(Press-News.org) Naturopathic medicine, or herbal medicine, is all the rage, especially among young people. But how much of this is supported by science?
Ginger is known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects, making it a popular herbal supplement to treat inflammatory diseases.
And according to a Michigan Medicine led END
New research finds ginger counters certain autoimmune diseases in mice
The main bioactive compound of ginger root lowers autoantibody production and helps halt disease progression in mice with antiphospholipid syndrome and lupus
2021-01-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
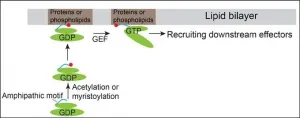
HKUST researchers discover a novel mechanism of recruiting ARF family proteins to specific subcellul
2021-01-06
The small GTPases of the ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) family are key initiators of various physiological processes including secretion, endocytosis, phagocytosis and signal transduction. Arf family proteins function to mediate recruitment of cytosolic effectors to specific subcellular compartments. This process facilitates Arf effectors to perform cargo recognition, lipid modification or other cellular functions. Blocking the activities of Arf family proteins inhibits secretion of important molecules from the cell and also inhibits cellular uptake of nutrients. Defects in Arfs or their regulatory proteins are related to various inherited diseases, including X-linked intellectual disability (XLID), Joubert syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome and cilia dysfunction. Thus, studying molecular ...
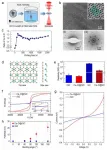
2D CaCl crystals with +1 calcium ions displaying unexpected metallicity and ferromagnetism
2021-01-06
Calcium ions are presented in rocks, bones, shells, biominerals, geological deposits, ocean sediments, and many other important materials. Calcium ions also play major roles in the retention of carbon dioxide in natural waters, water hardness, signal transduction and tissue generation. As one of the alkaline earth metals, the calcium atom has two valence electrons according to the octet rule. Up to now, the only known valence state of calcium ions under ambient conditions is +2, and the corresponding crystals with calcium ions are insulating.
By using cryo-electron ...
New review says the ineffective 'learning styles' theory persists in education
2021-01-06
A new review by Swansea University reveals there is widespread belief, around the world, in a teaching method that is not only ineffective but may actually be harmful to learners.
For decades educators have been advised to match their teaching to the supposed 'learning styles' of students. There are more than 70 different classification systems, but the most well-known (VARK) sees individuals being categorised as visual, auditory, read-write or kinesthetic learners.
However, a new paper by Professor Phil Newton, of Swansea University Medical School, highlights that this ineffective approach is still believed by teachers and calls for a more evidence-based approach to teacher-training.
He explained that various reviews, carried out since the mid-2000s, have concluded there is no ...
Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 immune response several months post-infection hints at protective immunity
2021-01-06
Researchers who studied antibody and immune cell responses in more than 180 men and women who had recovered from COVID-19 report these patients' immune memory to the virus - across all immune cell types studied - was measurable for up to 8 months after symptoms appeared. The results indicate "that durable immunity against secondary COVID-19 disease is a possibility in most individuals," the authors say. As the number of daily COVID-19 cases worldwide continues to mount, whether an initial infection with SARS-CoV-2 leads to long-lasting protective immunity against COVID-19 remains a question. Studying the nature of the humoral response to the virus, which ...
Researchers discover how a bio-pesticide works against spider mites
2021-01-06
Scientists have uncovered why a food-ingredient-based pesticide made from safflower and cottonseed oils is effective against two-spotted spider mites that attack over a thousand species of plants while sparing the mites' natural predators.
An international team of scientists has uncovered how a bio-pesticide works against spider mites while sparing their natural predators.
The findings, published in the journal Engineering in Life Sciences on October 7, 2020, could present farmers and gardeners with an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic pesticides.
Food ingredients have long been used as alternative pesticides against arthropod pests, such as insects, ticks, and mites, because they tend to be less toxic to mammals and pose less impact to the environment. The ...
Identifying strategies to advance research on traumatic brain injury's effect on women
2021-01-06
Analysis from a workshop convened by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) in 2017 reveals gaps in and opportunities for research to improve understanding of the effects of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in women. A new paper in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation summarizes and updates the findings presented during the "Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury in Women" workshop and provides strategies for advancing research efforts in this area. NINDS is part of the National Institutes of Health.
"We are making advances in understanding ...
Sexual dysfunction hits some women harder than others as they age
2021-01-06
CLEVELAND, Ohio (January 5, 2021)--Sexual dysfunction often accompanies the menopause transition. Yet, not all women experience it the same. A new study identified the determinants that affect a woman's risk of sexual dysfunction and sought to determine the effectiveness of hormone therapy in decreasing that risk and modifying sexual behavior. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Although hot flashes easily rank as the most common symptom of menopause, the transition is often accompanied by other issues, including changes that affect a woman's ...
Link between dietary fiber and depression partially explained by gut-brain interactions
2021-01-06
CLEVELAND, Ohio (January 5, 2021)--Fiber is a commonly recommended part of a healthy diet. That's because it's good for your health in so many ways--from weight management to reducing the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer. A new study also finds that it might be linked with a reduced risk of depression, especially in premenopausal women. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Depression is a common and serious mental health condition that not only affects a person's ability to perform daily activities but can also lead to suicide. ...
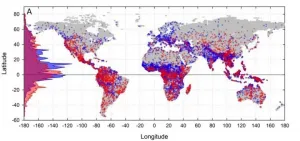
New work provides insight into the relationship between complexity and diversity
2021-01-06
Most forms of life -- species of mammals, birds, plants, reptiles, amphibians, etc. -- are most diverse at Earth's equator and least diverse at the poles. This distribution is called the latitudinal gradient of biodiversity.
A group of Santa Fe Institute collaborators was intrigued by the fact that human cultural diversity shows exactly the same distribution with latitude: human cultures are more diverse near the equator and least at the poles. Their big question was: why? Life is more diverse within richer environments, but it's not clear why human cultural diversity would show this pattern too.
To find answers, the group conducted a biogeographic and macroecological study of the distribution of mammal species ...
COVID-19 generally 'mild' in young children: Evidence review
2021-01-06
A systematic review and meta-analysis of international COVID-19 literature, led by UNSW Sydney, has confirmed that while children under five years old were likely to recover from the infection, half of those infected were infants and almost half of the infected under-fives were asymptomatic.
These findings will help to inform future policy and decision-making about potential COVID-19 vaccination for young children and maternal immunisation programs during pregnancy - but the scientists say future research is needed to explore the potential risk of transmission from infants to their mothers, families and other caregivers, and to find out more about whether asymptomatic under-fives can spread the disease.
The collaborative study between researchers from UNSW Sydney, Telethon ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] New research finds ginger counters certain autoimmune diseases in miceThe main bioactive compound of ginger root lowers autoantibody production and helps halt disease progression in mice with antiphospholipid syndrome and lupus