(Press-News.org) TEMPE, Ariz. – World leaders face multiple barriers in their efforts to reach agreement on greenhouse gas emission policies. And, according to Arizona State University researchers, without globally consistent, independent emissions assessments, climate agreements will remain burdened by errors, self-reporting, and the inability to verify emissions progress.
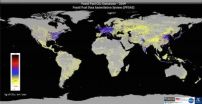
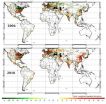
Now, an international research team led by ASU scientists has developed a new approach to estimate CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels — one that provides crucial information to policymakers. Called the "Fossil Fuel Data Assimilation System" or FFDAS, this new system was used to quantify 15 years of CO2 emissions, every hour, for the entire planet — down to the city scale. Until now, scientists have estimated greenhouse gas emissions at courser scales or used less reliable techniques.
Researchers unveiled the new system in an article published Sept. 10 in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
The FFDAS uses information from satellite feeds, national fuel accounts, and a new global database on power plants to create high-resolution planetary maps. These maps provide a scientific, independent assessment of the planet's greenhouse gas emissions — something policy-makers can use and the public can understand.
"With this system, we are taking a big step toward creating a global monitoring system for greenhouse gases, something that is needed as the world considers how best to meet greenhouse gas reductions," said Kevin Robert Gurney, lead investigator and associate professor in ASU's School of Life Sciences. "Now we can provide all countries with detailed information about their CO2 emissions and show that independent, scientific monitoring of greenhouse gases is possible."
The research team combined information from space-based "nighttime lights," a new population database, national statistics on fuel use, and a global database on power plants to create a CO2 emissions map broken down by hour, year and region.
"The accuracy of the FFDAS results is confirmed by independent, ground-based data in the United States," said Salvi Asefi-Najafabady, lead author of the report and postdoctoral researcher at ASU. "This makes us confident that the system is working well and can provide useable, policy-salient information."
"This is an incredibly helpful tool for national and international policymakers and the public to get a grasp of whether strategies to reduce greenhouse gases are effective," said Jennifer Morgan, Director of the Climate and Energy Program at World Resources Institute. "It serves as a complementary approach to current bottom-up accounting methodologies. No longer will there be a delay in understanding the latest GHG trends."
The FFDAS showed surprising detail on global emissions before and after the Global Financial Crisis, with portions of the U.S., Europe and India recovering sooner and more dramatically. The multiyear results also showed the dramatic rise of CO2 emissions in China and South Asia. Hence, the sub-national details offer insights into economic activity at scales for which traditional economic data has been limited.
"It used to take years to assemble all the statistics on CO2 emissions", said Peter Rayner, lead investigator from the University of Melbourne, Australia. "With this system, once the satellite data is flowing we can update our emissions maps each year. It gives a quick check on efforts to limit climate change."
INFORMATION:
The research team includes ASU, University of Melbourne, Australia, NOAA's National Geophysical Data Center, Colorado State University and Purdue University. NASA funded the three-year FFDAS project.
NASA ROSES grant NNX11AH86G and NASA CMS grant NNX12AP52G.
Study maps 15 years of carbon dioxide emissions on Earth
Project provides scientific accounting of worldwide CO2 emissions
2014-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dartmouth research links genetic mutation and melanoma progression
2014-09-11
Dartmouth researchers have found that the genetic mutation BRAFV600E, frequently found in metastatic melanoma, not only secretes a protein that promotes the growth of melanoma tumor cells, but can also modify the network of normal cells around the tumor to support the disease's progression. Targeting this mutation with Vemurafenib reduces this interaction, and suggests possible new treatment options for melanoma therapy. They report on their findings in "BRAFV600E melanoma cells secrete factors that activate stromal fibroblasts and enhance tumourigenicity," which was recently ...
Ceramics don't have to be brittle
2014-09-11
Imagine a balloon that could float without using any lighter-than-air gas. Instead, it could simply have all of its air sucked out while maintaining its filled shape. Such a vacuum balloon, which could help ease the world's current shortage of helium, can only be made if a new material existed that was strong enough to sustain the pressure generated by forcing out all that air while still being lightweight and flexible.
Caltech materials scientist Julia Greer and her colleagues are on the path to developing such a material and many others that possess unheard-of combinations ...
Scientists report first semiaquatic dinosaur, Spinosaurus
2014-09-11
WASHINGTON (Sept. 11, 2014)—Scientists today unveiled what appears to be the first truly semiaquatic dinosaur, Spinosaurus aegyptiacus. New fossils of the massive Cretaceous-era predator reveal it adapted to life in the water some 95 million years ago, providing the most compelling evidence to date of a dinosaur able to live and hunt in an aquatic environment. The fossils also indicate that Spinosaurus was the largest known predatory dinosaur to roam the Earth, measuring more than 9 feet longer than the world's largest Tyrannosaurus rex specimen. These findings, published ...
Malaria parasites sense and react to mosquito presence to increase transmission
2014-09-11
Many pathogens are transmitted by insect bites. The abundance of vectors (as the transmitting insects are called) depends on seasonal and other environmental fluctuations. An article published on September 11thin PLOS Pathogens demonstrates that Plasmodium parasites react to mosquitoes biting their hosts, and that the parasite responses increase transmission to the mosquito vector.
Sylvain Gandon, from the CNRS in Montpellier, France, and colleagues first studied the theoretical evolution of parasite evolution in a variable environment. Using a mathematical model, they ...
Evolutionary tools improve prospects for sustainable development
2014-09-11
Solving societal challenges in food security, emerging diseases and biodiversity loss will require evolutionary thinking in order to be effective in the long run. Inattention to this will only lead to greater challenges such as short-lived medicines and agricultural treatments, problems that may ultimately hinder sustainable development, argues a new study published online today in Science Express, led by University of California, Davis and the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate at the University of Copenhagen.
For the first time, scientists have reviewed ...
Dartmouth study may shed light on molecular mechanisms of birth defects among older women
2014-09-11
Dartmouth researchers studying cell division in fruit flies have discovered a pathway that may improve understanding of molecular mistakes that cause older women to have babies with Down syndrome.
The study shows for the first time that new protein linkages occur in immature egg cells after DNA replication and that these replacement linkages are essential for these cells to maintain meiotic cohesion for long periods.
The study appears in the journal PLOS Genetics. A PDF is available on request.
As women age, so do their eggs and during a woman's thirties, the chance ...
The sound of an atom has been captured
2014-09-11
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology are first to show the use of sound to communicate with an artificial atom. They can thereby demonstrate phenomena from quantum physics with sound taking on the role of light. The results will be published in the journal Science.
The interaction between atoms and light is well known and has been studied extensively in the field of quantum optics. However, to achieve the same kind of interaction with sound waves has been a more challenging undertaking. The Chalmers researchers have now succeeded in making acoustic waves couple ...
New genetic targets discovered in fight against muscle-wasting disease
2014-09-11
Scientists have pinpointed for the first time the genetic cause in some people of an incurable muscle-wasting disease, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD).
The international research team led by the University of Leicester say the finding of two target genes opens the possibility of developing drugs to tackle the disease in these patients. Their work has been published today in the journal PLOS Genetics.
The research was funded by The Wellcome Trust and was only possible by the University of Leicester team collaborating with groups in Germany (University of Greifswald), ...
New species of electrons can lead to better computing
2014-09-11
In a research paper published this week in Science, the collaboration led by MIT's theory professor Leonid Levitov and Manchester's Nobel laureate Sir Andre Geim report a material in which electrons move at a controllable angle to applied fields, similar to sailboats driven diagonally to the wind.
The material is graphene – one atom-thick chicken wire made from carbon – but with a difference. It is transformed to a new so-called superlattice state by placing it on top of boron nitride, also known as `white graphite', and then aligning the crystal lattices of the two materials. ...
'Hot Jupiters' provoke their own host suns to wobble
2014-09-11
Blame the "hot Jupiters."
These large, gaseous exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) can make their suns wobble when they wend their way through their own solar systems to snuggle up against their suns, according to new Cornell University research to be published in Science, Sept. 11.
Images: https://cornell.box.com/lai
"Although the planet's mass is only one-thousandth of the mass of the sun, the stars in these other solar systems are being affected by these planets and making the stars themselves act in a crazy way," said Dong Lai, Cornell professor of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
[Press-News.org] Study maps 15 years of carbon dioxide emissions on EarthProject provides scientific accounting of worldwide CO2 emissions