One-third of women with ADHD report being sexually abused during childhood
2015-04-15
(Press-News.org) Adults who have ADHD are much more likely to report they were sexually and physically abused before they turned 16 than their peers without ADHD, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Toronto.
Among women, 34 per cent of those with ADHD reported they were sexually abused before they turned 18. In contrast, 14 per cent of women without ADHD reported that they had experienced childhood sexual abuse. Twice as many women with ADHD reported that they had experienced childhood physical abuse than women without this condition (44% vs 21%).
"These findings suggest there is a silent epidemic of abuse among people and particularly women with ADHD," says co-author Esme Fuller-Thomson, professor and Sandra Rotman Endowed Chair at U of T's Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work and the Faculty of Medicine.
Fuller-Thomson's research also noted that a greater percentage of men with ADHD than men without ADHD reported that they were sexually abused (11 per cent vs six per cent) or physically abused (41 per cent vs 31 per cent) during their childhood.
Investigators examined a nationally representative sample of 12,877 women and 10,496 men in the 2012 Canadian Community Health Survey-Mental Health.
Fuller-Thomson emphasized that the data cannot clarify the direction of the association. "It may be that early maltreatment affects neurobiological development," says Fuller-Thomson. "It is also possible that children with ADHD are more vulnerable to abuse."
The results appeared in a study published online this week in Child Abuse & Neglect.
"The questions in the survey did not identify who was abusing the children, it could have been a family member or a non-related adult" said study co-author, Danielle Lewis, a graduate student in U of T's Masters of Social Work program. "No matter who is the perpetrator, it is very important that health professionals working with children with ADHD screen them for sexual and physical abuse."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-15
A species of bone-eating worm that was believed to have evolved in conjunction with whales has been dated back to prehistoric times when it fed on the carcasses of giant marine reptiles.
Scientists at Plymouth University found that Osedax - popularised as the 'zombie worm' - originated at least 100 million years ago, and subsisted on the bones of prehistoric reptiles such as plesiosaurs and sea turtles.
Reporting in the Royal Society journal Biology Letters this month, the research team at Plymouth reveal how they found tell-tale traces of Osedax on plesiosaur fossils ...
2015-04-15
UCLA researchers have found that 77 percent of California primary care and specialty physicians understand the basics of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and 59 percent support it. The survey, conducted by doctors from the UCLA department of family medicine, was published in the peer-reviewed journal Family Medicine.
Researchers also found that a majority of the 525 doctors surveyed believe ACA will steer the country's health care in the right direction.
The doctors' stance on the law appeared to be closely correlated with their political affiliations ...
2015-04-15
New research from New Zealand's University of Otago is providing the most comprehensive picture of the evolutionary history of baleen whales, which are not only the largest animals ever to live on earth, but also among the most unusual.
Most other mammals feed on plants or grab a single prey animal at a time, but baleen whales are famous for their gigantic mouths and their ability to gulp and filter an enormous volume of water and food.
In a paper appearing in the UK journal Royal Society Open Science, Otago Geology PhD graduate Dr Felix Marx and Professor Ewan Fordyce ...
2015-04-15
New York, NY--April 15, 2015--A research team led by Shree K. Nayar, T.C. Chang Professor of Computer Science at Columbia Engineering, has invented a prototype video camera that is the first to be fully self-powered--it can produce an image each second, indefinitely, of a well-lit indoor scene. They designed a pixel that can not only measure incident light but also convert the incident light into electric power. The team is presenting its work at the International Conference on Computational Photography at Rice University in Houston, April 24 to 26.
"We are in the middle ...
2015-04-15
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY'S HAAS SCHOOL OF BUSINESS -CEOs make a lot of money from incentive pay tied to stock performance. Although such schemes help align executives' interests with shareholders, they are not necessarily the best schemes as compared to schemes that rely on trust between board and executives.
"Ironically, the necessary trust is easier to establish when the alternative of using stock-based pay is less powerful. Our research found that government-imposed limits on contingent compensation make stock-based pay a worse alternative, facilitating superior ...
2015-04-15
Thermoluminescence is used extensively in archaeology and the earth sciences to date artefacts and rocks. When exposed to radiation quartz, a material found in nature, emits light proportional to the energy it absorbs. Replicating the very low dose of background radiation from natural sources present in quartz is a key precondition for precise and accurate dating results. Italian scientists have now developed a method to control the accuracy of the dose calibrations delivered to the samples during laboratory irradiation with heavy particles, replicating natural radiation ...
2015-04-15
According to the World Health Organization, breast cancer is the most common cancer in women both in the developed and less developed world, and in the long term the scientists hope that the new method will lead to better prevention and early treatment of the disease.
"The method is better than mammography, which can only be used when the disease has already occurred. It is not perfect, but it is truly amazing that we can predict breast cancer years into the future," said Rasmus Bro, a professor of chemometrics in the Department of Food Science at University of Copenhagen. ...
2015-04-15
Today it is not possible to predict spreading from malignant melanomas. Melanoma metastases are furthermore extremely difficult to eliminate as traditional treatment such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy is mostly ineffective. Only ten per cent of the patients survive once they reach an advanced stage with distant metastases.
New research now demonstrates that the presence of the protein megalin in a malignant melanoma is an indicator of cancer cells that are particularly aggressive. The protein improves the ability of the cancer cells to divide and to survive. Accordingly, ...
2015-04-15
COLLEGE STATION, TX - The bedding plants sold in retail outlets are typically grown in greenhouse production environments where professionals can monitor irrigation, light, and temperature. When the greenhouse-grown plants reach the retail market, however, they are often subjected to a range of less-than-ideal light levels, temperatures, and irrigation schedules that can be detrimental to plant quality and vigor. Researchers are looking for ways to increase bedding plants' shelf life to offset the negative impacts of postharvest handling.
A new research study of the popular ...
2015-04-15
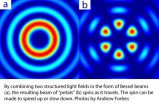
Light must travel in a straight line and at a constant speed, or so the laws of nature suggest. Now, researchers at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg have demonstrated that laser light traveling along a helical path through space, can accelerate and decelerate as it spins into the distance.
This is the first time that angular acceleration has been observed with light, and is therefore likely to lead to new applications using these structured light fields.
The results are contained in a research paper by Professor Andrew Forbes from the Wits School of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] One-third of women with ADHD report being sexually abused during childhood