INFORMATION:
The study was funded in part by National Institutes of Health grant HL078103.
Co-authors of the study are J. Daniel Bourland, Ph.D., Ashlee Clark, M.S., James B. Daunais, Ph.D., Warwick D. Johnston, B.A., Sara R. Jones, Ph.D., Robert A. Kraft, Ph.D., Adreanna Massey, B.A., David Neely, B.S., Beth Uberseder, B.S., and Jeff D. Williamson, M.D., of Wake Forest Baptist and Stephanie L. Willard, Ph.D., of the University of Pennsylvania.
Common antidepressant may change brain
Structural differences found in depressed, non-depressed people
2015-09-04
(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - Sept. 4, 2015 - A commonly prescribed antidepressant may alter brain structures in depressed and non-depressed individuals in very different ways, according to new research at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
The study - conducted in nonhuman primates with brain structures and functions similar to those of humans - found that the antidepressant sertraline, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) marketed as Zoloft, significantly increased the volume of one brain region in depressed subjects but decreased the volume of two brain areas in non-depressed subjects.
"These observations are important for human health because Zoloft is widely prescribed for a number of disorders other than depression," said Carol A. Shively, Ph.D., professor of pathology-comparative medicine at Wake Forest Baptist and lead author of the study, published in the current online issue of the journal Neuropharmacology.
In the study, 41 middle-aged female monkeys were fed a diet formulated to replicate that consumed by many Americans for 18 months, during which time depressive behavior in the animals was recorded. Female monkeys were chosen for this study because depression is nearly twice as common in women as men and the use of antidepressants is most common in women ages 40 to 59.
After the 18-month pre-study phase, the monkeys were divided into two groups balanced for body weight, body mass index and depressive behavior. For the next 18 months, 21 monkeys received sertraline in daily doses comparable to those taken by humans while a group of 20 received a placebo. This treatment regimen is analogous to a human taking an antidepressant for approximately five years.
MRI images taken at the end of the treatment phase revealed that in depressed subjects the drug significantly increased the volume of one region of the brain, the anterior cingulate cortex, while decreasing the volume of this same region and the hippocampus in non-depressed subjects. Both of these areas are highly interconnected with other areas of the brain; are critical in a wide array of functions including memory, learning, spatial navigation, will, motivation and emotion; and are implicated in major depressive disorder.
In humans, Shively said, volume differences in neural structures have been noted in depressed and non-depressed individuals, with the most commonly reported differences being smaller volumes of the cingulate cortex and hippocampus in depressed people. One potential mechanism through which drugs such as Zoloft can be effective as antidepressants is by promoting neuron growth and connectivity in these brain regions.
But SSRIs, including Zoloft, are prescribed for a variety of disorders besides depression, including bulimia, hot flashes, obsessive-compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, stroke recovery and sexual dysfunction, and there are no studies of the effects of these drugs on brain volumes in individuals not diagnosed with depression.
"The study's findings regarding the different effects of sertraline on brain-region volumes in depressed versus non-depressed subjects are compelling," Shively said. "But given the number of different disorders for which SSRIs are prescribed, the findings need to be investigated further in patient populations to see if these drugs produce similar effects in humans."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate change could leave Pacific Northwest amphibians high and dry
2015-09-04
Far above the wildfires raging in Washington's forests, a less noticeable consequence of this dry year is taking place in mountain ponds. The minimal snowpack and long summer drought that have left the Pacific Northwest lowlands parched also affect the region's amphibians due to loss of mountain pond habitat.
According to a new paper published Sept. 2 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, this summer's severe conditions may be the new normal within just a few decades.
"This year is an analog for the 2070s in terms of the conditions of the ponds in response to climate," ...
Highly effective seasickness treatment on the horizon
2015-09-04
The misery of motion sickness could be ended within five to ten years thanks to a new treatment being developed by scientists.
The cause of motion sickness is still a mystery but a popular theory among scientists says it is to do with confusing messages received by our brains from both our ears and eyes, when we are moving.
It is a very common complaint and has the potential to affect all of us, meaning we get a bit queasy on boats or rollercoasters. However, around three in ten people experience hard-to-bear motion sickness symptoms, such as dizziness, severe nausea, ...
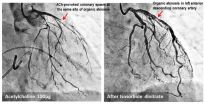
Spasm at site of atherosclerotic coronary artery narrowing increases risk of heart attack
2015-09-04
This news release is available in Japanese.
Researchers at Kumamoto University in Japan have found that patients with coronary spasm have a higher risk of experiencing future heart attack particularly when a spasm occurs at the site of atherosclerotic coronary artery narrowing, i.e., coronary atherosclerotic stenosis.
Angina is caused by the narrowing of the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart, and vasospastic angina patients account for about 40% of all angina patients. The incidence and progression of the disease can be reduced through appropriate drug treatment ...
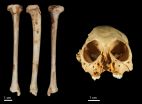
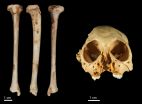
GVSU professor, student help discover one-million-year-old monkey fossil
2015-09-04
ALLENDALE, Mich. -- An international team of scientists, including a Grand Valley State University professor and alumni, recently discovered a species of monkey fossil the team has dated to be more than one million years old.
The discovery was made after the team recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The species was roughly the size of a small cat, dwelled in trees, and lived largely on a diet of fruits and leaves.
"We know that there ...
Polar bears may survive ice melt, with or without seals
2015-09-04
As climate change accelerates ice melt in the Arctic, polar bears may find caribou and snow geese replacing seals as an important food source, shows a recent study published in the journal PLOS ONE. The research, by Linda Gormezano and Robert Rockwell at the American Museum of Natural History, is based on new computations incorporating caloric energy from terrestrial food sources and indicates that the bears' extended stays on land may not be as grim as previously suggested.
"Polar bears are opportunists and have been documented consuming various types and combinations ...
Bring on the night, say National Park visitors in new study
2015-09-04
Natural wonders like tumbling waterfalls, jutting rock faces and banks of wildflowers have long drawn visitors to America's national parks and inspired efforts to protect their beauty.
According to a study published Sept. 4 in Park Science, visitors also value and seek to protect a different kind of threatened natural resource in the parks: dark nighttime skies.
Almost 90 percent of visitors to Maine's Acadia National Park interviewed for the study agreed or strongly agreed with the statements, "Viewing the night sky is important to me" and "The National Park Service ...
Researchers show effectiveness of non-surgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis
2015-09-04
(Boston)--Patients with spinal stenosis (SS) experienced good short term benefit, lasting from weeks to months, after receiving epidural steroid injections (ESI).
These findings, which appear in a letter in the journal Pain Medicine, contradict a previously published New England Journal Medicine (NEJM) study that found epidural steroid injections were not helpful in spinal stenosis cases.
It has been one year since the publication of "A Randomized Trial of Epidural Glucocorticoid Steroid Injections for Spinal Stenosis." This was a large scale clinical trial evaluating ...
The million year old monkey: New evidence confirms the antiquity of fossil primate
2015-09-04
An international team of scientists have dated a species of fossil monkey found across the Caribbean to just over 1 million years old.
The discovery was made after the researchers recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The fossil was embedded in a limestone rock that was dated using the Uranium-series technique.
In a paper published this week in the well renowned international journal, the Journal of Human Evolution, the team use three-dimensional ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kevin stream high clouds over Baja California
2015-09-04
Tropical Storm Kevin's center was several hundred miles south-southwest of Baja California when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and saw some associated high clouds streaming over the peninsula.
The MODIS and the AIRS instruments aboard Aqua captured visible and infrared images of Kevin on September 3 at 20:50 UTC (4:50 p.m. EDT). The visible image from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided look at Kevin's clouds. MODIS showed a somewhat elongated tropical storm with a fragmented band of thunderstorms wrapping into the low-level ...
Scientists unlock the secrets of a heat-loving microbe
2015-09-04
Scientists studying how a heat-loving microbe transfers its DNA from one generation to the next say it could further our understanding of an extraordinary superbug.
Sulfolobus is part of the Archaea kingdom - a single-cell organism similar to bacteria - which was isolated in hot springs on the island of Hokkaido, Japan.
Some Archaea live ordinary lives in mundane environments such as lakes, seas and insect and mammal intestinal tracts, while others live extraordinary lives pushed to extremes in incredibly harsh habitats such as deep sea hydrothermal vents, volcanic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
[Press-News.org] Common antidepressant may change brainStructural differences found in depressed, non-depressed people