Revolutionary discovery leads to invention of new 'building blocks'
University of Akron polymer researchers create a new class of hybrid materials
2015-04-23
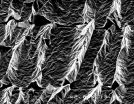
(Press-News.org) Polymer science will have to add a new giant molecule to its lexicon thanks to a cutting-edge discovery at The University of Akron. Taking a revolutionary "building blocks" approach, researchers have pioneered a way to create a new class of very large polymer molecules, called macromolecules, which assemble themselves into strong, stable structures. The work has been done in collaboration with researchers at Peking University in China and The University of Tokyo in Japan. Their findings have been published in the April 24, 2015 issue of Science magazine.
A team led by Stephen Z.D. Cheng, Ph.D., professor at The University of Akron's college of polymer science and polymer engineering, designed and synthesized the new polymer molecules called tetrahedrons, a solid with four equal triangular faces. Through a reaction called "click chemistry," these tetrahedron building blocks can then be precisely manipulated to unite with other tetrahedrons.
"It had never been done before in soft matter, where it's engineering could be particularly useful," explains Cheng, "and it took 3 years to design."
"This research quite possibly marks the first time we have documented this experimental transformation from nano-sized giant tetrahedral to supramolecular lattices," said Joe Akkara, a materials science program director from the National Science Foundation, which funded the research. "This class of new hybrid materials could be custom designed for many functional materials including applications in nano-technologies "
The team's work opens the door to developing new materials for applications not yet imagined, such as electric, magnetic and optic functions. Over the next couple of years, they will work with a variety of industries to identify practical uses for this scientific breakthrough.
Cheng and his experts have received a $700,000, five-year grant from the National Science Foundation to continue pursuing this new pathway for designing and constructing the novel macromolecule.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-23
We know of about two dozen runaway stars, and have even found one runaway star cluster escaping its galaxy forever. Now, astronomers have spotted 11 runaway galaxies that have been flung out of their homes to wander the void of intergalactic space.
"These galaxies are facing a lonely future, exiled from the galaxy clusters they used to live in," said astronomer Igor Chilingarian (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics/Moscow State University). Chilingarian is the lead author of the study, which is appearing in the journal Science.
An object is a runaway if it's ...
2015-04-23
You think that your immune system is there to protect you. But what happens when it starts working against you?
In the earliest stages of cancer formation, the immune system is forced to make a momentous decision. It either activates and suppresses tumor growth to help the body fight disease, or it becomes dysfunctional, helping the tumor grow and making treatment more difficult. Because this tipping point occurs before a person even realizes something is wrong, doctors are unable to directly observe this critical stage.
"We believe that when immune cells enter a tumor ...
2015-04-23
WORCESTER, MA - Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School have applied a powerful tool in a new way to characterize genetic variants associated with human disease. The work, published today in Cell, will allow scientists to more easily and efficiently describe genomic variations underlying complex, multi-gene diseases.
"Up to this point, we've only been able to investigate one disease-causing mutation at a time," said principal investigator Marian Walhout, PhD, co-director of the Program in Systems Biology and professor of molecular medicine at UMMS. ...
2015-04-23
The oncologists Manuel Hidalgo, Director of the Clinical Research Programme of the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), and Ignacio Garrido-Laguna, member of the Experimental Therapeutics Program at Huntsman Cancer Institute of the University of Utah (USA), have recently published a review of state-of-the-art clinical treatments for pancreatic cancer -- including the most current therapies and innovative research -- in the prestigious scientific journal Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.
In their study, which reviews around 200 scientific articles published ...
2015-04-23
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Using a technique that introduces tiny wrinkles into sheets of graphene, researchers from Brown University have developed new textured surfaces for culturing cells in the lab that better mimic the complex surroundings in which cells grow in the body.
"We know that cells are shaped by their surroundings," said Ian Y. Wong, assistant professor of engineering and one of the study's authors. "We've shown that you can make textured environments for cell culture fairly easily using graphene."
Traditionally, cell culture in the lab has ...
2015-04-23
An enzyme secreted by the body's fat tissue controls energy levels in the brain, according to new research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The findings, in mice, underscore a role for the body's fat tissue in controlling the brain's response to food scarcity, and suggest there is an optimal amount of body fat for maximizing health and longevity.
The study appears April 23 in the journal Cell Metabolism.
"We showed that fat tissue controls brain function in a really interesting way," said senior author Shin-ichiro Imai, MD, PhD, professor of ...
2015-04-23
Dolphins that raise their voices to be heard in noisy environments expend extra energy in doing so, according to new research that for the first time measures the biological costs to marine mammals of trying to communicate over the sounds of ship traffic or other sources.
While dolphins expend only slightly more energy on louder whistles or other vocalizations, the metabolic cost may add up over time when the animals must compensate for chronic background noise, according to the research by scientists at NOAA Fisheries' Northwest Fisheries Science Center and the University ...
2015-04-23
TORONTO, ON. (23 April, 2015) - A new study led by University of Toronto researcher Dr. David Lam has discovered the trigger behind the most severe forms of cancer pain. Released in top journal Pain this month, the study points to TMPRSS2 as the culprit: a gene that is also responsible for some of the most aggressive forms of androgen-fuelled cancers.
Head of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Faculty of Dentistry, Lam's research initially focused on cancers of the head and neck, which affect more than 550,000 people worldwide each year. Studies have shown that these ...
2015-04-23
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A 47-year-old African-American woman has heavy menstrual bleeding and iron-deficiency anemia. She reports the frequent need to urinate during the night and throughout the day. A colonoscopy is negative and an ultrasonography shows a modestly enlarged uterus with three uterine fibroids, noncancerous growths of the uterus. She is not planning to become pregnant. What are her options?
Elizabeth (Ebbie) Stewart, M.D., chair of Reproductive Endocrinology at Mayo Clinic, says the woman has several options, but determining her best option is guided by her ...
2015-04-23
ANN ARBOR--Use of clean fuels and updated pollution control measures in the school buses 25 million children ride every day could result in 14 million fewer absences from school a year, based on a study by the University of Michigan and the University of Washington.
In research believed to be the first to measure the individual impact on children of the federal mandate to reduce diesel emissions, researchers found improved health and less absenteeism, especially among asthmatic children.
A change to ultra low sulfur diesel fuel reduced a marker for inflammation in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Revolutionary discovery leads to invention of new 'building blocks'
University of Akron polymer researchers create a new class of hybrid materials