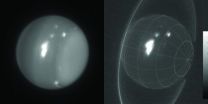
(Press-News.org) The normally bland face of Uranus has become increasingly stormy, with enormous cloud systems so bright that for the first time ever, amateur astronomers are able to see details in the planet's hazy blue-green atmosphere.
"The weather on Uranus is incredibly active," said Imke de Pater, professor and chair of astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley, and leader of the team that first noticed the activity when observing the planet with adaptive optics on the W. M. Keck II Telescope in Hawaii.
"This type of activity would have been expected in 2007, when Uranus's once every 42-year equinox occurred and the sun shined directly on the equator," noted co-investigator Heidi Hammel of the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy. "But we predicted that such activity would have died down by now. Why we see these incredible storms now is beyond anybody's guess."
In all, de Pater, Hammel and their team detected eight large storms on Uranus's northern hemisphere when observing the planet with the Keck Telescope on August 5 and 6. One was the brightest storm ever seen on Uranus at 2.2 microns, a wavelength that senses clouds just below the tropopause, where the pressure ranges from about 300 to 500 mbar, or half the pressure at Earth's surface. The storm accounted for 30 percent of all light reflected by the rest of the planet at this wavelength.
When amateur astronomers heard about the activity, they turned their telescopes on the planet and were amazed to see a bright blotch on the surface of a normally boring blue dot.
'I got it!'
French amateur astronomer Marc Delcroix processed the amateur images and confirmed the discovery of a bright spot on an image by French amateur Régis De-Bénedictis, then in others taken by fellow amateurs in September and October. He had his own chance on Oct. 3 and 4 to photograph it with the Pic du Midi one-meter telescope, where on the second night, "I caught the feature when it was transiting, and I thought, 'Yes, I got it!'" said Delcroix.
"I was thrilled to see such activity on Uranus. Getting details on Mars, Jupiter or Saturn is now routine, but seeing details on Uranus and Neptune are the new frontiers for us amateurs and I did not want to miss that," said Delcroix, who works for an auto parts supplier in Toulouse and has been observing the skies - Jupiter in particular - with his backyard telescope since 2006 and, since 2012, occasionally with the Pic du Midi telescope. "I was so happy to confirm myself these first amateur images on this bright storm on Uranus, feeling I was living a very special moment for planetary amateur astronomy."
Interestingly, the extremely bright storm seen by Keck in the near infrared is not the one seen by the amateurs, which is much deeper in the atmosphere than the one that initially caused all the excitement. De Pater's colleague Larry Sromovsky, a planetary scientist at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, identified the amateur spot as one of the few features on the Keck images from August 5 that was only seen at 1.6 microns, and not at 2.2 microns. The 1.6 micron light is emitted from deeper in the atmosphere, which means that this feature is below the uppermost cloud layer of methane-ice in Uranus's atmosphere.
"The colors and morphology of this cloud complex suggests that the storm may be tied to a vortex in the deeper atmosphere similar to two large cloud complexes seen during the equinox," Sromovsky said.
Such vortices could be anchored much deeper in the atmosphere and extend over large vertical distances, as inferred from similar vortices on Jupiter, including its Great Red Spot.
An expanded team of astronomers led by Kunio M. Sayanagi, an Assistant Professor at Hampton University in Virginia, leveraged the amateur observations to activate a "Target of Opportunity" proposal on the Hubble Space Telescope, which imaged the entire planet on Oct. 14. Observing at a variety of wavelengths, HST revealed multiple storm components extending over a distance of more than 9,000 kilometers (5,760 miles) and clouds at a variety of altitudes.
De Pater, Sromovsky, Hammel and Pat Fry of the University of Wisconsin will report the details of their observations on Nov. 12 at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society's Division of Planetary Sciences in Tucson, Ariz.
Ice giant
Uranus is an ice giant, about four times the diameter of Earth, with an atmosphere of hydrogen and helium, with just a bit of methane to give it a blue tint. Because it is so distant - 30 times farther from the sun than Earth - astronomers were able to see little detail on its surface until adaptive optics on the Keck telescopes revealed features much like those on Jupiter.
De Pater and her colleagues have been following Uranus for more than a decade, charting the weather on the planet, including bands of circulating clouds, massive swirling storms and convective features at its north pole. Bright clouds are probably caused by gases such as methane rising in the atmosphere and condensing into highly reflective clouds of methane ice.
Because Uranus has no internal source of heat, its atmospheric activity was thought to be driven solely by sunlight, which is now weak in the northern hemisphere. Hence astronomers were surprised when these observations showed such intense activity.
Observations taken with the Keck telescope by Christoph Baranec, an Assistant Professor at the University of Hawaii on Manoa, revealed that the storm was still active, but had a different morphology and possibly reduced intensity.
"If indeed these features are high-altitude clouds generated by flow perturbations associated with a deeper vortex system, such drastic fluctuations in intensity would indeed be possible," Sromovsky added.
"These unexpected observations remind us keenly of how little we understand about atmospheric dynamics in outer planet atmospheres," the authors wrote in their paper.
INFORMATION:
In the fight against HIV, microbicides--chemical compounds that can be applied topically to the female genital tract to protect against sexually transmitted infections--have been touted as an effective alternative to condoms. However, while these compounds are successful at preventing transmission of the virus in a petri dish, clinical trials using microbicides have largely failed. A new study from the Gladstone Institutes and the University of Ulm now reveals that this discrepancy may be due to the primary mode of transportation of the virus during sexual transmission, ...
VIDEO:
The video illustrates the complete experiment. First the participant shown wearing the Oculus head-mounted display and the OptiTrack motion capture suit gives comfort to the crying virtual child. We see...
Click here for more information.
Self-compassion can be learned using avatars in an immersive virtual reality, finds new research led by UCL. This innovative approach reduced self-criticism and increased self-compassion and feelings of contentment in naturally self-critical ...
It is claimed one in five students have taken the 'smart' drug Modafinil to boost their ability to study and improve their chances of exam success. But new research into the effects of Modafinil has shown that healthy students could find their performance impaired by the drug.
The study carried out by Dr Ahmed Dahir Mohamed, in the School of Psychology at The University of Nottingham Malaysia Campus, and published today, Wednesday 12 November 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE, showed the drug had negative effects in healthy people.
Dr Mohamed said: "We looked ...
CORAL GABLES, Fla. (Nov. 12, 2014) -- Crowdsourcing utilizes the input of a crowd of online users to collaboratively solve problems. To advance this emerging technology, researchers at the University of Miami are developing a computing model that uses crowdsourcing to combine and optimize human efforts and machine computing elements.
The new model can be used to efficiently perform the complex tasks of face recognition--a method used in law enforcement. It's a new approach to using social networks as a formal part of the criminal investigation process, explained computer ...
Making friends is often extremely difficult for people with social anxiety disorder and to make matters worse, people with this disorder tend to assume that the friendships they do have are not of the highest quality.
The problem with this perception, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis, is that it's not necessarily true from the point of view of their friends.
"People who are impaired by high social anxiety typically think they are coming across much worse than they really are," said study co-author Thomas Rodebaugh, PhD, associate professor ...
While the Martinis Lab at UC Santa Barbara has been focusing on quantum computation, former postdoctoral fellow Pedram Roushan and several colleagues have been exploring qubits (quantum bits) for quantum simulation on a smaller scale. Their research appears in the current edition of the journal Nature.
"While we're waiting on quantum computers, there are specific problems from various fields ranging from chemistry to condensed matter that we can address systematically with superconducting qubits," said Roushan, who is now a quantum electronics engineer at Google. "These ...
It's not uncommon to see cameras mounted on store ceilings, propped up in public places or placed inside subways, buses and even on the dashboards of cars.
Cameras record our world down to the second. This can be a powerful surveillance tool on the roads and in buildings, but it's surprisingly hard to sift through vast amounts of visual data to find pertinent information - namely, making a split-second identification and understanding a person's actions and behaviors as recorded sequentially by cameras in a variety of locations.
Now, University of Washington electrical ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - Peering deep into time with one of the world's newest, most sophisticated telescopes, astronomers have found a galaxy - AzTEC-3 - that gives birth annually to 500 times the number of suns as the Milky Way galaxy, according to a new Cornell University-led study published Nov. 10 in the Astrophysical Journal.
Lead author Dominik Riechers, Cornell assistant professor of astronomy, and an international team of researchers gazed back - with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile - over 12.5 billion years to find bustling galaxies creating ...
New York, NY - The female mosquitoes that spread dengue and yellow fever didn't always rely on human blood to nourish their eggs. Their ancestors fed on furrier animals in the forest. But then, thousands of years ago, some of these bloodsuckers made a smart switch: They began biting humans and hitchhiked all over the globe, spreading disease in their wake.
"It was a really good evolutionary move," says Leslie B. Vosshall, the Robin Chemers Neustein Professor and head of the Laboratory of Neurogenetics and Behavior at The Rockefeller University, and a Howard Hughes Medical ...
As cities and incomes increase around the world, so does consumption of refined sugars, refined fats, oils and resource- and land-intense agricultural products such as beef. A new study led by University of Minnesota ecologist David Tilman shows how a shift away from this trajectory and toward healthier traditional Mediterranean, pescatarian or vegetarian diets could not only boost human lifespan and quality of life, but also slash greenhouse gas emissions and save habitat for endangered species.
The study, published in the November 12 online edition of Nature by Tilman ...