(Press-News.org) EVANSTON, Ill. --- A new approach to analyzing baseball-pitching biomechanics may one day give players more personalized feedback and help prevent elbow injuries.
In a computer simulation study of baseball pitching, Northwestern University biomedical engineers found that the strength of the elbow muscles of a baseball pitcher likely play a bigger role in injury risk and prevention than previously thought.
The motion analysis approach currently used in the baseball industry to provide athletes with injury-risk feedback is not sophisticated enough to estimate what an individual player's muscles are doing during a pitching motion or how his muscles are contributing to injury risk.
"Muscles matter in baseball," said James Buffi, first author of the study. "We showed that a pitcher could be at a really high risk or a really low risk of elbow injury, depending on how strong and capable his muscles are."
Buffi is a recent Ph.D. graduate in biomedical engineering at Northwestern's McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science.
He conducted the research with senior author Wendy M. Murray, associate professor of biomedical engineering at McCormick. Murray also has joint appointments in the departments of physical medicine and rehabilitation and physical therapy and human movement sciences at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
"Pitching is an extreme and difficult motion," said Murray, who also is a research scientist at the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago. "Pitchers are literally throwing so hard that the motion itself acts to tear the elbow joint apart. But why doesn't it? The answer is the strength of the muscles and the ligaments. That's what keeps the bones together."
Results of the study are detailed online in the journal Annals of Biomedical Engineering.
Many baseball pitchers experience an elbow injury at some point in their career. The most common is failure of the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL), which requires ligament reconstruction known as Tommy John surgery.
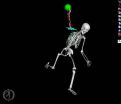
To better understand the stress pitching puts on the UCL, the Northwestern researchers used a specific computer model developed from bone, muscle and ligament geometry measurements taken in cadavers, as well as muscle volume and strength measurements taken in living subjects. This is the same model developed and used by the researchers to study arm and hand control for advanced prosthetic devices.
They developed a computer simulation of a real high school pitcher's throwing motion to investigate how individual muscles can affect UCL loading and how changes in muscle output can either relieve or exacerbate the load on the UCL.
"Our simulations illustrate that if the muscles were doing nothing, then the bones that make up the elbow joint could have been pulled apart during that single pitch. In contrast, we also were able to implement reasonable assumptions about muscle performance that showed how the very same pitch could result in no load on the UCL at all," Murray said.
While this study only looked at one pitcher and one motion, the simulation approach allowed the researchers to repeat the engineering analysis of the mechanics of that pitch while making different assumptions about what complicated muscles and ligaments are doing and how they are working during a pitch.
The researchers evaluated how effectively the muscles countered the dangerous load at the elbow joint during a pitch and used a variety of assumptions to understand how sensitive the simulation results were to muscle strength and other model parameters.
With more research, this approach could enable targeted training of specific muscles and more accurate assessments of UCL vulnerability, Buffi said. He is planning to use this research and further this work in a career in the baseball industry.
"Elbow injuries are a huge problem in baseball, from little to major leagues, and our study shows that muscles play a part," Buffi said. "If you're not accounting for muscles, even if you know the total elbow load on a pitcher, he could be at a really high risk or a really low risk of injury depending on how strong and capable his muscles are."
INFORMATION:
April 8, 2015--Researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia Business School studied bed capacity --measured by the number of staffed beds -- in New York City hospital obstetrics units and found a significant excess number of beds, which overall cost the city an estimated $26.4 million each year. The findings, coupled with the current trends of an aging population and the declining birth rate, suggest that many obstetrics units could reduce their bed capacity and still assure timely access to care. Study findings are published in the ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--Biologists at MIT and the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research have discovered a vulnerability of brain cancer cells that could be exploited to develop more-effective drugs against brain tumors.
The study, led by researchers from the Whitehead Institute and MIT's Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, found that a subset of glioblastoma tumor cells is dependent on a particular enzyme that breaks down the amino acid glycine. Without this enzyme, toxic metabolic byproducts build up inside the tumor cells, and they die.
Blocking this enzyme ...
BOSTON (April 8, 2015) -- A two-year epidemiological study of Puerto Rican adults with type 2 diabetes in the greater Boston area who were using insulin and lived next to roads with heavy traffic had markedly increased C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation, compared to those living in lower traffic areas. Individuals taking oral diabetes medications did not experience increases in CRP concentration. The study, published online in Environmental Pollution, builds on the research team's previous work suggesting that oral diabetes medications may provide a protective ...
Since 2007, California has had one of the most aggressive incentive programs in the country for putting solar-electric panels on the rooftops of homes and businesses. Its $2.2 billion California Solar Initiative (CSI)has provided a per-watt rebate for installing residential and commercial photovoltaic systems. During this period, the solar industry in the state has experienced double-digit growth and to date has installed more than 245,000 systems capable of producing 2,365 megawatts of electricity.
As a result, CSI has been widely touted as a major success. However, ...
Numerous studies over the past 30 years have linked exposure to nature with improved human health and well-being. These findings are of growing importance: In the near future, 70% of the world's population will live in cities, where they will face a rising tide of lifestyle-related disease. Still, little is known about the mechanisms underlying the nature-health connection, and confusion awaits those who would transform existing findings into action.
In the June issue of BioScience, a group of biologists and public health experts led by Danielle F. Shanahan address this ...
The ceremonial opening kick of the 2014 FIFA World Cup in Sao Paolo, Brazil, which was performed--with the help of a brain-controlled exo-skeleton--by a local teen who had been paralyzed from the waste down due to a spinal cord injury, was a seminal moment for the area of neuroscience that strives to connect the brain with functional prosthetics. The public display was a representative of thousands of such neuroprosthetic advances in recent years, and the tens of years of brain research and technological development that have gone into them. And while this display was quite ...
Strong vertical wind shear has taken a toll on Tropical Cyclone Ikola and that was pretty clear in a visible-light image from NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite today, April 8.
When Suomi NPP flew over Tropical Cyclone Ikola at 07:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EDT), the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard captured a visible image of the storm.
VIIRS is a scanning radiometer that collects visible and infrared imagery and "radiometric" measurements. Basically it means that VIIRS data is used to measure cloud and aerosol properties, ocean color, sea and ...
A University of Calgary study has found that rats fed a fibre supplement while on a high fat and high sugar diet show a much lower weight gain than those who did not eat the fibre. A team of researchers from the university's Cumming School of Medicine and the Faculty of Kinesiology says the study helps scientists better understand the mechanisms of weight control and energy balance.
"Our data shows that a simple dietary intervention, with a prebiotic oligofructose fibre, reduced weight gain, and this may also lead to the long-term maintenance of a lower body weight in ...
Argonne, Ill. - A clearer understanding of the origin recognition complex (ORC) - a protein complex that directs DNA replication - through its crystal structure offers new insight into fundamental mechanisms of DNA replication initiation. This will also provide insight into how ORC may be compromised in a subset of patients with Meier-Gorlin syndrome, a form of dwarfism in humans.
ORC is a six-subunit protein complex that directly binds DNA to recruit other protein factors involved in DNA replication. Researchers collected data at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a U.S. ...
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's GPM satellite provided scientists with a look "under the hood" of Tropical Cyclone Joalane's clouds at the rate in which rain was falling throughout the storm.
The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core observatory satellite flew over intensifying cyclone Joalane in the South Indian Ocean on April 6, 2015 at 0406 UTC (12:06 a.m. EDT). GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) found that intense convective thunderstorms within Joalane were dropping rain at a rate of over 63 mm (2.5 inches) per hour.
Cyclone Joalane was located ...