Want to diagnose brain diseases? A mass spectrometry imaging may one day help you
Researchers from Osaka University developed a new method for brain tissue analysis in high spatial resolution that requires no sample preparation
2021-01-07
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan - Medical professionals all want to be able to quickly and correctly diagnose diseases. Their future ability to do so will depend on identifying what biochemicals are present in tissue sections, where the biomolecules are, and at what concentrations. For this purpose, mass spectrometry imaging--which can identify multiple biochemicals in a single experiment--will be useful. However, the stability of biomolecular sampling needs improvement to obtain the chemical distribution information with high spatial resolution.
In the recent study published in Analytical Chemistry, researchers from Osaka University used mass spectrometry to image the distribution of fat molecules in mouse brain tissue. They acquired data at a spatial resolution of 6.5 micrometers, enabling analysis on a cellular level.
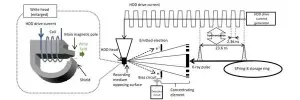
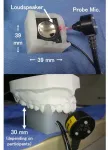
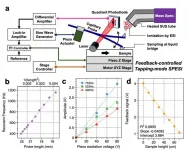
The researchers used a very small capillary to gently extract lipid molecules from a tissue section, and a carefully designed setup for fine 3D directional control. Although biological tissue may often seem smooth to the naked eye, on an ultrasmall scale it's rather rough. The ability to account for this ultrasmall-scale roughness is central to obtaining reproducible biochemical data at high spatial resolution.
"In our experiments, the probe's vibration amplitude is constant even when the sample height changes," says Yoichi Otsuka, first author. "We can also measure changes in sample height up to 20 micrometers, and it can be increased up to 180 micrometers."
The researchers' first experiments were to measure irregular distributions of molecules across an uneven surface: microwells filled with various concentrations of a dye. The measured concentrations correlated with the known concentrations, and the measured surface topography was close to the actual microwell diameter. Experiments with mouse brain sections yielded a multi-dimensional data of multiple molecules such as the distribution of certain hexosylceramides--lipids that are important in aging.
"Principle component analysis helped us integrate our wide-ranging data," explains Takuya Matsumoto, senior author. "For example, we could assign the classes of lipids that are primarily present in the cortex and brainstem."
Correlating such data with disease progression will require further study and perhaps additional development of the researchers' biomolecule extraction setup. The researchers anticipate that their approach will be useful for quantitatively imaging the myriad neural networks in brain tissue. Ultimately, they hope to help medical practitioners reliably diagnose diseases such as brain cancer in a tissue section with the support of molecular information in high spatial resolution.
INFORMATION:
The article, "High-spatial-resolution multimodal imaging by tapping-mode scanning probe electrospray ionization with feedback control," was published in Analytical Chemistry at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04144
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-07
A scalpel-free alternative to brain surgery has the potential to benefit people with Parkinson's disease symptoms that are much more severe on one side of the body, new research suggests.
More testing is needed, but the approach, which uses a technology called focused ultrasound, could offer a new option for patients whose symptoms are poorly controlled by medications and those who cannot or do not wish to undergo traditional brain surgery.
"This small brain region, the subthalamic nucleus, had a very strong and potent effect on parkinsonian symptoms when we targeted it with precise, focused ultrasound energy," ...
2021-01-07
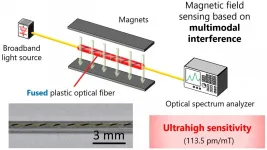
The invention of optical fibers has revolutionized not only telecommunications but also sensing technology. Optical fiber sensors can measure strain, temperature, pressure, and many other physical parameters along the fibers, but they are currently immune to electromagnetic noise -- interference from other external electric or magnetic interactions. It is a desirable trait, until the effect of the electromagnetic field on the fibers needs to be measured. Now, an international team of researchers has used what was previously considered a 'damaged' part of an optical fiber to develop such a magnetic field sensor.
They published details of their approach on Nov. 5 in Advanced Photonics Research.
"This nature of immunity ...
2021-01-07
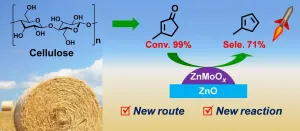
Methylcyclopentadiene (MCPD) is an important monomer in the production of RJ-4 fuel, a high-energy-density rocket fuel, and various valuable products.
Currently, MCPD is mainly obtained from the by-products of petroleum cracking tar at a very low yield of ~ 0.7 kg ton-1 and high price of ~10,000 USD ton-1. The exploration of highly efficient processes to convert renewable biomass to MCPD is stimulated by the energy and environment problems.
Recently, a group led by Prof. LI Ning and Prof. ZHANG Tao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) synthesized bio-based MCPD via direct hydrodeoxygenation of 3-methylcyclopent-2-enone (MCP) derived from cellulose.
Their study was published in Nature Communications on Jan. 4.
The researchers ...
2021-01-07
By comparing thousands of bacterial genomes, scientists in Gothenburg, Sweden have traced back the evolutionary history of antibiotic resistance genes. In almost all cases where an origin could be determined, the gene started to spread from bacteria that, themselves, can cause disease.
While human DNA is only passed down from parent to child, bacteria also have the habit of sharing some of their genes across species. This often applies to genes that make the bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
The use and overuse of antibiotics provide an advantage to those bacteria that have acquired resistance genes, thus further promoting the spread of resistance and making it more difficult to treat infections. This development threatens large parts of modern healthcare.
The rapid advances in DNA ...
2021-01-07
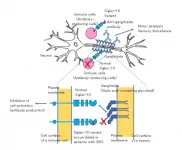
Tokyo, Japan - Guillain-Barré syndrome is an infamous autoimmune neuropathy, yet genetic variants predisposing individuals to this disease have yet to be described. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) discovered two novel genetic variants in a protein made by antibody-forming immune cells, providing a mechanism for the development of the disease.
The body's immune system is supposed to fight off invaders; however, in autoimmune diseases this defense goes rogue and attacks the host instead through the production of autoantibodies. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an acutely developing, autoimmune peripheral neuropathy that leads to muscle ...
2021-01-07
Using synchrotron radiation at SPring-8 - a large-scale synchrotron radiation facility - Tohoku University, Toshiba Corporation, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) have successfully imaged the magnetization dynamics of a hard disk drive (HDD) write head for the first time, with a precision of one ten-billionth of a second. The method makes possible precise analysis of write head operations, accelerating the development of the next-generation write heads and further increasing HDD capacity.
Details of the research were published in the Journal of Applied Physics on October 6 and presented at the 44th Annual Conference on Magnetics in Japan, on December 14.
International Data Corporation predicts a five-fold increase ...
2021-01-07
The genomes of egg-laying monotreme mammals, platypus and echidna, have been published in the prestigious journal Nature, providing a valuable public resource for research in mammalian biology and evolution, with applications for their conservation and health.
Monotremes display a unique mix of mammalian and reptilian features and form the most distantly related, and least understood, group of living mammals. Their genetic blueprint provides fundamental insights into their unique biology and into the evolution of all mammals.
"The platypus and ...
2021-01-07
The perception of our own voice depends on sound transmission through air (air-conducted) as well as through the skull bone (bone-conducted or BC). The transmission properties of BC speech are, however, not well understood. Now, scientists from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology report their latest findings on BC transmission under the influence of oral cavity sound pressure, which can boost BC-based technology and basic research on hearing loss and speech impairment.
Ever wondered why your voice sounds different in a recording compared to how you perceive it as you speak? You are not alone. The ...
2021-01-07
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. The treatment of bacterial and fungal infections relies particularly on antimicrobial drugs, while the focus in treating viral infections is the alleviation of symptoms.
Initial therapy for infection is often empiric and guided by clinical presentation. Its efficacy on the pathogen is, however, only seldom understood at therapy initiation. Although methods for assessing treatment responses exist, the effectiveness is mainly determined through monitoring symptoms and signs of infections.
Advances in sequencing technology have made characterization of genomes and gene expression products increasingly practical. The technology has also made it possible ...
2021-01-07
Combining electronic structure calculations and machine learning (ML) techniques has become a common approach in the atomistic modelling of matter. Using the two techniques together has allowed researchers, for instance, to create models that use atomic coordinates as the only inputs to inexpensively predict any property that can be computed by the first-principles calculations that had been used to train them.
While the earliest and by now most advanced efforts have focused on using predictions of total energies and atomic forces to construct interatomic potentials, more recent efforts have targeted additional properties of crystals and molecules such as ionization energies, NMR chemical shieldings, dielectric response properties and charge density. In the paper "Learning ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Want to diagnose brain diseases? A mass spectrometry imaging may one day help you
Researchers from Osaka University developed a new method for brain tissue analysis in high spatial resolution that requires no sample preparation