Moderate exercise helps prevent gestational diabetes and reduce weight gain during pregnancy
2015-06-04
(Press-News.org) Women who exercise during pregnancy are less likely to have gestational diabetes, and the exercise also helps to reduce maternal weight gain, finds a study published on 3 June 2015 in BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
Gestational diabetes is one of the most frequent complications of pregnancy. It is associated with an increased risk of serious disorders such as pre-eclampsia, hypertension, preterm birth, and with induced or caesarean birth. It can have long term effects on the mother including long term impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. The children of mothers with gestational diabetes are more likely to become overweight or obese and have a higher risk of developing diabetes themselves.
Gaining more weight than is recommended during pregnancy carries similar risks, and these women are also less likely to lose the excess weight after the baby is born.
In this systematic review, the research team from Spain looked at the results of enrolling healthy pregnant women, who did little or no exercise, into exercise programmes. Analysis of 13 trials, involving more than 2,800 women, found that exercise reduced the risk of gestational diabetes by more than 30% - for women who exercised throughout pregnancy this was even greater (36%). This effect was strongest for women who combined toning, strength, flexibility and aerobic exercise.
Exercise was also helpful in reducing excessive weight gain - those who exercised were on average a kilogram lighter. This held true for the weight gain even if the exercise programme was started in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Gema Sanabria- Martinez, from Virgen de la Luz Hospital and lead author of the study, said, "Exercise is not something to be feared during pregnancy - the moderate levels of exercise used in these studies had significantly positive effects on health and were found to be safe for both mother and baby."
Mike Marsh, BJOG Deputy Editor-in-chief added, "This careful analysis of previous studies shows a beneficial effect of exercise on healthy pregnant women who ordinarily did little or no exercise. It may influence recommendations for exercise in pregnancy in such women. Further studies are needed to establish whether this effect is seen in all pregnant women."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-04
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (June 4, 2015) - Leveraging a novel system designed to examine the double-strand DNA breaks that occur as a consequence of gene amplification during DNA replication, Whitehead Institute scientists are bringing new clarity to the causes of such genomic damage. Moreover, because errors arising during DNA replication and gene amplification result in chromosomal abnormalities often found in malignant cells, these new findings may bolster our understandings of certain drivers of cancer progression.
At the core of system, developed in the lab of Whitehead ...
2015-06-04
About 10 years ago, Peter Hews stumbled across some bones sticking out of a cliff along the Oldman River in southeastern Alberta, Canada. Now, scientists describe in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on June 4 that those bones belonged to a nearly intact skull of a very unusual horned dinosaur--a close relative of the familiar Triceratops that had been unknown to science until now.
"The specimen comes from a geographic region of Alberta where we have not found horned dinosaurs before, so from the onset we knew it was important," says Dr. Caleb Brown of the Royal ...
2015-06-04
Infectious diseases kill more people worldwide than any other single cause, but treatment often fails because a small fraction of bacterial cells can transiently survive antibiotics and recolonize the body. A study published June 4 in Molecular Cell reveals that these so-called persisters form in response to adverse conditions through the action of a molecule called Obg, which plays an important role in all major cellular processes in multiple bacterial species. By revealing a shared genetic mechanism underlying bacterial persistence, the study paves the way for novel diagnostic ...
2015-06-04
A team of researchers led by the University of Cambridge has described for the first time in humans how the epigenome - the suite of molecules attached to our DNA that switch our genes on and off - is comprehensively erased in early primordial germ cells prior to the generation of egg and sperm. However, the study, published today in the journal Cell, shows some regions of our DNA - including those associated with conditions such as obesity and schizophrenia - resist complete reprogramming.
Although our genetic information - the 'code of life' - is written in our DNA, ...
2015-06-04
Our social connections and social compass define us to a large degree as human. Indeed, our tendency to act to benefit others without benefit to ourselves is regarded by some as the epitome of human nature and culture. But is it truly a quality unique to humans, or is this apparent virtue common to other species such as rats?
"We would not hesitate about helping an older person trying to cross the road", says Dr. Cristina Márquez, who conducted this study with Scott Rennie and Diana Costa from the Behavioural Neuroscience Lab, led by Dr. Marta Moita. "This type of ...
2015-06-04
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The process that allows our brains to learn and generate new memories also leads to degeneration as we age, according to a new study by researchers at MIT.
The finding, reported in a paper published today in the journal Cell, could ultimately help researchers develop new approaches to preventing cognitive decline in disorders such as Alzheimer's disease.
Each time we learn something new, our brain cells break their DNA, creating damage that the neurons must immediately repair, according to Li-Huei Tsai, the Picower Professor of Neuroscience and director ...
2015-06-04
SEATTLE - Eating less late at night may help curb the concentration and alertness deficits that accompany sleep deprivation, according to results of a new study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania that will be presented at SLEEP 2015, the 29th annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies LLC.
"Adults consume approximately 500 additional calories during late-night hours when they are sleep restricted," said the study's senior author David F. Dinges, PhD, director of the Unit for Experimental Psychiatry ...
2015-06-04
Medicare costs for older patients with oral cavity and pharyngeal cancers increased based on demographics, co-existing illnesses and treatment selection, according to a report published online by JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery.
Many cases of oral cavity cancer and most cases of pharyngeal cancer are diagnosed at advanced stages when management of the disease is complex and treatment is aggressive and involves multiple specialists. The publicly funded Medicare program provides an opportunity for researchers to estimate the cost of care for older patients with ...
2015-06-04
Placenta doesn't prevent postpartum depression, ease pain, boost energy or aid lactation
Celebrities spike trend, but no studies show human benefits
Unknown risks to women and babies
CHICAGO -- Celebrities such as Kourtney Kardashian blogged and raved about the benefits of their personal placenta 'vitamins' and spiked women's interest in the practice of consuming their placentas after childbirth.
But a new Northwestern Medicine review of 10 current published research studies on placentophagy did not turn up any human or animal data to support the common ...
2015-06-04
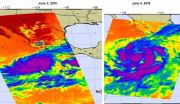
One of the instruments that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite looks at tropical cyclones using infrared light. In a comparison of infrared data from June 3 and 4, images show that Hurricane Blanca had weakened and became less organized.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite measured cloud top temperatures in Blanca on June 3 at 20:17 UTC (4:23 p.m. EDT) when maximum sustained winds were near 140 mph (220 kph) with higher gusts. At the time, Blanca was a category 4 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Moderate exercise helps prevent gestational diabetes and reduce weight gain during pregnancy