(Press-News.org) An international team of astronomers studying 200,000 galaxies has measured the energy generated within a large portion of space more precisely than ever before, discovering that it's only half what it was 2 billion years ago and fading - the Universe is slowly dying.
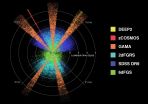
Researchers from the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) in Western Australia used seven of the world's most powerful telescopes to observe galaxies at 21 different wavelengths from the far ultraviolet to the far infrared.
Initial observations were conducted using the Anglo-Australian Telescope in New South Wales and supporting observations were made by two orbiting space telescopes operated by NASA and another belonging to the European Space Agency.
The research is part of the Galaxy and Mass Assembly (GAMA) project, the largest multi-wavelength survey ever put together.
"We used as many space and ground-based telescopes we could get our hands on, to measure the energy output of over 200,000 galaxies across as broad a wavelength range as possible," says ICRAR Professor Simon Driver, who presented the findings at the International Astronomical Union's General Assembly in Honolulu.
The survey data, released to astronomers around the world, includes 200,000 galaxies each measured at 21 wavelengths from the ultraviolet to the far infrared and will help scientists better understand how different types of galaxies form.
Professor Driver, who heads up the GAMA team, says the study set out to map and model all of the energy generated within a set volume of space.
All energy in the Universe was created in the Big Bang with some portion locked up as mass. Stars shine by converting this mass into energy as described by Einstein's famous equation E=MC2.
"While most of the energy sloshing around was created in the aftermath of the Big Bang, additional energy is constantly being released by stars as they fuse elements like hydrogen and helium together," Professor Driver says.
"This newly released energy is either absorbed by dust as it travels through the host galaxy, or escapes into intergalactic space and travels until it hits something such as another star, planet, or very occasionally a telescope mirror."
The fact that the Universe is slowly fading has been known since the late 1990s but this work shows that it's happening across all wavelengths from the ultraviolet to the infrared, representing the most comprehensive assessment of the energy output of the nearby Universe.
"The Universe is fated to decline from here on in, like an old age that lasts forever. The Universe has basically plonked itself down on the sofa, pulled up a blanket and is about to nod off for an eternal doze," Professor Driver says.
The team of researchers hope to expand the work to map energy production over the entire history of the Universe. To do this, they will use a swathe of new facilities including the world's largest radio telescope, the Square Kilometre Array, due to be built in Australia and South Africa in the next decade.
INFORMATION:
More Information:
Professor Driver will present this work at the General Assembly of the International Astronomical Union in Honolulu on Monday, August 10.
The Galaxy and Mass Assembly Survey, or GAMA, is a collaboration involving nearly 100 scientists from more than 30 universities located in Australia, Europe and the United States.
ICRAR is a joint venture between Curtin University and The University of Western Australia with support and funding from the State Government of Western Australia.
Original publication details:
'Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA): Panchromatic Data Release (far-UV--far-IR) and the low-z energy budget' submitted to the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Available at http://www.simondriver.org/mwavev02.pdf
Supporting Multimedia:
Imagery and a galaxy 'fly-through' are available at high resolution from: http://www.icrar.org/universeisdying
Contact Details:
Professor Simon Driver (ICRAR - UWA)
Ph: +61 400 714 513 E: simon.driver@icrar.org
Professor Andrew Hopkins (Australian Astronomical Observatory)
Ph: +61 432 855 049 E: andrew.hopkins@aao.gov.au
Dr Luke Davies (ICRAR - UWA)
Ph: +61 466 277 672 E: luke.davies@icrar.org
Pete Wheeler (Media Contact, ICRAR)
Ph: +61 +61 423 982 018 E: pete.wheeler@icrar.org
An international team of astronomers studying more than 200 000 galaxies has measured the energy generated within a large portion of space more precisely than ever before. This represents the most comprehensive assessment of the energy output of the nearby Universe. They confirm that the energy produced in a section of the Universe today is only about half what it was two billion years ago and find that this fading is occurring across all wavelengths from the ultraviolet to the far infrared. The Universe is slowly dying.
The study involves many of the world's most powerful ...
Through identification of increased toxin production by epidemic forms of group A streptococcus (the "flesh-eating" bacterium), for the first time scientists are able to pinpoint the molecular events that contribute to large intercontinental epidemics of disease. The study was based on sequencing almost 5,000 group A streptococcus genomes collected over decades.
Researchers from Houston Methodist Research Institute, Houston Methodist Hospital, institutions in Finland and Iceland, and the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases report their discoveries ...
Fast Facts:
Study reveals simple things hospitals can do to improve a patient's experience, including ongoing rounds by nurses and hospital leadership.
Study findings outline the following core practices that high-ranking hospitals employ: a devotion to consistency, personal and focused interactions with patients, and a culture that demands involvement of all levels of caregivers and services.
Based on responses to questionnaires and letters sent to CEOs and medical personnel from a nationwide sample of 53 hospitals, Johns Hopkins investigators have identified ...
Athens, Ga. - The time since the introduction of a non-native marine species best explains its global range, according to new research by an international team of scientists led by University of Georgia ecologist James E. Byers. The study, published in the open access journal Nature Scientific Reports, also contains a warning: The vast majority of marine invaders have not yet finished spreading.
Invasion by non-native species is a worldwide problem that causes billions of dollars of damage annually--more than $120 billion in the U.S. alone, according to a 2005 study ...
Berkeley -- The effort to improve food safety by clearing wild vegetation surrounding crops is not helping, and in some cases may even backfire, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley.
The findings, to be reported Monday, Aug. 10, in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, call into question the effectiveness of removing non-crop vegetation as a way to reduce field contamination of fresh produce by disease-causing pathogens. This practice led to extensive loss of habitat in a region that is globally ...
Human memory is the result of different mental processes, such as learning, remembering and forgetting. However, these distinct processes cannot be observed directly. Researchers at the University of Basel now succeeded at describing them using computational models. The scientists were thus for the first time able to identify gene sets responsible for steering specific memory processes. Their results have been published in the current issue of the journal PNAS.
Thanks to our memory we are able to learn foreign languages, solve exams and remember beautiful moments from ...
Scientists have found that a newly identified and highly infectious tadpole disease is found in a diverse range of frog populations across the world. The discovery sheds new light on some of the threats facing fragile frog populations, which are in decline worldwide.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal, led by the University of Exeter and the Natural History Museum, describes the molecular methods used to test frog tadpoles for a newly identified infectious agent.
Tadpoles from six countries across three continents were ...
A new study led by bioengineers at the University of California, San Diego defines the core set of genes and functions that a bacterial cell needs to sustain life. The research, which answers the fundamental question of what minimum set of functions bacterial cells require to survive, could lead to new cell engineering approaches for E. coli and other microorganisms, the researchers said.
The findings are published online in the early edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of August 10, 2015.
This core set of genes is "the smallest common ...
Astronomers at the 29th International Astronomical Union General Assembly will announce on August 14 the discovery of a new transiting "circumbinary" planet, bringing the number of such known planets into double digits. A circumbinary planet orbits two stars, and like the fictional planet "Tatooine" from Star Wars, this planet has two suns in its sky. The discovery marks an important milestone and comes only four years after the first Kepler circumbinary planet was detected. Once thought to be rare or even impossible, these ten discoveries confirm that such planets are ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Remarriages often combine two families into one stepfamily unit. When that stepfamily unit dissolves after a divorce, little is known about the relationships between former stepparents and stepchildren. Now, researchers in the University of Missouri College of Human Environmental Sciences found stepchildren's views of former stepparents depended on emotional reactions to the divorce, patterns of support or resource exchanges, and parental encouragement or discouragement to continue step-relationships. Whether stepchildren maintained relationships with their ...