(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich. --U.S. children's hospitals delivering the highest-quality care for children undergoing heart surgery, also appear to provide care most efficiently at a low cost, according to research led by the University of Michigan and presented Tuesday at the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions in Chicago.
Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defects, and each year more than 30,000 congenital heart operations are performed across U.S. children's hospitals. Congenital heart defects are also one of the most expensive pediatric conditions to treat.
Given the many current initiatives in healthcare aimed at both improving quality of care and reducing costs, or optimizing value, University of Michigan researchers along with collaborators across several different U.S. children's hospitals decided to study whether it is possible to deliver high-quality heart care but also at a low cost, says the study's lead author, Sara K. Pasquali, M.D., associate professor of pediatric cardiology within the Michigan Congenital Heart Center at U-M's C.S. Mott Children's Hospital and U-M's Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy.
The researchers studied 30,670 patients ages 0-18 years undergoing heart surgery across 27 different hospitals, using a unique dataset of merged clinical and cost information from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons and Children's Hospital Association.
According to Pasquali, costs of care differed by 5-fold across these hospitals. The lowest -cost hospitals had significantly lower mortality rates compared to the other hospitals. The low-cost hospitals also had shorter lengths of stay after surgery and fewer post-operative complications.
Interestingly, the low-cost hospitals tended to be larger volume centers, who were able to achieve these outcomes despite treating a more high-risk patient population.
"The care of children with congenital heart conditions is complex and requires significant investment of resources. It has been unclear whether there are centers able to provide high quality care, but also at a low cost," says Pasquali, who is a member of the Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation at U-M.
"Understanding these relationships is critical in the appropriate design of policies aiming to optimize healthcare value in this population and others. For example, one would not want to provide incentives to low-cost hospitals if these low costs were due to poor clinical outcomes, such as high rates of mortality."
What this new research shows, Pasquali says, is that lower-cost hospitals seem to be doing the right thing: they are delivering the highest-quality care to children undergoing heart surgery.
"In addition, these results suggest that initiatives that aiming to improve quality of care and outcomes, may also hold the potential to reduce costs in this population she says.
INFORMATION:
Additional authors: Of the University of Michigan: Edward L. Bove, Michael G. Gaies, Jennifer C. Hirsch-Romano. Of Johns Hopkins: Jeffrey P. Jacobs, Marshall L. Jacobs. Of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia: J. William Gaynor. Of Duke Clinical Research Institute: Eric D. Peterson, Xia He. Of Boston Children's Hospital: John E. Mayer. Of Primary Children's Hospital: Nelangi M. Pinto. Of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center: Samir S. Shah. Of Children's Hospital Association: Matt Hall.
Funding: This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Disclosure: None
About congenital heart services at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital:
The specialists at the Congenital Heart Center at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital are skilled at treating the full spectrum of congenital heart conditions. As one of the highest volume programs in the country, we perform approximately 900 procedures a year. U.S. News and World Report ranked our program in the top 10 in the country for cardiology and heart surgery. More information is available at http://www.mottchildren.org/congenital.
A Georgia Tech professor is offering an alternative to the celebrated "Turing Test" to determine whether a machine or computer program exhibits human-level intelligence. The Turing Test - originally called the Imitation Game - was proposed by computing pioneer Alan Turing in 1950. In practice, some applications of the test require a machine to engage in dialogue and convince a human judge that it is an actual person.
Creating certain types of art also requires intelligence observed Mark Riedl, an associate professor in the School of Interactive Computing at Georgia Tech, ...
Empagliflozin (trade name Jardiance) has been approved since May 2014 for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in whom diet and exercise alone do not provide adequate glycaemic control. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether the drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapies in these patient groups.
According to the findings, such an added benefit is not proven: For four of five research questions, the manufacturer presented no relevant data in its dossier. For the fifth ...
Following a 5,000 km long ocean survey, research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences presents a new way to measure how the acidification of water is affecting marine ecosystems over an entire oceanic basin.
As a result of man-made emissions, the content of CO2 in the atmosphere and oceans has increased dramatically during recent decades. In the ocean, the accumulating CO2 is gradually acidifying the surface waters, making it harder for shelled organisms like corals (Figure 1) and certain open sea plankton to build their calcium carbonate ...
Flexible electronic sensors based on paper -- an inexpensive material -- have the potential to some day cut the price of a wide range of medical tools, from helpful robots to diagnostic tests. Scientists have now developed a fast, low-cost way of making these sensors by directly printing conductive ink on paper. They published their advance in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Anming Hu and colleagues point out that because paper is available worldwide at low cost, it makes an excellent surface for lightweight, foldable electronics that could be made and ...
Now that car makers have demonstrated through hybrid vehicle success that consumers want less-polluting tailpipes, they are shifting even greener. In 2015, Toyota will roll out the first hydrogen fuel-cell car for personal use that emits only water. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, explains how hydrogen could supplant hybrid and electric car technology -- and someday, even spur the demise of the gasoline engine.
Melody M. Bomgardner, a senior editor at C&EN, notes that the first fuel-cell vehicles ...
Exposure to peanut proteins in household dust may be a trigger of peanut allergy, according to a study published today in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
The study was conducted in 359 children aged 3-15 months taking part in the NIH-sponsored Consortium for Food Allergy Research (CoFAR) study. These children were at high risk of developing a peanut allergy based on having likely milk or egg allergy or eczema. The study found that the risk of having strong positive allergy tests to peanut increased with increasingly higher amounts of peanut found in ...
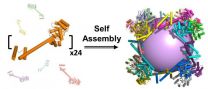
UCLA biochemists have created the largest-ever protein that self-assembles into a molecular "cage." The research could lead to synthetic vaccines that protect people from the flu, HIV and other diseases.
At a size hundreds of times smaller than a human cell, it also could lead to new methods of delivering pharmaceuticals inside of cells, or to the creation of new nanoscale materials.
The protein assembly, which is shaped like a cube, was constructed from 24 copies of a protein designed in the laboratory of Todd Yeates, a UCLA professor of chemistry and biochemistry. ...
A new treatment for Marfan syndrome, a rare genetic disease that can lead to heart problems, works as well as the currently recommended medical therapy, beta blockers, according to an article in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Angela Sharkey, M.D., professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University, and a study author, said researchers found losartan, which had been more effective in an animal model of Marfan syndrome, was equally effective to a high dose of the beta blocker atenolol.
"While there may be certain patients who respond better to one drug or another, ...
Researchers from the University of Melbourne found unlike other laser treatments, this new faster laser did not result in damage to the retina, the sensitive light detecting tissue at the back of the eye.
Associate Professor Erica Fletcher from the Department of Anatomy and Neuroscience said this was the first report detailing how this new laser treatment may improve eye health in those with AMD. In the early stages, the disease is characterised by the presence of small fatty deposits called drusen and thickening in a membrane at the back of the eye.
Published this ...
Barcelona, Spain: A new drug that targets not only common cancer-causing genetic mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but also a form of the mutation that causes resistance to treatment, has shown promising results in patients in a phase I/II clinical trial. The research will be presented today (Friday) at the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain.
Approximately 10-15% of Caucasian and 30-35% of Asian patients with NSCLC have a mutation in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which ...