of Cell.
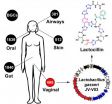
The scientists purified and solved the structure of one of the molecules they identified, an antibiotic they named lactocillin, which is made by a common bacterial species, Lactobacillus gasseri, found in the microbial community within the vagina. ...
Cells put off protein production during times of stress
2014-09-11
DURHAM, N.C. -- Living cells are like miniature factories, responsible for the production of more than 25,000 different proteins with very specific 3-D shapes. And just as an overwhelmed assembly line can begin making mistakes, a stressed cell can end up producing misshapen proteins that are unfolded or misfolded.
Now Duke University researchers in North Carolina and Singapore have shown that the cell recognizes the buildup of these misfolded proteins and responds by reshuffling its workload, much like a stressed out employee might temporarily move papers from an overflowing ...
A non-toxic strategy to treat leukemia
2014-09-11
A study comparing how blood stem cells and leukemia cells consume nutrients found that cancer cells are far less tolerant to shifts in their energy supply than their normal counterparts. The results suggest that there could be ways to target leukemia metabolism so that cancer cells die but other cell types are undisturbed.
Harvard Stem Cell Institute scientists at the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Regenerative Medicine and the Harvard University Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology led the work, published in the journal Cell, in collaboration with ...
Scientists discover neurochemical imbalance in schizophrenia
2014-09-11
Using human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs), researchers at Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at University of California, San Diego have discovered that neurons from patients with schizophrenia secrete higher amounts of three neurotransmitters broadly implicated in a range of psychiatric disorders.
The findings, reported online Sept. 11 in Stem Cell Reports, represent an important step toward understanding the chemical basis for schizophrenia, a chronic, severe and disabling brain disorder that affects an estimated one in 100 persons at some ...