(Press-News.org) Berkeley -- The effort to improve food safety by clearing wild vegetation surrounding crops is not helping, and in some cases may even backfire, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley.
The findings, to be reported Monday, Aug. 10, in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, call into question the effectiveness of removing non-crop vegetation as a way to reduce field contamination of fresh produce by disease-causing pathogens. This practice led to extensive loss of habitat in a region that is globally important for food production and natural resources.
The practice was implemented largely in response to a 2006 outbreak of pathogenic E. coli in packaged spinach that killed three people and sickened hundreds of others in the United States. That outbreak was traced to a farm in California's Central Coast, a region that supplies more than 70 percent of the country's salad vegetables. The disease-causing E. coli strain was found throughout the farm environment -- including in the feces of nearby cattle and wild pigs -- but the cause of the outbreak has never been officially determined.
"Wildlife took much of the blame for that outbreak, even though rates of E. coli in wildlife are generally very low," said study lead author Daniel Karp, a NatureNet postdoctoral research fellow in UC Berkeley's Department of Environmental Science, Policy and Management and The Nature Conservancy. "Now, growers are pressured by buyers to implement practices meant to discourage wildlife from approaching fields of produce. This includes clearing bushes, plants and trees that might serve as habitat or food sources for wild animals. Our study found that this practice has not led to the reductions in E. coli and Salmonella that people were hoping for."
Instead, the study authors noted that the presence of diverse habitats bordering food crops can actually provide a number of agricultural benefits.
"There is strong evidence that natural habitats surrounding crop fields encourage wild bee populations and help the production of pollinated food crops," said study senior author Claire Kremen, a UC Berkeley professor of environmental science, policy and management. "There have also been studies that suggest that a landscape with diverse plant life can filter out agrichemical runoff and even bacteria. Changing this dynamic shouldn't be taken lightly."
'No reason to continue' habitat removal
The researchers analyzed about 250,000 tests of produce, irrigation waters and rodents conducted by industry and academics from 2007 through 2013. The tests were conducted on samples from 295 farms in the United States, Mexico and Chile, and targeted the presence of pathogenic E. coli, Salmonella and generic strains of E. coli. The researchers combined the test data with a fine-scale land-use map to identify characteristics of the landscape surrounding the agricultural fields.
The researchers found that the removal of riparian or other vegetation did not result in lower detection of pathogens in produce, water or rodents. Overall, the prevalence of pathogenic E. coli in leafy green vegetables had increased since the outbreak, even as growers removed non-crop flora. In fact, the growers who removed the most vegetation experienced the greatest increase in pathogenic E. coli and Salmonella in their vegetables over time.
"Clearing surrounding vegetation is a costly, labor-intensive practice that threatens wildlife habitat," said Karp. "Since it does not improve food safety, there is no reason to continue this practice."
The study did find, however, that the likelihood of detecting pathogenic E. coli was greater when fields were within 1.5 kilometers of grazeable land than when they were farther away.
"It is unclear whether it was the cattle or wildlife grazing on those lands that were responsible for the elevated pathogen levels, but there are a number of ways that farming and ranching can co-exist in a diversified system," said Karp.
Some suggestions include:
Leaving strips of vegetation between the grazed areas and fresh produce areas
Fencing off upstream waterways from cattle to prevent waste from going downstream
Planting crops that are usually cooked before being eaten - such as corn, artichokes and wheat - between fresh produce fields and grazeable lands
Reforming farming practices
After the 2006 E. coli outbreak in spinach, California's agricultural industry implemented a voluntary certification program called the Leafy Green Products Handler Marketing Agreement. At the federal level, in 2011 President Obama signed the Food Safety Modernization Act, considered one of the most sweeping reforms in farming practices in decades. Both efforts shift the focus to preventing rather than responding to outbreaks.
Notably, neither the federal law nor the state program calls for the removal of wildlife habitat surrounding crops, but private buyers, keen on retaining consumer confidence in their products, may still require growers to take steps that go beyond government regulations.
"The real worry for me is that federal law will be interpreted as the floor rather than the ceiling of what farmers should do," said Karp. "There is this misguided idea that agricultural fields should be a sanitized, sterilized environment, like a hospital, but nature doesn't work that way."
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors of the study are Sasha Gennet, senior scientist at The Nature Conservancy; Christopher Kilonzo, Melissa Partyka and Edward Atwill at UC Davis; and Nicolas Chaumont at Stanford University.
The UC Berkeley Center for Diversified Farming Systems, Berkeley Food Institute, The Nature Conservancy NatureNet Fellowship, and The Nature Conservancy of California helped support this research.
Human memory is the result of different mental processes, such as learning, remembering and forgetting. However, these distinct processes cannot be observed directly. Researchers at the University of Basel now succeeded at describing them using computational models. The scientists were thus for the first time able to identify gene sets responsible for steering specific memory processes. Their results have been published in the current issue of the journal PNAS.
Thanks to our memory we are able to learn foreign languages, solve exams and remember beautiful moments from ...
Scientists have found that a newly identified and highly infectious tadpole disease is found in a diverse range of frog populations across the world. The discovery sheds new light on some of the threats facing fragile frog populations, which are in decline worldwide.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal, led by the University of Exeter and the Natural History Museum, describes the molecular methods used to test frog tadpoles for a newly identified infectious agent.
Tadpoles from six countries across three continents were ...
A new study led by bioengineers at the University of California, San Diego defines the core set of genes and functions that a bacterial cell needs to sustain life. The research, which answers the fundamental question of what minimum set of functions bacterial cells require to survive, could lead to new cell engineering approaches for E. coli and other microorganisms, the researchers said.
The findings are published online in the early edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of August 10, 2015.
This core set of genes is "the smallest common ...
Astronomers at the 29th International Astronomical Union General Assembly will announce on August 14 the discovery of a new transiting "circumbinary" planet, bringing the number of such known planets into double digits. A circumbinary planet orbits two stars, and like the fictional planet "Tatooine" from Star Wars, this planet has two suns in its sky. The discovery marks an important milestone and comes only four years after the first Kepler circumbinary planet was detected. Once thought to be rare or even impossible, these ten discoveries confirm that such planets are ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Remarriages often combine two families into one stepfamily unit. When that stepfamily unit dissolves after a divorce, little is known about the relationships between former stepparents and stepchildren. Now, researchers in the University of Missouri College of Human Environmental Sciences found stepchildren's views of former stepparents depended on emotional reactions to the divorce, patterns of support or resource exchanges, and parental encouragement or discouragement to continue step-relationships. Whether stepchildren maintained relationships with their ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Researchers who have revealed a highly efficient way that bacteria use toxins to interrupt the immune response say that until now, the trickery of these toxins has been underappreciated in science.
Bacteria harm the body by releasing toxins - proteins that are exceptionally effective poisons. Always targeting essential molecules, toxins typically go after molecules that are either scarce or whose role is to send important signals. In both cases, only a small number of toxins is required to cause damage.
In contrast, some toxins appear to deviate from ...
Alexandria, Va., USA - Today, the International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR) published two reports including a critical review titled "Diet and Dental Caries - the Pivotal Role of Free Sugars Reemphasized." In this study, authors Aubrey Sheiham, University College London, England; and W. Philip James, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, England, demonstrate the sensitivity of cariogenesis (the development of caries) to even very low sugars intakes. In this critical review, the authors reviewed the literature on the role of sucrose ...
Scientists at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center have identified a molecular partnership in pancreatic cancer cells that might help to explain how the disease spreads -- metastasizes -- in some cases. Their findings reveal urgently needed new targets to treat pancreatic cancer, which strikes nearly 50,000 people in the U.S. each year and has only a 5 percent survival rate five years after diagnosis.
One of the molecular partners is annexin A2, a protein that scientists say was already linked to poor survival rates in these cancers. In a report published in the Aug. ...
(Broadcast-quality video and infographics available with this story)
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- With more kids online and using cell phones at increasingly younger ages, two issues have quickly climbed higher on the public's list of major health concerns for children across the U.S: sexting and Internet safety.
Compared with 2014, Internet safety rose from the eighth to the fourth biggest problem, ahead of school violence and smoking, in the 2015 annual survey of top children's health concerns conducted by the C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's ...
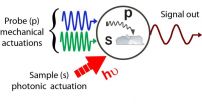
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Aug. 10, 2015 - A microscope being developed at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory will allow scientists studying biological and synthetic materials to simultaneously observe chemical and physical properties on and beneath the surface.
The Hybrid Photonic Mode-Synthesizing Atomic Force Microscope is unique, according to principal investigator Ali Passian of ORNL's Quantum Information System group. As a hybrid, the instrument, described in a paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, combines the disciplines of nanospectroscopy and ...