(Press-News.org) Irvine, Calif., Nov. 13, 2014 -- A new bloodstream infection test created by UC Irvine researchers can speed up diagnosis times with unprecedented accuracy, allowing physicians to treat patients with potentially deadly ailments more promptly and effectively.
The UCI team, led by Weian Zhao, assistant professor of pharmaceutical sciences, developed a new technology called Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection. In as little as 90 minutes, IC 3D can detect bacteria in milliliters of blood with single-cell sensitivity; no cell culture is needed.
The work appears online today in Nature Communications.
"We are extremely excited about this technology because it addresses a long-standing unmet medical need in the field," Zhao said. "As a platform technology, it may have many applications in detecting extremely low-abundance biomarkers in other areas, such as cancers, HIV and, most notably, Ebola."
Bloodstream infections are a major cause of illness and death. In particular, infections associated with antimicrobial-resistant pathogens are a growing health problem in the U.S. and worldwide. According to the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, more than 2 million people a year globally get antibiotic-resistant blood infections, with about 23,000 deaths. The extremely high mortality rate for blood infections is due, in part, to the inability to rapidly diagnose and treat patients in the early stages.
Recent molecular diagnosis methods, including polymerase chain reaction, can reduce the assay time to hours but are often not sensitive enough to detect bacteria that occur at low concentrations in blood, as is common in patients with blood infections.
The IC 3D technology differs from other diagnostic techniques in that it converts blood samples directly into billions of very small droplets. Fluorescent DNA sensor solution infused into the droplets detects those with bacterial markers, lighting them up with an intense fluorescent signal. Zhao said that separating the samples into so many small drops minimizes the interference of other components in blood, making it possible to directly detect target bacteria without the purification typically required in conventional assays.
To identify bacteria-containing droplets among billions of others in a timely fashion, the team incorporated a three-dimensional particle counter developed by UCI biomedical engineer Enrico Gratton and his colleagues that tags fluorescent particles within several minutes.
"The IC 3D instrument is designed to read a large volume in each measurement, to speed up diagnosis," Gratton said. "Importantly, using this technique, we can detect a positive hit with very high confidence."
INFORMATION:
A UCI spinoff, Velox Biosystems, is now further developing the IC 3D technology.
Dong-Ku Kang, M. Monsur Ali, Kaixiang Zhang, Dr. Susan Huang, Ellena Peterson and Michelle Digman of UCI contributed to the work, which received startup funding from UCI's Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Sue & Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center, and Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center. The National Institutes of Health (grants UL1 TR000153, P41 GM103540 and P50-GM076516) also provided support.
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UCI is the youngest member of the prestigious Association of American Universities. The campus has produced three Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UCI has more than 28,000 students and offers 192 degree programs. Located in one of the world's safest and most economically vibrant communities, it's Orange County's second-largest employer, contributing $4.8 billion annually to the local economy.
Media access: Radio programs/stations may, for a fee, use an on-campus ISDN line to interview UC Irvine faculty and experts, subject to availability and university approval. For more UC Irvine news, visit news.uci.edu. Additional resources for journalists may be found at communications.uci.edu/for-journalists.
Contact:
Tom Vasich
949-824-6455
tmvasich@uci.edu
The Sudbury Basin located in Ontario, Canada is one of the largest known impact craters on Earth, as well as one of the oldest due to its formation more than 1.8 billion years ago. Researchers who took samples from the site and subjected them to a detailed geochemical analysis say that a comet may have hit the area to create the crater.
"Our analysis revealed a chondritic platinum group element signature within the crater's fallback deposits; however, the distribution of these elements within the impact structure and other constraints suggest that the impactor was a comet. ...
Among overweight and obese adults who had asthma and participated in weight loss programs, more severe asthma, male sex, and improvements in eating behaviors were all linked with better success at losing weight.
The finding that individuals with more severe asthma may have a greater motivation to lose weight suggests that these individuals should be targeted for intervention. Also, gender tailoring of weight loss programs may be useful to enhance weight loss success, said Lisa Wood, senior author of the Respirology study.
INFORMATION: ...
People can gauge the accuracy of their decisions, even if their decision making performance itself is no better than chance, according to a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
In the study, people who showed chance-level decision making still reported greater confidence about decisions that turned out to be accurate and less confidence about decisions that turned out to be inaccurate. The findings suggest that the participants must have had some unconscious insight into their decision making, even though ...
Philadelphia, PA (November 13, 2014) -- Patients on dialysis are very vulnerable during emergencies or disasters, but many are unprepared for such situations, according to two studies that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Dialysis patients are highly dependent on technologies to sustain their lives, with ongoing needs for transportation, electricity, and water for the dialysis apparatus. Interruption of these needs by a natural disaster can be devastating.
Naoka Murakami, MD, PhD ...
TORONTO, Nov. 13, 2014--Canadians with cystic fibrosis are living almost 20 years longer than they did two decades ago, according to a research paper published today.
The median survival age was 49.7 years in 2012, up from 31.9 years in 1990, Dr. Anne Stephenson, a respirologist and research at St. Michael's Hospital wrote in the European Respiratory Journal. Since the paper was written, Dr. Stephenson has updated the median survival age to include Cystic Fibrosis Canada data from 2013 and reported the median age of survival has in fact reached 50.9 years.
In addition, ...
Scientists from the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles describe a new distinctive fly species of the highly diverse genus Megaselia. The study published in the Biodiversity Data Journal proposes an innovative method for streamlining Megaselia species descriptions to save hours of literature reviews and comparisons.
The new species, M. shadeae, is easily distinguished by a large, central, pigmented and bubble-like wing spot. The description is part of the the Zurquí All Diptera Biodiversity Inventory (ZADBI) project, and represents the first of an incredible ...
Mice bred to carry a gene variant found in a third of ALS patients have a faster disease progression and die sooner than mice with the standard genetic model of the disease, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. Understanding the molecular pathway of this accelerated model could lead to more successful drug trials for all ALS patients.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, commonly known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a degeneration of lower and upper motor neurons in the brainstem, spinal cord and the motor cortex. The disease, which affects 12,000 Americans, ...
Philadelphia, November 13, 2014 - Associations between opioid-related overdoses and increased prescription of opioids for chronic noncancer pain are well known. But some suggest that overdose occurs predominately in individuals who obtain opioids from nonmedical sources. In a new study published in the November issue of the journal PAIN®, researchers in Denmark found an increased risk of death associated with chronic pain without opioid treatment, as well as an even higher risk among those prescribed opioids for long-term use and a somewhat lower risk associated with ...
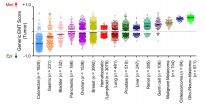
Scientists at the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS) and their collaborators have developed a scoring scheme that predicts the ability of cancer cells to spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis. This system, which is the first of its kind, opens up the possibility to explore new treatments that suppress metastasis in cancer patients. The findings were published in EMBO Molecular Medicine in September.
Led by Professor Jean Paul Thiery, Senior Principal Investigator, and Dr Ruby Huang, ...
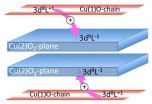
Swedish materials researchers at Linköping and Uppsala University and Chalmers University of Technology, in collaboration with researchers at the Swiss Synchrotron Light Source (SLS) in Switzerland investigated the superconductor YBa2Cu3O7-x (abbreviated YBCO) using advanced X-ray spectroscopy.
Their findings are published in the Nature journal Science Reports.
YBCO is a well-known ceramic copper-based material that can conduct electricity without loss (superconductivity) when it is cooled below its critical temperature Tc=-183° C. Since the resistance and ...