(Press-News.org) Women awaiting liver transplants in the United States are known to be about one-third more likely than men to become too ill to undergo surgery or die before receiving a liver. Now a study headed by UC San Francisco and Columbia University highlights the role that frailty plays in this gender gap.
The study followed 1,405 patients with cirrhosis, of whom 41 percent were women, awaiting liver transplantation at nine transplant centers in the United States. The men, whose ages ranged from 49 to 63, were more likely to have chronic hepatitis C and alcoholic liver disease (27 percent versus 22, and 33 percent versus 19 percent). The women, whose ages ranged from 50 to 63, were more likely to have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and autoimmune cholestatic liver disease (23 percent versus 16 percent, and 23 percent versus 9 percent).
The researchers, led by first author Jennifer Lai, MD, MBA, a general and transplant hepatologist at the UCSF Department of Medicine, found that both genders had similar levels of liver disease severity, but fewer women had high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. Despite this, they were significantly frailer according to testing using the Liver Frailty Index (LFI), which showed weaker gender-adjusted grip, worse balance and that they were slower to stand up from a sitting position.
"This is the first time that frailty has been identified and quantified as a risk factor among women with cirrhosis who are waiting for liver transplants," said Lai. "The importance of this finding is that this gender gap can potentially be mitigated through early interventions as basic as providing adequate caloric and protein intake and engaging in regular exercise. Clinicians can advise women on diet and exercise interventions that build strength." These steps may be helpful for women undergoing other organ transplants, since frailty may play a role there too, the authors noted.
While the causes of frailty were not explored, Lai said that it is generally attributed to physical inactivity, chronic liver failure and poor diet.
Over the course of the study, the women had a 36 percent higher risk of waitlist mortality, which was defined as death or delisting for being too sick for transplantation. After adjusting for LFI scores and other variables, the researchers concluded that frailty accounted for 13 percent of the gender gap in waitlist mortality. While the study does not address the other factors that make up for the gender disparity, the authors note differences in kidney function and the higher percentage of male donors, who may be poor matches for women given their smaller stature.
The greatest significance of the study, said Lai, is at the level of the population of liver transplant patients in the United States.
"The waitlist mortality gender gap has persisted for 15 years across the entire U.S. liver transplant system and will continue to persist if it is not recognized," she said. Fortunately, "now that it has been recognized, it can be addressed."
INFORMATION:
Authors: Senior author is Elizabeth C Verna, MD, MSc, of Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation at Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Co-authors are Jennifer Dodge, MPH, and Charles E. McCulloch, PhD, of UCSF; Daniel R. Ganger, MD, of Northwestern Medicine; Michael L. Volk, MD, MSc, of Loma Linda University Health; Michael A. Dunn, MD, and Andres Duarte-Rojo, MD, of the Thomas A. Starzl Transplantation Institute and the University of Pittsburgh; Matthew R. Kappus, MD, of the Duke University School of Medicine; Robert S. Rahimi, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center; Daniela P. Ladner, MD, of Northwestern Medicine and Northwestern University; Brian Boyarsky, MD, and Dorry L. Segev, MD, PhD, of Johns Hopkins School of Medicine; Mara McAdams-DeMarco, PhD, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Funding: Lai, Dodge, Boyarsky, McCulloch and Segev are supported by the National Institutes of Health.
Disclosures: The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. Learn more at ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
In an in-depth study of how COVID-19 affects a patient's brain, National Institutes of Health researchers consistently spotted hallmarks of damage caused by thinning and leaky brain blood vessels in tissue samples from patients who died shortly after contracting the disease. In addition, they saw no signs of SARS-CoV-2 in the tissue samples, suggesting the damage was not caused by a direct viral attack on the brain. The results were published as a correspondence in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"We found that the brains of patients who contract infection from SARS-CoV-2 may be susceptible to microvascular blood vessel damage. Our results ...
The U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) is collaborating with private industry on cutting-edge fusion research aimed at achieving commercial fusion energy. This work, enabled through a public-private DOE grant program, supports efforts to develop high-performance fusion grade plasmas. In one such project PPPL is working in coordination with MIT's Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC) and Commonwealth Fusion Systems, a start-up spun out of MIT that is developing ...
In a first-of-its-kind study within cycad horticulture literature, University of Guam researchers have found that the use of anti-transpirants neither help nor hinder successful propagation of cycad stem cuttings.
The Guam-based study, published Oct. 22 in the journal Tropical Conservation Science, investigated whether retaining leaves during the propagation of cycad stem cuttings conferred any benefit to propagation success. Additionally, two anti-transpirant products were utilized to investigate their efficacy during the propagation process.
Leaves perform a variety of critical functions for plants, including ...
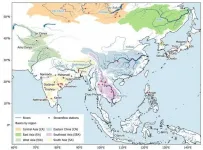
813 years of annual river discharge at 62 stations, 41 rivers in 16 countries, from 1200 to 2012. That is what researchers at the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) produced after two years of research in order to better understand past climate patterns of the Asian Monsoon region.
Home to many populous river basins, including ten of the world's biggest rivers (Figure 1), the Asian Monsoon region provides water, energy, and food for more than three billion people. This makes it crucial for us to understand past climate patterns so that we can better predict long term changes in ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - The introduction of computer simulation to the identification of symptoms in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has potential to provide an additional objective tool to gauge the presence and severity of behavioral problems, Ohio State University researchers suggest in a new publication.
Most mental health disorders are diagnosed and treated based on clinical interviews and questionnaires - and, for about a century, data from cognitive tests has been ...
Kraków, 30 December 2020
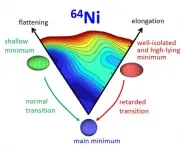
The map of nuclear deformation takes the form of a mountain landscape
Until recently, scientists believed that only very massive nuclei could have excited zero-spin states of increased stability with a significantly deformed shape. Meanwhile, an international team of researchers from Romania, France, Italy, the USA and Poland showed in their latest article that such states also exist in much lighter nickel nuclei. Positive verification of the theoretical model used in these experiments allows describing the properties of nuclei unavailable in Earth laboratories.
More than ...
New Orleans, LA - Research conducted at LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center of Excellence reports that a combination of an LSU Health-patented drug and selected DHA derivatives is more effective in protecting brain cells and increasing recovery after stroke than a single drug. The findings are published in Brain Circulation, available here.
Nicolas Bazan, MD, PhD, Boyd Professor, Professor of Neurology and Director of the Neuroscience Center of Excellence at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, and Ludmila ...
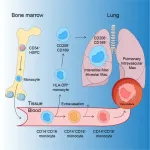
In some cases, immune cells in the lungs can contribute to worsening a virus attack. In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden describe how different kinds of immune cells, called macrophages, develop in the lungs and which of them may be behind severe lung diseases. The study, which was published in Immunity, may contribute to future treatments for COVID-19, among other diseases.
The structure of the lungs exposes them to viruses and bacteria from both the air and the blood. Macrophages are immune cells that, among other things, protect the lungs from such attacks. ...
East Hanover, NJ. December 30, 2020. A team of rehabilitation researchers has studied processing speed deficits in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), comparing their brain activation patterns with those of healthy age-matched controls, and older healthy individuals. They found that the SCI group and older controls had similar activation patterns, but the SCI group differed significantly from their age-matched controls.
The article, "The neural mechanisms underlying processing speed deficits in individuals who have sustained a spinal cord injury: A pilot study" (doi: 10.1007/s10548-020-00798-x) was ...
BOSTON -- A peer-reviewed paper published in The New England Journal of Medicine provides data from the much-anticipated COVE study, which evaluated mRNA-1273, a vaccine candidate against COVID-19 manufactured by Moderna, Inc. Results from the primary analysis of the study, which will continue for two years, provide evidence that the vaccine can prevent symptomatic infection. Among the more than 30,000 participants randomized to receive the vaccine or a placebo, 11 of those in the vaccine group developed symptomatic COVID-19 compared to 185 participants who received the placebo, demonstrating 94.1 percent efficacy in preventing symptomatic COVID-19. Cases ...