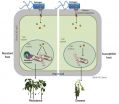
(Press-News.org) (SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Researchers at UC Davis have conducted a comprehensive study to determine whether pediatric telemedicine consultations with rural emergency departments save money compared to telephone consults. The answer is a resounding yes. While telemedicine systems are expensive to install and maintain, they more than pay their way, saving an average $4,662 per use. The study was published in the journal Medical Decision Making.
"Our previous work showed that telemedicine was good for kids, families and providers, but we didn't really address the cost issue," said James Marcin, UC Davis interim head of pediatric critical care medicine. "Now we know, not only does it improve quality, safety and satisfaction, but it also saves money."
Public health researchers worked closely with health economists to determine the actual costs of a telemedicine consult, as well as the potential savings. On one side of the ledger, hospitals must invest in equipment, software and IT support. In addition, urban hospitals must pay to have subspecialists on call to assist their rural colleagues. These and other costs averaged out to $3,641 per consultation.
However, the value of these consultations far exceeded these expenses. The study found that, compared to telephone, telemedicine consults produced extensive savings. In many cases, savings accrued from reduced transfers between hospitals. In particular, moving patients by air ambulance can dramatically increase the cost of care. Telemedicine consults reduced the number of patients being transferred by 31 percent.
To make these findings, the team reviewed the Pediatric Critical Care Telemedicine Program at UC Davis, tracking its interactions with eight rural emergency departments between 2003 and 2009. They collected detailed information on the costs of implementing and maintaining the telemedicine program and weighed those against the transfer logs at the eight hospitals, as well as the costs of ED visits. The team focused on five conditions: asthma, bronchiolitis, dehydration, fever and pneumonia. These diagnoses stand out because, with appropriate guidance, they can be treated at the rural hospitals.
Marcin and his team will continue to study the relationship between telemedicine and patient costs and are excited to share this information with payers, hospital administrators, physicians groups and other interested parties. Given its ability to both improve quality and reduce costs, Marcin believes telemedicine should play a larger role in health care.
"In California, physicians get paid for telemedicine consultations, but in many states they don't," says Marcin. "Given its ability to reduce medication errors and increase patient, family and physician satisfaction, as well as lowering costs, I think it makes sense to actually pay physicians a little more for this service to incentivize the model."
INFORMATION:
Other authored included: Nikki H. Yang, Madan Dharmar, Byung-Kwang Yoo, J. Paul Leigh, Nathan Kuppermann, Patrick S. Romano and Thomas S. Nesbitt.
This study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ 1 K08 HS 13179-01); Emergency Medical Services for Children (HRSA H34MC04367-01-00);Office for the Advancement of Telehealth (HRSA 5R01HS019712);the California Healthcare Foundation (CHCF #02-2210); and the William Randolph Hearst Foundations.
UC Davis Children's Hospital is the Sacramento region's only nationally ranked, comprehensive hospital for children, serving infants, children, adolescents and young adults with primary, subspecialty and critical care. It includes the Central Valley's only pediatric emergency department and Level I pediatric trauma center, which offers the highest level of care for critically ill children. The 129-bed children's hospital includes the state-of-the-art 49-bed neonatal and 24-bed pediatric intensive care and pediatric cardiac intensive care units. With more than 120 physicians in 33 subspecialties, UC Davis Children's Hospital has more than 74,000 clinic and hospital visits and 13,000 emergency department visits each year. For more information, visit http://children.ucdavis.edu.
Lawrence Livermore researchers have determined that a tunnel bomb explosion by Syrian rebels was less than 60 tons as claimed by sources.
Using seismic stations in Turkey, Livermore scientists Michael Pasyanos and Sean Ford created a method to determine source characteristics of near earth surface explosions. They found the above-ground tunnel bomb blast under the Wadi al-Deif Army Base near Aleppo last spring was likely not as large as originally estimated and was closer to 40 tons.
Seismology has long been used to determine the source characteristics of underground ...
This news release is available in French. Montreal, May 21, 2015 - A new study published by the team of Naguib Mechawar, Ph.D., a researcher at the Douglas Institute (CIUSSS de l'Ouest-de-l'île-de-Montréal) and Associate Professor in the Department of Psychiatry at McGill University, suggests that the integration of new neurons in the adult brain is a phenomenon more generally compromised in the brains of depressed patients.
This new work confirms that neurogenesis in the human olfactory bulb is a marginal phenomenon in adults. These findings shed light ...
Alexandria, VA - In the years following the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster, forest fires billowed plumes of contaminated smoke, carrying radioactive particles throughout Europe on the wind. Now, researchers fear that a shift to a hotter, drier climate in Eastern Europe could increase the frequency of these fires.
Researchers from the University of South Carolina in Columbia used satellite imagery of fires in the 2000s and field measurements of radioisotope levels to model changes in the distribution of radiation over the region. The researchers found that fires likely ...
Researchers have developed a model to assess how dams affect the viability of sea-run fish species that need to pass dams as they use both fresh and marine waters during their lifetimes. NOAA's Northeast Fisheries Science Center (NEFSC) and Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office (GARFO) have partnered on this project to test how varying passage efficiency at dams related to survival rates for these species.
Using a model of endangered Atlantic salmon in Maine's Penobscot River as a case study, NOAA researchers found that abundance, distribution and number of fish ...
Hamilton, ON (May 21, 2015) - Scientists at McMaster University have discovered how to make adult sensory neurons from human patients simply by having them roll up their sleeve and providing a blood sample.
Specifically, stem cell scientists at McMaster can now directly convert adult human blood cells to both central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) neurons as well as neurons in the peripheral nervous system (rest of the body) that are responsible for pain, temperature and itch perception. This means that how a person's nervous system cells react and respond to ...
One of the reasons pluripotent stem cells are so popular in medical research is that they can be differentiated into any cell type. However, typical differentiation protocols lead to a heterogeneous population from which the desired type must be purified. Normally, antibodies that react to surface receptors unique to the desired cell are used for this purpose. However, in many cases the purification levels remain poor and the cells can be damaged. New RNA technology produced at CiRA may avoid these problems.
Professor Hirohide Saito at the Dept. of Reprogramming Science ...
Receptors carrying built-in decoys are the latest discovery in the evolutionary battle between plants and pathogens. The decoy domains within the receptor detect pathogens and raise the cell's alarm when there is an infection.
Plants display component parts of their immune system on receptors to trick pathogens into binding with them, which then triggers defence mechanisms. The discovery comes from Professor Jonathan Jones' group at The Sainsbury Laboratory, published in the high-impact journal Cell with a companion paper on a similar discovery from the Deslandes group ...
Almost 90 per cent of men with advanced prostate cancer carry genetic mutations in their tumours that could be targeted by either existing or new cancer drugs, a landmark new study reveals.
Scientists in the UK and the US have created a comprehensive map of the genetic mutations within lethal prostate cancers that have spread around the body, in a paper being hailed as the disease's 'Rosetta Stone'.
Researchers say that doctors could now start testing for these 'clinically actionable' mutations and give patients with advanced prostate cancer existing drugs or drug combinations ...
May 21, 2015 - A University of Wyoming faculty member led a research team that discovered a certain type of soil bacteria can use their social behavior of outer membrane exchange (OME) to repair damaged cells and improve the fitness of the bacteria population as a whole.
Daniel Wall, a UW associate professor in the Department of Molecular Biology, and others were able to show that damaged sustained by the outer membrane (OM) of a myxobacteria cell population was repaired by a healthy population using the process of OME. The research revealed that these social organisms ...
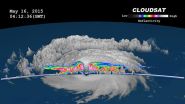
When Dolphin was a typhoon on May 16, NASA's CloudSat satellite completed a stunning eye overpass of Typhoon Dolphin in the West Pacific at 0412 UTC (12:12 a.m. EDT). By May 22, Dolphin's remnants were moving through the Northern Pacific.
NASA's CloudSat satellite sends pulses of microwave energy through the clouds, and some of the energy in the pulses is reflected back to the spacecraft. The time delay between when the pulse is sent and when the reflected energy is received back at the spacecraft is mapped into a distance of the cloud from the surface of the Earth, and ...