(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers led by Swinburne University of Technology has demonstrated the world's fastest and most powerful optical neuromorphic processor for artificial intelligence (AI), which operates faster than 10 trillion operations per second (TeraOPs/s) and is capable of processing ultra-large scale data.
Published in the prestigious journal Nature, this breakthrough represents an enormous leap forward for neural networks and neuromorphic processing in general.
Artificial neural networks, a key form of AI, can 'learn' and perform complex operations with wide applications to computer vision, natural language processing, facial recognition, speech translation, playing strategy games, medical diagnosis and many other areas. Inspired by the biological structure of the brain's visual cortex system, artificial neural networks extract key features of raw data to predict properties and behaviour with unprecedented accuracy and simplicity.
Led by Swinburne's Professor David Moss, Dr Xingyuan (Mike) Xu (Swinburne, Monash University) and Distinguished Professor Arnan Mitchell from RMIT University, the team achieved an exceptional feat in optical neural networks: dramatically accelerating their computing speed and processing power.
The team demonstrated an optical neuromorphic processor operating more than 1000 times faster than any previous processor, with the system also processing record-sized ultra-large scale images - enough to achieve full facial image recognition, something that other optical processors have been unable to accomplish.
"This breakthrough was achieved with 'optical micro-combs', as was our world-record internet data speed reported in May 2020," says Professor Moss, Director of Swinburne's Optical Sciences Centre and recently named one of Australia's top research leaders in physics and mathematics in the field of optics and photonics by The Australian.
While state-of-the-art electronic processors such as the Google TPU can operate beyond 100 TeraOPs/s, this is done with tens of thousands of parallel processors. In contrast, the optical system demonstrated by the team uses a single processor and was achieved using a new technique of simultaneously interleaving the data in time, wavelength and spatial dimensions through an integrated micro-comb source.
Micro-combs are relatively new devices that act like a rainbow made up of hundreds of high-quality infrared lasers on a single chip. They are much faster, smaller, lighter and cheaper than any other optical source.
"In the 10 years since I co-invented them, integrated micro-comb chips have become enormously important and it is truly exciting to see them enabling these huge advances in information communication and processing. Micro-combs offer enormous promise for us to meet the world's insatiable need for information," Professor Moss says.
"This processor can serve as a universal ultrahigh bandwidth front end for any neuromorphic hardware --optical or electronic based -- bringing massive-data machine learning for real-time ultrahigh bandwidth data within reach," says co-lead author of the study, Dr Xu, Swinburne alum and postdoctoral fellow with the Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Department at Monash University.
"We're currently getting a sneak-peak of how the processors of the future will look. It's really showing us how dramatically we can scale the power of our processors through the innovative use of microcombs," Dr Xu explains.
RMIT's Professor Mitchell adds, "This technology is applicable to all forms of processing and communications - it will have a huge impact. Long term we hope to realise fully integrated systems on a chip, greatly reducing cost and energy consumption".
"Convolutional neural networks have been central to the artificial intelligence revolution, but existing silicon technology increasingly presents a bottleneck in processing speed and energy efficiency," says key supporter of the research team, Professor Damien Hicks, from Swinburne and the Walter and Elizabeth Hall Institute.
He adds, "This breakthrough shows how a new optical technology makes such networks faster and more efficient and is a profound demonstration of the benefits of cross-disciplinary thinking, in having the inspiration and courage to take an idea from one field and using it to solve a fundamental problem in another."
INFORMATION:
The international research collaboration was led by Professor David Moss (Swinburne); Dr Xingyuan (Mike) Xu (Swinburne and Monash) and Distinguished Professor Arnan Mitchell (RMIT) with key support from Mengxi Tan and Dr Jiayang Wu (Swinburne); Professor Damien Hicks (Swinburne and Walter and Elizabeth Hall Institute (WEHI)); Andrea Boes and Thach G Nguyen (RMIT); Dr Bill Corcoran (Monash); Sai T Chu (City University of Hong Kong); Brent Little (Xi'an Institute of Optics); and Roberto Morandotti (INRS in Montreal, Canada).
Media contact
Cherish Philip George, Communications and Media
Swinburne University of Technology
M +61 410 276 413 | E: cphilipgeorge@swin.edu.au
El Niño events have long been perceived as a driver for low rainfall in the winter and spring in Hawai'i, creating a six-month wet-season drought. However, a recent study by researchers in the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) revealed the connection between Hawai'i winter rainfall and El Niño is not as straightforward as previously thought.
Studies in the past decade suggested that there are at least two types of El Niño: the Eastern Pacific and Central Pacific, when the warmest pool of water is located in the eastern or central portions of the ocean basin, respectively. El Niño events usually ...
WASHINGTON--Black and Hispanic people with COVID-19 and diabetes are more likely than Caucasians to die or have serious complications, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. ...
With an estimated lifespan between 25 to 40 years, the queen conch (Strombus gigas) is a prized delicacy long harvested for food and is revered for its beautiful shell. Second only to the spiny lobster, it is one of the most important benthic fisheries in the Caribbean region. Unfortunately, the species faces a challenge of survival: how to endure and thrive, as populations are in a steady state of decline from overfishing, habitat degradation and hurricane damage. In some places, the conch populations have dwindled so low that the remaining conch cannot find breeding partners. This dire situation is urgent in ecological and economic terms.
To preserve this most significant molluscan fishery in the Caribbean, ...
Osaka, Japan - Medical professionals all want to be able to quickly and correctly diagnose diseases. Their future ability to do so will depend on identifying what biochemicals are present in tissue sections, where the biomolecules are, and at what concentrations. For this purpose, mass spectrometry imaging--which can identify multiple biochemicals in a single experiment--will be useful. However, the stability of biomolecular sampling needs improvement to obtain the chemical distribution information with high spatial resolution.
In the recent study published in Analytical Chemistry, researchers from Osaka University used mass spectrometry to image the distribution of ...
A scalpel-free alternative to brain surgery has the potential to benefit people with Parkinson's disease symptoms that are much more severe on one side of the body, new research suggests.
More testing is needed, but the approach, which uses a technology called focused ultrasound, could offer a new option for patients whose symptoms are poorly controlled by medications and those who cannot or do not wish to undergo traditional brain surgery.
"This small brain region, the subthalamic nucleus, had a very strong and potent effect on parkinsonian symptoms when we targeted it with precise, focused ultrasound energy," ...
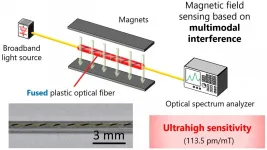
The invention of optical fibers has revolutionized not only telecommunications but also sensing technology. Optical fiber sensors can measure strain, temperature, pressure, and many other physical parameters along the fibers, but they are currently immune to electromagnetic noise -- interference from other external electric or magnetic interactions. It is a desirable trait, until the effect of the electromagnetic field on the fibers needs to be measured. Now, an international team of researchers has used what was previously considered a 'damaged' part of an optical fiber to develop such a magnetic field sensor.
They published details of their approach on Nov. 5 in Advanced Photonics Research.
"This nature of immunity ...
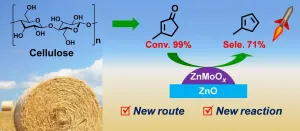
Methylcyclopentadiene (MCPD) is an important monomer in the production of RJ-4 fuel, a high-energy-density rocket fuel, and various valuable products.
Currently, MCPD is mainly obtained from the by-products of petroleum cracking tar at a very low yield of ~ 0.7 kg ton-1 and high price of ~10,000 USD ton-1. The exploration of highly efficient processes to convert renewable biomass to MCPD is stimulated by the energy and environment problems.
Recently, a group led by Prof. LI Ning and Prof. ZHANG Tao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) synthesized bio-based MCPD via direct hydrodeoxygenation of 3-methylcyclopent-2-enone (MCP) derived from cellulose.
Their study was published in Nature Communications on Jan. 4.
The researchers ...
By comparing thousands of bacterial genomes, scientists in Gothenburg, Sweden have traced back the evolutionary history of antibiotic resistance genes. In almost all cases where an origin could be determined, the gene started to spread from bacteria that, themselves, can cause disease.
While human DNA is only passed down from parent to child, bacteria also have the habit of sharing some of their genes across species. This often applies to genes that make the bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
The use and overuse of antibiotics provide an advantage to those bacteria that have acquired resistance genes, thus further promoting the spread of resistance and making it more difficult to treat infections. This development threatens large parts of modern healthcare.
The rapid advances in DNA ...
Tokyo, Japan - Guillain-Barré syndrome is an infamous autoimmune neuropathy, yet genetic variants predisposing individuals to this disease have yet to be described. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) discovered two novel genetic variants in a protein made by antibody-forming immune cells, providing a mechanism for the development of the disease.
The body's immune system is supposed to fight off invaders; however, in autoimmune diseases this defense goes rogue and attacks the host instead through the production of autoantibodies. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an acutely developing, autoimmune peripheral neuropathy that leads to muscle ...
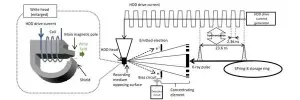
Using synchrotron radiation at SPring-8 - a large-scale synchrotron radiation facility - Tohoku University, Toshiba Corporation, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) have successfully imaged the magnetization dynamics of a hard disk drive (HDD) write head for the first time, with a precision of one ten-billionth of a second. The method makes possible precise analysis of write head operations, accelerating the development of the next-generation write heads and further increasing HDD capacity.
Details of the research were published in the Journal of Applied Physics on October 6 and presented at the 44th Annual Conference on Magnetics in Japan, on December 14.
International Data Corporation predicts a five-fold increase ...