Click here for more information.
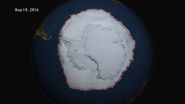
Sea ice surrounding Antarctica reached a new record high extent this year, covering more of the southern oceans than it has since scientists began a long-term satellite record to map sea ice extent in the late 1970s. The upward trend in the Antarctic, however, is only about a third of the magnitude of the rapid loss of sea ice in the Arctic Ocean.
The new Antarctic sea ice record reflects the diversity and complexity of Earth's environments, said NASA researchers. Claire Parkinson, a senior scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, has referred to changes in sea ice coverage as a microcosm of global climate change. Just as the temperatures in some regions of the planet are colder than average, even in our warming world, Antarctic sea ice has been increasing and bucking the overall trend of ice loss.
"The planet as a whole is doing what was expected in terms of warming. Sea ice as a whole is decreasing as expected, but just like with global warming, not every location with sea ice will have a downward trend in ice extent," Parkinson said.
Since the late 1970s, the Arctic has lost an average of 20,800 square miles (53,900 square kilometers) of ice a year; the Antarctic has gained an average of 7,300 square miles (18,900 sq km). On Sept. 19 this year, for the first time ever since 1979, Antarctic sea ice extent exceeded 7.72 million square miles (20 million square kilometers), according to the National Snow and Ice Data Center. The ice extent stayed above this benchmark extent for several days. The average maximum extent between 1981 and 2010 was 7.23 million square miles (18.72 million square kilometers).
The single-day maximum extent this year was reached on Sept. 20, according to NSIDC data, when the sea ice covered 7.78 million square miles (20.14 million square kilometers). This year's five-day average maximum was reached on Sept. 22, when sea ice covered 7.76 million square miles (20.11 million square kilometers), according to NSIDC.
A warming climate changes weather patterns, said Walt Meier, a research scientist at Goddard. Sometimes those weather patterns will bring cooler air to some areas. And in the Antarctic, where sea ice circles the continent and covers such a large area, it doesn't take that much additional ice extent to set a new record.
"Part of it is just the geography and geometry. With no northern barrier around the whole perimeter of the ice, the ice can easily expand if conditions are favorable," he said.
Researchers are investigating a number of other possible explanations as well. One clue, Parkinson said, could be found around the Antarctic Peninsula – a finger of land stretching up toward South America. There, the temperatures are warming, and in the Bellingshausen Sea just to the west of the peninsula the sea ice is shrinking. Beyond the Bellingshausen Sea and past the Amundsen Sea, lies the Ross Sea – where much of the sea ice growth is occurring.
That suggests that a low-pressure system centered in the Amundsen Sea could be intensifying or becoming more frequent in the area, she said – changing the wind patterns and circulating warm air over the peninsula, while sweeping cold air from the Antarctic continent over the Ross Sea. This, and other wind and lower atmospheric pattern changes, could be influenced by the ozone hole higher up in the atmosphere – a possibility that has received scientific attention in the past several years, Parkinson said.
"The winds really play a big role," Meier said. They whip around the continent, constantly pushing the thin ice. And if they change direction or get stronger in a more northward direction, he said, they push the ice further and grow the extent. When researchers measure ice extent, they look for areas of ocean where at least 15 percent is covered by sea ice.
While scientists have observed some stronger-than-normal pressure systems – which increase winds – over the last month or so, that element alone is probably not the reason for this year's record extent, Meier said. To better understand this year and the overall increase in Antarctic sea ice, scientists are looking at other possibilities as well.
Melting ice on the edges of the Antarctic continent could be leading to more fresh, just-above-freezing water, which makes refreezing into sea ice easier, Parkinson said. Or changes in water circulation patterns, bringing colder waters up to the surface around the landmass, could help grow more ice.
Snowfall could be a factor as well, Meier said. Snow landing on thin ice can actually push the thin ice below the water, which then allows cold ocean water to seep up through the ice and flood the snow – leading to a slushy mixture that freezes in the cold atmosphere and adds to the thickness of the ice. This new, thicker ice would be more resilient to melting.
"There hasn't been one explanation yet that I'd say has become a consensus, where people say, 'We've nailed it, this is why it's happening,'" Parkinson said. "Our models are improving, but they're far from perfect. One by one, scientists are figuring out that particular variables are more important than we thought years ago, and one by one those variables are getting incorporated into the models."
For Antarctica, key variables include the atmospheric and oceanic conditions, as well as the effects of an icy land surface, changing atmospheric chemistry, the ozone hole, months of darkness and more.
"Its really not surprising to people in the climate field that not every location on the face of Earth is acting as expected – it would be amazing if everything did," Parkinson said. "The Antarctic sea ice is one of those areas where things have not gone entirely as expected. So it's natural for scientists to ask, 'OK, this isn't what we expected, now how can we explain it?'"
INFORMATION:
Video: http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-scientist-to-discuss-climate-and-wildfires-at-library-of-congress-lecture/#.VDRYLxawTpg