Why tool-wielding crows are left- or right-beaked
2014-12-04
(Press-News.org) New Caledonian crows--well known for their impressive stick-wielding abilities--show preferences when it comes to holding their tools on the left or the right sides of their beaks, in much the same way that people are left- or right-handed. Now researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on December 4 suggest that those bill preferences allow each bird to keep the tip of its tool in view of the eye on the opposite side of its head. Crows aren't so much left- or right-beaked as they are left- or right-eyed.
"If you were holding a brush in your mouth and one of your eyes [was] better than the other at brush length, you would hold the brush so that its tip fell in view of the better eye," says Alejandro Kacelnik of the University of Oxford. "This is what the crows do."
The new study also suggests that the birds' extreme binocular vision--characterized by an unusually wide field of view in comparison to other species--actually helps the crows see better with one eye at a time.
"Binocular vision is often connected to allowing the brain to compare the images seen by each eye, inferring properties of the scene from the differences between these images," explains Antone Martinho of the University of Oxford. "We thought that their binocular fields would facilitate binocular vision, perhaps allowing the birds to judge the distance from tool tip to target. It turned out that, most frequently, they only see the tool tip and target with one eye at a time."
In other words, the birds are using their notable binocular vision for better monocular vision, allowing each eye to see further toward the other side of the beak. The birds' unusually wide binocular field is among the first known examples of a physical adaptation to enable tool use, the researchers say.
The crows are one of the most innovative tool users in the animal kingdom, and for good reason. They must use sticks to extract larvae from burrows. In some ways, the New Caledonian crows have a tougher problem to solve than humans do when it comes to using tools, because they don't have the luxury of moving their eyes and beaks independently like humans can with their eyes and hands.
Nevertheless, the findings are a reminder of our shared animal natures, the researchers say.
"Birds and humans face similar problems in tool use and many other activities," Kacelnik says. "Studying similar problems across species helps to put all of them in perspective."
INFORMATION:
Current Biology, Martinho III et al.: "Monocular tool control, eye dominance, and laterality in New Caledonian crows."
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-04
Blood cancers are more common in men than in women, but it has not been clear why this is the case. A study published by Cell Press December 4th in Cell Stem Cell provides an explanation, revealing that female sex hormones called estrogens regulate the survival, proliferation, and self-renewal of stem cells that give rise to blood cancers. Moreover, findings in mice with blood neoplasms--the excessive production of certain blood cells--suggest that a drug called tamoxifen, which targets estrogen receptors and is approved for the treatment of breast cancer, may also be a ...
2014-12-04
In a breakthrough study to be published on the December 4th issue of the prestigious scientific journal Cell, a research team led by Miguel Soares at the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC; Portugal) discovered that specific bacterial components in the human gut microbiota can trigger a natural defense mechanism that is highly protective against malaria transmission.
Over the past few years, the scientific community became aware that humans live under a continuous symbiotic relationship with a vast community of bacteria and other microbes that reside in the gut. ...
2014-12-04
This discovery has a potential application in the treatment of certain blood disorders for which there is currently no cure. The study was led by Dr. Simón Méndez-Ferrer of the CNIC, working in partnership with the laboratories of Doctors Jürg Schwaller and Radek Skoda of the University Hospital in Basel (Switzerland). The study's authors have demonstrated in mice that tamoxifen, a drug already approved and widely used for the treatment of breast cancer, blocks the symptoms and the progression of a specific group of blood disorders known as myeloproliferative ...
2014-12-04
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- In a study in the journal Neuron, scientists describe a new high data-rate, low-power wireless brain sensor. The technology is designed to enable neuroscience research that cannot be accomplished with current sensors that tether subjects with cabled connections.
Experiments in the paper confirm that new capability. The results show that the technology transmitted rich, neuroscientifically meaningful signals from animal models as they slept and woke or exercised.
"We view this as a platform device for tapping into the richness of ...
2014-12-04
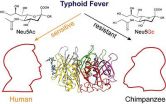
The bacterium Salmonella Typhi causes typhoid fever in humans, but leaves other mammals unaffected. Researchers at University of California, San Diego and Yale University Schools of Medicine now offer one explanation -- CMAH, an enzyme that humans lack. Without this enzyme, a toxin deployed by the bacteria is much better able to bind and enter human cells, making us sick. The study is published in the Dec. 4 issue of Cell.
In most mammals (including our closest evolutionary cousins, the great apes), the CMAH enzyme reconfigures the sugar molecules found on these animals' ...
2014-12-04
The link between obesity and cardiovascular diseases is well acknowledged. Being obese or overweight is a major risk factor for the development of elevated blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases. But it has net been known how obesity increases the risk of high blood pressure, making it difficult to develop evidence based therapies for obesity, hypertension and heart disease.
In a ground-breaking study, published today in the prestigious journal, Cell (embargo midday EST), researchers from Monash University in Australia, Warwick, Cambridge in the UK and several American ...
2014-12-04
Leptin, a hormone that regulates the amount of fat stored in the body, also drives the increase in blood pressure that occurs with weight gain, according to researchers from Monash University and the University of Cambridge.
Being obese or overweight is a major risk factor for the development of high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Whilst a number of factors may be involved, the precise explanation for the link between these two conditions has been unclear.
In a study published today in the journal Cell, a research team led by Professor Michael Cowley, ...
2014-12-04
PHILADELPHIA--People with mental illness are more likely to have been tested for HIV than those without mental illness, according to a new study from a team of researchers at Penn Medicine and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published online this week in AIDS Patient Care and STDs. The researchers also found that the most seriously ill - those with schizophrenia and bipolar disease - had the highest rate of HIV testing.
The study assessed nationally representative data from 21,785 adult respondents from the 2007 National Health Interview Survey ...
2014-12-04
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Take two poisonous mushrooms, and call me in the morning. While no doctor would ever write this prescription, toxic fungi may hold the secrets to tackling deadly diseases.
A team of Michigan State University scientists has discovered an enzyme that is the key to the lethal potency of poisonous mushrooms. The results, published in the current issue of the journal Chemistry and Biology, reveal the enzyme's ability to create the mushroom's molecules that harbor missile-like proficiency in attacking and annihilating a single vulnerable target in the ...
2014-12-04
Some National Football League (NFL) players have been seeking out unproven stem cell therapies to help accelerate recoveries from injuries, according to a new paper from Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy. While most players seem to receive treatment within the United States, several have traveled abroad for therapies unavailable domestically and may be unaware of the risks involved, the paper found.
The paper is published in the 2014 World Stem Cell Report, which is a special supplement to the journal Stem Cells and Development and is the official publication ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Why tool-wielding crows are left- or right-beaked