(Press-News.org) Washington, DC (September 18, 2014) — While dialysis can cause blood pressure changes that damage the brain, cooling dialysis fluids can protect against such effects. The findings come from a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The cooling intervention can be delivered without additional cost and is simple to perform.
While dialysis is an essential treatment for many patients with kidney disease, it can cause damage to multiple organs, including the brain and heart, due to the sudden removal of bodily fluids.
To characterize dialysis-induced brain injury and to see whether cooled dialysis fluids (called dialysate) might help reduce such injury, Christopher McIntyre, DM, and his colleagues randomized 73 new dialysis patients to dialyze with body temperature dialysate or dialysate cooled to 0.5◦C below body temperature for 1 year. (Dr. McIntyre was at the University of Nottingham in the UK while conducting this work but is now at the University of Western Ontario and the London Health Sciences Centre, in Canada.)
The study demonstrated that dialysis drives progressive white matter brain injury due to blood pressure instability; however, patients who dialyzed at 0.5◦C below body temperature were completely protected against such white matter changes.
"This study demonstrates that paying attention to improving the tolerability of dialysis treatment—in this case by the simple and safe intervention of reducing the temperature of dialysate—does not just make patients feel better, but also can completely protect the brain from progressive damage," said Dr. McIntyre.
INFORMATION:
Highlight
Dialysis drives progressive white matter brain injury due to blood pressure instability; however, patients who dialyzed at 0.5◦C below body temperature were completely protected against such white matter changes.
Conventional dialysis can cause significant circulatory stress that damages multiple organs.
Study co-authors include Aghogho Odudu, MBChB, PhD and Mohamed Tarek Eldehni MD, MSc.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the UK National Institute of Health Research. Dr. McIntyre has received research funding and speaking honoraria from several dialysis companies (Fresenius, Baxter, Gambro, Braun).
The article, entitled "Randomized Clinical Trial of Dialysate Cooling and Its Effect on Brain White Matter," will appear online at http://jasn.asnjournals.org/ on September 18, 2014.
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with more than 14,000 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients.
Cooling of dialysis fluids protects against brain damage
Simple step may help protect against cognitive, psychological, and functional abnormalities in dialysis patients
2014-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vitamin E, selenium supplements unlikely to effect age-related cataracts in men
2014-09-18
Taking daily supplements of selenium and/or vitamin E appears to have no significant effect on the development of age-related cataracts in men, writes Author William G. Christen, Sc.D., of Brigham & Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
Some research, including animal studies, has suggested that dietary nutrients can have an effect on the onset and progression of cataracts. Vitamin E and selenium are of particular interest.
The authors report the findings for cataracts from the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT) Eye ...
Exercise boosts tumor-fighting ability of chemotherapy, Penn team finds
2014-09-18
Study after study has proven it true: exercise is good for you. But new research from University of Pennsylvania scientists suggests that exercise may have an added benefit for cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Their work, performed in a mouse model of melanoma, found that combining exercise with chemotherapy shrunk tumors more than chemotherapy alone.
Joseph Libonati, an associate professor in the School of Nursing and director of the Laboratory of Innovative and Translational Nursing Research, was the senior author on the study, which appears in the American ...
Researchers study vital 'on/off switches' that control when bacteria turn deadly
2014-09-18
MADISON, Wis. — No matter how many times it's demonstrated, it's still hard to envision bacteria as social, communicating creatures.
But by using a signaling system called "quorum sensing," these single-celled organisms radically alter their behavior to suit their population. In short, some bacteria "know" how many of them are present, and act accordingly.
Once the population of quorum-sensing bacteria reaches the millions, it may change from innocuous to pathogenic, or from unhelpful to helpful. The quorum-sensing messages are carried in small molecules that the bacteria ...
Researchers develop unique waste cleanup for rural areas
2014-09-18
PULLMAN, Wash. - Washington State University researchers have developed a unique method to use microbes buried in pond sediment to power waste cleanup in rural areas.
The first microbe-powered, self-sustaining wastewater treatment system could lead to an inexpensive and quick way to clean up waste from large farming operations and rural sewage treatment plants while reducing pollution.
Professor Haluk Beyenal and graduate student Timothy Ewing in the Voiland College of Engineering and Architecture discuss the system in the online edition of Journal of Power Sources ...
Video games could dramatically streamline educational research
2014-09-18
PULLMAN, Wash. – "Seeking educational curriculum researchers. Humans need not apply."
A Washington State University professor has figured out a dramatically easier and more cost-effective way to do research on science curriculum in the classroom – and it could include playing video games.
Called "computational modeling," it involves a computer "learning" student behavior and then "thinking" as students would. Rich Lamb, who teaches science education at WSU's College of Education, said the process could revolutionize the way educational research is done.
Lamb's research ...
Tree rings and arroyos
2014-09-18
Boulder, Colo., USA – A new GSA Bulletin study uses tree rings to document arroyo evolution along the lower Rio Puerco and Chaco Wash in northern New Mexico, USA. By determining burial dates in tree rings from salt cedar and willow, investigators were able to precisely date arroyo sedimentary beds 30 cm thick or greater. They then combined this data with aerial imagery, LiDAR, longitudinal profiles, and repeat surveys to reconstruct the history of these arroyos.
Arroyos are deep, oversized channels that have vertical or steeply cut walls made up of silt, clay, or sand. ...
Spouse's personality influences career success, study finds
2014-09-18
As people spend more and more time in the workplace, it's natural for co-workers to develop close bonds — what's often referred to as a "workplace spouse" or an "office wife."
But when it comes to pay raises, promotions and other measures of career success, it's the husband or wife at home who may be exerting a bigger influence on workplace performance, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis. "Our study shows that it is not only your own personality that influences the experiences that lead to greater occupational success, but that your spouse's ...
Marcellus drilling boom may have led to too many hotel rooms
2014-09-18
Drilling in Pennsylvania's Marcellus Shale region led to a rapid increase in both the number of hotels and hotel industry jobs, but Penn State researchers report that the faltering occupancy rate may signal that there are now too many hotel rooms.
"Demand is still high in many of the counties in the Marcellus Shale region, but the occupancy rate is starting to come down," said Daniel Mount, an associate professor in hospitality management. "The case could be made that this is a sign that hotels were overbuilt."
Marcellus drilling operations generated approximately $685 ...
Survey: Fortune 500 employees can expect to pay more for health insurance
2014-09-18
Employees working for Fortune 500 companies can expect to pay higher employee contributions for their health insurance, according to a survey of chief human resource officers about the impact of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (also known as PPACA or Obamacare) conducted by the Darla Moore School of Business at the University of South Carolina this past May/June.
Patrick Wright, a professor in strategic human resource management, directs the annual the HR@Moore Survey of Chief HR Officers. The survey is distributed to more than 560 CHROs of Fortune 500 ...
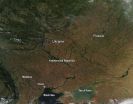
Agricultural fires in the Ukraine
2014-09-18
Numerous fires (marked with red dots) are burning in Eastern Europe, likely as a result of regional agricultural practices. The body of water at the lower left of this true-color Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) image is the Sea of Azov. The Sea is bordered by Ukraine to the northwest, west and southwest and by Russia to the northeast, east, and southeast. To its left is the Black Sea.
The location, widespread nature, and number of fires suggest that these fires were deliberately set to manage land. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
[Press-News.org] Cooling of dialysis fluids protects against brain damageSimple step may help protect against cognitive, psychological, and functional abnormalities in dialysis patients