A better pen-and-ink system for drawing flexible circuits
2021-01-06
(Press-News.org) Conductive ink is a great tool for printing flexible electronic circuits on surfaces. But these inks can be costly, they do not work on some materials, and devices to apply them can plug up. Now, scientists report in ACS Applied Electronic Materials that they have developed inexpensive conductive inks for clog-free ballpoint pens that can allow users to "write" circuits almost anywhere -- even on human skin.
Flexible electronics are widely used in applications such as biosensors, electronic skin and energy storage. Recent advances to produce such devices include pens that can draw circuits on surfaces, without the need for a printer. These pens can write on a variety of textures, and some can even draw on rough or irregular surfaces unsuitable for printing. However, it's difficult to make ballpoint pens that maintain good circuit-writing performance because the tips can clog. Another challenge is that the metal inks typically used in these systems are expensive to make. And it's unclear how stable these pens and inks are over time. So Yu Liao, Jun Qian and colleagues set out to design a cheap and effective pen-and-ink system.
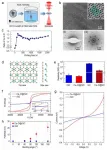
Building on prior work, the scientists developed a water-based ink containing conductive carbon particles composed of graphene nanosheets, multiwalled carbon nanotubes and carbon black. Maleic anhydride modified rosin resin was added as a binder to reduce the ink's solid content and viscosity, and xanthan gum was added to stabilize the dispersion so the carbon wouldn't settle out of the ink. The researchers optimized viscosity and the size of the conductive particles relative to the pen tip to create a system that provided stable and smooth writing performance on both flat and irregular surfaces -- even a loofah. Circuits drawn on paper with the pen withstood multiple cycles of folding without deterioration. The ink remained stable after sitting for 12 hours, released no harmful gases during use and cost much less than others reported in the literature, the researchers note. The pens could be used to draw flexible, wearable electronic devices on soft substrates or human skin.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The abstract that accompanies this paper is available here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS' main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-06
Often considered the world's oddest mammal, Australia's beaver-like, duck-billed platypus exhibits an array of bizarre characteristics: it lays eggs instead of giving birth to live babies, sweats milk, has venomous spurs and is even equipped with 10 sex chromosomes. Now, an international team of researchers led by University of Copenhagen has conducted a unique mapping of the platypus genome and found answers regarding the origins of a few of its stranger features.
It lays eggs, but nurses, it is toothless, has a venomous spur, has webbed feet, fur that glows and has 10 sex chromosomes. Ever since Europeans discovered the platypus in Australia during ...
2021-01-06
Using copper foil, glass containers and a conventional household microwave oven, University of Wyoming researchers have demonstrated that pulverized coal powder can be converted into higher-value nano-graphite.
The discovery is another step forward in the effort to find alternative uses for Wyoming's Powder River Basin coal, at a time when demand for coal to generate electricity is declining due to concerns about climate change.
In a paper published in the journal Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects, the UW researchers report that they created an environment in a microwave oven to successfully convert raw coal powder into nano-graphite, which is ...
2021-01-06
Hoppy beers such as pale ales are becoming increasingly popular. One reason is their pleasant fruity aroma that partially stems from compounds called thiols. Brewers have been looking for an accurate way to track thiols in beer, but current methods typically are not sensitive enough or require use of potentially harmful substances. Now, researchers in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry present an automated, solvent-less process to assess thiols at very low concentrations.
Thiols, along with other compounds such as terpenes and esters, contribute to the enjoyable odors in "hop-forward" beer styles. Although very small amounts ...
2021-01-06
Naturopathic medicine, or herbal medicine, is all the rage, especially among young people. But how much of this is supported by science?
Ginger is known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects, making it a popular herbal supplement to treat inflammatory diseases.
And according to a Michigan Medicine led END ...
2021-01-06
The small GTPases of the ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) family are key initiators of various physiological processes including secretion, endocytosis, phagocytosis and signal transduction. Arf family proteins function to mediate recruitment of cytosolic effectors to specific subcellular compartments. This process facilitates Arf effectors to perform cargo recognition, lipid modification or other cellular functions. Blocking the activities of Arf family proteins inhibits secretion of important molecules from the cell and also inhibits cellular uptake of nutrients. Defects in Arfs or their regulatory proteins are related to various inherited diseases, including X-linked intellectual disability (XLID), Joubert syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome and cilia dysfunction. Thus, studying molecular ...
2021-01-06
Calcium ions are presented in rocks, bones, shells, biominerals, geological deposits, ocean sediments, and many other important materials. Calcium ions also play major roles in the retention of carbon dioxide in natural waters, water hardness, signal transduction and tissue generation. As one of the alkaline earth metals, the calcium atom has two valence electrons according to the octet rule. Up to now, the only known valence state of calcium ions under ambient conditions is +2, and the corresponding crystals with calcium ions are insulating.
By using cryo-electron ...
2021-01-06
A new review by Swansea University reveals there is widespread belief, around the world, in a teaching method that is not only ineffective but may actually be harmful to learners.
For decades educators have been advised to match their teaching to the supposed 'learning styles' of students. There are more than 70 different classification systems, but the most well-known (VARK) sees individuals being categorised as visual, auditory, read-write or kinesthetic learners.
However, a new paper by Professor Phil Newton, of Swansea University Medical School, highlights that this ineffective approach is still believed by teachers and calls for a more evidence-based approach to teacher-training.
He explained that various reviews, carried out since the mid-2000s, have concluded there is no ...
2021-01-06
Researchers who studied antibody and immune cell responses in more than 180 men and women who had recovered from COVID-19 report these patients' immune memory to the virus - across all immune cell types studied - was measurable for up to 8 months after symptoms appeared. The results indicate "that durable immunity against secondary COVID-19 disease is a possibility in most individuals," the authors say. As the number of daily COVID-19 cases worldwide continues to mount, whether an initial infection with SARS-CoV-2 leads to long-lasting protective immunity against COVID-19 remains a question. Studying the nature of the humoral response to the virus, which ...
2021-01-06
Scientists have uncovered why a food-ingredient-based pesticide made from safflower and cottonseed oils is effective against two-spotted spider mites that attack over a thousand species of plants while sparing the mites' natural predators.
An international team of scientists has uncovered how a bio-pesticide works against spider mites while sparing their natural predators.
The findings, published in the journal Engineering in Life Sciences on October 7, 2020, could present farmers and gardeners with an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic pesticides.
Food ingredients have long been used as alternative pesticides against arthropod pests, such as insects, ticks, and mites, because they tend to be less toxic to mammals and pose less impact to the environment. The ...
2021-01-06
Analysis from a workshop convened by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) in 2017 reveals gaps in and opportunities for research to improve understanding of the effects of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in women. A new paper in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation summarizes and updates the findings presented during the "Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury in Women" workshop and provides strategies for advancing research efforts in this area. NINDS is part of the National Institutes of Health.
"We are making advances in understanding ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A better pen-and-ink system for drawing flexible circuits