(Press-News.org) A scalpel-free alternative to brain surgery has the potential to benefit people with Parkinson's disease symptoms that are much more severe on one side of the body, new research suggests.
More testing is needed, but the approach, which uses a technology called focused ultrasound, could offer a new option for patients whose symptoms are poorly controlled by medications and those who cannot or do not wish to undergo traditional brain surgery.
"This small brain region, the subthalamic nucleus, had a very strong and potent effect on parkinsonian symptoms when we targeted it with precise, focused ultrasound energy," said researcher Jeff Elias, MD, a neurosurgeon at UVA Health and a pioneer in the field of focused ultrasound. "The key for the ultimate adoption of this new procedure will be further refinements of the technology to ensure reliability and safety."
About Focused Ultrasound
Focused ultrasound offers a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgery approaches. The technology focuses sound waves inside the body, much like a magnifying glass focuses light. This allows doctors to interrupt faulty brain circuits or destroy unwanted tissue. Magnetic-resonance imaging (MRI) allows doctors to monitor the procedure in real time - and to make adjustments as needed to obtain the best patient outcomes.
To determine if the technology could benefit patients with "asymmetrical" Parkinson's symptoms, Elias and Binit Shah, MD, from UVA's Department of Neurology, collaborated with Spain's Centro Intregral de Neurociencias to evaluate the approach in 40 volunteers in a randomized, double-blinded study. Twenty-seven study participants received treatment with focused ultrasound, while 13 others received a simulated treatment, so that the researchers could compare the results between the real procedure and the placebo. The average age of study participants was 57.
The volunteers' symptoms before and after the procedure were assessed on a scale of 1-44. Those who received the focused ultrasound procedure saw an improvement of 10 points, while those who received the sham treatment saw a difference of less than two points.
The study also looked at the safety of the procedure. Side effects included unwanted movements, muscle weakness, speech disturbances and difficulty walking. In most cases, these were temporary, but some effects persisted in six patients a year later.
The results warrant additional studies in larger numbers of volunteers conducted over longer periods of time, the researchers conclude.
"Parkinson's disease affects patients in more ways than just tremor," Shah said. "The current FDA approval for focused ultrasound in Parkinson's disease treats only tremor. Targeting this new area allows us to improve tremor but also get more overall benefit for our patients than we previously were able to achieve."
INFORMATION:
About UVA's Focused Ultrasound Research
UVA has been at the leading edge of research into the technology's potential to treat disease. For example, the federal Food and Drug Administration approved focused ultrasound for the treatment of essential tremor, a common movement disorder, based on Elias' pioneering research. His work also paved the way for the FDA to authorize the technology to treat tremors caused by Parkinson's disease.
Other researchers at UVA are investigating the technology's potential to treat a wide variety of conditions, including epilepsy and breast cancer.
Findings Published
Elias and his colleagues have published their latest findings in the prestigious New England Journal of Medicine. The research team consisted of Raúl Martínez-Fernández, Jorge U. Máñez-Miró, Rafael Rodríguez-Rojas, Marta del Álamo, Binit B. Shah, Frida Hernández-Fernández, Jose A. Pineda-Pardo, Mariana H.G. Monje, Beatriz Fernández-Rodríguez, Scott A. Sperling, David Mata-Marín, Pasqualina Guida, Fernando Alonso-Frech, Ignacio Obeso, Carmen Gasca-Salas, Lydia Vela-Desojo, Elias and Jose A. Obeso.
The research was supported by InSightec, the manufacturer of the focused ultrasound technology; Charlottesville's Focused Ultrasound Foundation, a longtime supporter of UVA's focused ultrasound research; Fundación MAPFRE in Madrid; Fundación Hospitales de Madrid; and a University of Virginia Center of Excellence grant. Elias disclosed that his department at UVA has received research funding from InSightec, but the company had no role in the study design or analysis. A full list of author disclosures is included in the paper in the New England Journal of Medicine.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog at http://makingofmedicine.virginia.edu.
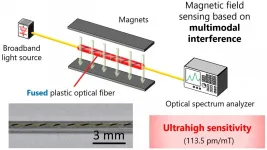
The invention of optical fibers has revolutionized not only telecommunications but also sensing technology. Optical fiber sensors can measure strain, temperature, pressure, and many other physical parameters along the fibers, but they are currently immune to electromagnetic noise -- interference from other external electric or magnetic interactions. It is a desirable trait, until the effect of the electromagnetic field on the fibers needs to be measured. Now, an international team of researchers has used what was previously considered a 'damaged' part of an optical fiber to develop such a magnetic field sensor.
They published details of their approach on Nov. 5 in Advanced Photonics Research.
"This nature of immunity ...
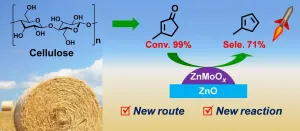
Methylcyclopentadiene (MCPD) is an important monomer in the production of RJ-4 fuel, a high-energy-density rocket fuel, and various valuable products.
Currently, MCPD is mainly obtained from the by-products of petroleum cracking tar at a very low yield of ~ 0.7 kg ton-1 and high price of ~10,000 USD ton-1. The exploration of highly efficient processes to convert renewable biomass to MCPD is stimulated by the energy and environment problems.
Recently, a group led by Prof. LI Ning and Prof. ZHANG Tao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) synthesized bio-based MCPD via direct hydrodeoxygenation of 3-methylcyclopent-2-enone (MCP) derived from cellulose.
Their study was published in Nature Communications on Jan. 4.
The researchers ...
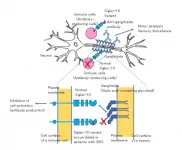
By comparing thousands of bacterial genomes, scientists in Gothenburg, Sweden have traced back the evolutionary history of antibiotic resistance genes. In almost all cases where an origin could be determined, the gene started to spread from bacteria that, themselves, can cause disease.
While human DNA is only passed down from parent to child, bacteria also have the habit of sharing some of their genes across species. This often applies to genes that make the bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
The use and overuse of antibiotics provide an advantage to those bacteria that have acquired resistance genes, thus further promoting the spread of resistance and making it more difficult to treat infections. This development threatens large parts of modern healthcare.
The rapid advances in DNA ...
Tokyo, Japan - Guillain-Barré syndrome is an infamous autoimmune neuropathy, yet genetic variants predisposing individuals to this disease have yet to be described. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) discovered two novel genetic variants in a protein made by antibody-forming immune cells, providing a mechanism for the development of the disease.
The body's immune system is supposed to fight off invaders; however, in autoimmune diseases this defense goes rogue and attacks the host instead through the production of autoantibodies. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an acutely developing, autoimmune peripheral neuropathy that leads to muscle ...
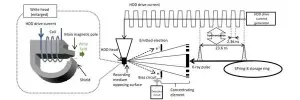
Using synchrotron radiation at SPring-8 - a large-scale synchrotron radiation facility - Tohoku University, Toshiba Corporation, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) have successfully imaged the magnetization dynamics of a hard disk drive (HDD) write head for the first time, with a precision of one ten-billionth of a second. The method makes possible precise analysis of write head operations, accelerating the development of the next-generation write heads and further increasing HDD capacity.
Details of the research were published in the Journal of Applied Physics on October 6 and presented at the 44th Annual Conference on Magnetics in Japan, on December 14.
International Data Corporation predicts a five-fold increase ...
The genomes of egg-laying monotreme mammals, platypus and echidna, have been published in the prestigious journal Nature, providing a valuable public resource for research in mammalian biology and evolution, with applications for their conservation and health.
Monotremes display a unique mix of mammalian and reptilian features and form the most distantly related, and least understood, group of living mammals. Their genetic blueprint provides fundamental insights into their unique biology and into the evolution of all mammals.
"The platypus and ...
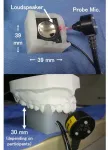
The perception of our own voice depends on sound transmission through air (air-conducted) as well as through the skull bone (bone-conducted or BC). The transmission properties of BC speech are, however, not well understood. Now, scientists from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology report their latest findings on BC transmission under the influence of oral cavity sound pressure, which can boost BC-based technology and basic research on hearing loss and speech impairment.
Ever wondered why your voice sounds different in a recording compared to how you perceive it as you speak? You are not alone. The ...
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. The treatment of bacterial and fungal infections relies particularly on antimicrobial drugs, while the focus in treating viral infections is the alleviation of symptoms.
Initial therapy for infection is often empiric and guided by clinical presentation. Its efficacy on the pathogen is, however, only seldom understood at therapy initiation. Although methods for assessing treatment responses exist, the effectiveness is mainly determined through monitoring symptoms and signs of infections.
Advances in sequencing technology have made characterization of genomes and gene expression products increasingly practical. The technology has also made it possible ...
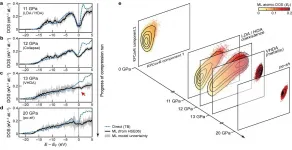
Combining electronic structure calculations and machine learning (ML) techniques has become a common approach in the atomistic modelling of matter. Using the two techniques together has allowed researchers, for instance, to create models that use atomic coordinates as the only inputs to inexpensively predict any property that can be computed by the first-principles calculations that had been used to train them.
While the earliest and by now most advanced efforts have focused on using predictions of total energies and atomic forces to construct interatomic potentials, more recent efforts have targeted additional properties of crystals and molecules such as ionization energies, NMR chemical shieldings, dielectric response properties and charge density. In the paper "Learning ...
It is during rare merging events that galaxies undergo dramatic changes in their appearance and in their stellar content. These systems are excellent laboratories to trace the formation of star clusters under extreme physical conditions.
The Milky Way typically forms star clusters with masses that are 10 thousand times the mass of our Sun. This doesn't compare to the masses of the star clusters forming in colliding galaxies, which can reach millions of times the mass of our Sun.
These dense stellar systems are also very luminous. Even after the collision, when the resulting galactic system begins to fade into a more quiescent phase, these very massive star clusters will shine throughout their host galaxy, as long-lasting witnesses of past merging events.
By studying the six galaxy ...