INFORMATION:
Study co-authors included Magdalena Wojcieszak, associate professor of communication, and doctoral students Jieyu Ding Featherstone (Department of Communication) and Christopher Calabrese (Department of Public Health Sciences), all of UC Davis.
Link to study: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0091743520304394?dgcid=author
Vaccine myths on social media can be effectively reduced with credible fact checking
Simple tags can make a difference
2021-01-07
(Press-News.org) Social media misinformation can negatively influence people's attitudes about vaccine safety and effectiveness, but credible organizations -- such as research universities and health institutions -- can play a pivotal role in debunking myths with simple tags that link to factual information, University of California, Davis, researchers, suggest in a new study.
Researchers found that fact-check tags located immediately below or near a post can generate more positive attitudes toward vaccines than misinformation alone, and perceived source expertise makes a difference.
"In fact, fact-checking labels from health institutions and research universities were seen as more 'expert' than others, indirectly resulting in more positive attitudes toward vaccines," said Jingwen Zhang, assistant professor of communication and lead author of the study.
The findings were published online Wednesday, Jan. 6, in the journal Preventive Medicine.
Has implications for COVID-19
The data was collected in 2018 -- before the COVID-19 pandemic -- but the study's results could influence public communications about COVID-19 vaccines, researchers said.
"The most important thing I learned from this paper is that fact checking is effective...giving people a simple label can change their attitude," Zhang said. "Secondly, I am calling for more researchers and scientists to engage in public health and science communications. We need to be more proactive. We are not using our power right now."
While there is a strong consensus in the medical community that vaccines are safe, cost-effective and successful in preventing diseases, widespread vaccine hesitancy has resurged in many countries, the study said. The United States has faced issues with lower-than-preferred vaccine participation for influenza and even measles, which medical experts blamed for a 2019 measles outbreak. "Because both individuals and groups can post misinformation, such as false claims about vaccines, social media have played a role in spreading misinformation," Zhang said.
Study authors tested the effects of simple fact-checking labels with 1,198 people nationwide who showed different levels of vaccine hesitancy. In the experiment, researchers used multiple misinformation messages covering five vaccine types and five categories of 13 different fact-checking sources. They avoided any explanations that repeated the false information.
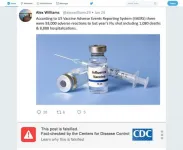
Using a mock twitter account, one post, for example, consisted of a misinformation claim on a specific vaccine and a picture of a vaccine bottle. It read: "According to a US Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) there were 93,000 adverse reactions to last year's Flu Shot including 1,080 deaths & 8,888 hospitalizations."
Researchers then used alternating fact-checking labels from various sources in media, health organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Johns Hopkins University, and algorithms. One read, for example, "This post is falsified. Fact-checked by the Centers For Disease Control. Learn why this is falsified."
The results showed that those exposed to fact-checking labels were more likely to develop more positive attitudes toward vaccines than misinformation alone. Further, the labels' effect was not moderated by vaccine skepticism, the type of vaccine misinformation or political ideology.
"What approaches are most effective at targeting vaccine misinformation on social media among users unlikely to visit fact-checking websites or engage with thorough corrections?" researchers asked in the paper. "This project shows that seeing a fact-checking label immediately below a misinformation post can make viewers more favorable toward vaccines."
She explained that a tag could be as simple as a reply to a misinforming tweet that explains the information is false, and links to credible information at a university or institutional web site.
Ideally, she said, tagging should be done by social media companies such as Facebook and Twitter. She said social media companies are working with entities, such as the WHO, to correct misinformation. "We are headed in the right direction, but more needs to happen," she said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Swinburne-led research team demonstrates world's fastest optical neuromorphic processor
2021-01-07
An international team of researchers led by Swinburne University of Technology has demonstrated the world's fastest and most powerful optical neuromorphic processor for artificial intelligence (AI), which operates faster than 10 trillion operations per second (TeraOPs/s) and is capable of processing ultra-large scale data.
Published in the prestigious journal Nature, this breakthrough represents an enormous leap forward for neural networks and neuromorphic processing in general.
Artificial neural networks, a key form of AI, can 'learn' and perform complex operations with wide applications to computer vision, natural language processing, facial recognition, speech translation, ...
Hawai'i drought during El Niño winter? Not always, according to new research
2021-01-07
El Niño events have long been perceived as a driver for low rainfall in the winter and spring in Hawai'i, creating a six-month wet-season drought. However, a recent study by researchers in the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) revealed the connection between Hawai'i winter rainfall and El Niño is not as straightforward as previously thought.
Studies in the past decade suggested that there are at least two types of El Niño: the Eastern Pacific and Central Pacific, when the warmest pool of water is located in the eastern or central portions of the ocean basin, respectively. El Niño events usually ...
Black people with type 1 diabetes, COVID-19 are four times more likely to be hospitalized for diabetic ketoacidosis
2021-01-07
WASHINGTON--Black and Hispanic people with COVID-19 and diabetes are more likely than Caucasians to die or have serious complications, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. ...
'hail to the queen' - saving the Caribbean queen conch
2021-01-07
With an estimated lifespan between 25 to 40 years, the queen conch (Strombus gigas) is a prized delicacy long harvested for food and is revered for its beautiful shell. Second only to the spiny lobster, it is one of the most important benthic fisheries in the Caribbean region. Unfortunately, the species faces a challenge of survival: how to endure and thrive, as populations are in a steady state of decline from overfishing, habitat degradation and hurricane damage. In some places, the conch populations have dwindled so low that the remaining conch cannot find breeding partners. This dire situation is urgent in ecological and economic terms.
To preserve this most significant molluscan fishery in the Caribbean, ...
Want to diagnose brain diseases? A mass spectrometry imaging may one day help you
2021-01-07
Osaka, Japan - Medical professionals all want to be able to quickly and correctly diagnose diseases. Their future ability to do so will depend on identifying what biochemicals are present in tissue sections, where the biomolecules are, and at what concentrations. For this purpose, mass spectrometry imaging--which can identify multiple biochemicals in a single experiment--will be useful. However, the stability of biomolecular sampling needs improvement to obtain the chemical distribution information with high spatial resolution.
In the recent study published in Analytical Chemistry, researchers from Osaka University used mass spectrometry to image the distribution of ...
Focused ultrasound shows promise for Parkinson's disease
2021-01-07
A scalpel-free alternative to brain surgery has the potential to benefit people with Parkinson's disease symptoms that are much more severe on one side of the body, new research suggests.
More testing is needed, but the approach, which uses a technology called focused ultrasound, could offer a new option for patients whose symptoms are poorly controlled by medications and those who cannot or do not wish to undergo traditional brain surgery.
"This small brain region, the subthalamic nucleus, had a very strong and potent effect on parkinsonian symptoms when we targeted it with precise, focused ultrasound energy," ...
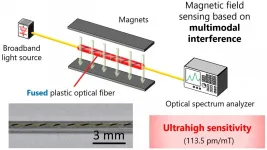
Researchers repurpose 'damaged' polymer optical fibers to precisely measure magnetic fields
2021-01-07
The invention of optical fibers has revolutionized not only telecommunications but also sensing technology. Optical fiber sensors can measure strain, temperature, pressure, and many other physical parameters along the fibers, but they are currently immune to electromagnetic noise -- interference from other external electric or magnetic interactions. It is a desirable trait, until the effect of the electromagnetic field on the fibers needs to be measured. Now, an international team of researchers has used what was previously considered a 'damaged' part of an optical fiber to develop such a magnetic field sensor.
They published details of their approach on Nov. 5 in Advanced Photonics Research.
"This nature of immunity ...
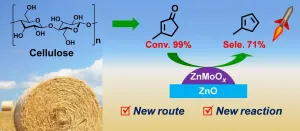
Researchers synthesize bio-based Methylcyclopentadiene with 3-Methylcyclopent-2-enone
2021-01-07
Methylcyclopentadiene (MCPD) is an important monomer in the production of RJ-4 fuel, a high-energy-density rocket fuel, and various valuable products.
Currently, MCPD is mainly obtained from the by-products of petroleum cracking tar at a very low yield of ~ 0.7 kg ton-1 and high price of ~10,000 USD ton-1. The exploration of highly efficient processes to convert renewable biomass to MCPD is stimulated by the energy and environment problems.
Recently, a group led by Prof. LI Ning and Prof. ZHANG Tao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) synthesized bio-based MCPD via direct hydrodeoxygenation of 3-methylcyclopent-2-enone (MCP) derived from cellulose.
Their study was published in Nature Communications on Jan. 4.
The researchers ...
Where antibiotic resistance comes from
2021-01-07
By comparing thousands of bacterial genomes, scientists in Gothenburg, Sweden have traced back the evolutionary history of antibiotic resistance genes. In almost all cases where an origin could be determined, the gene started to spread from bacteria that, themselves, can cause disease.
While human DNA is only passed down from parent to child, bacteria also have the habit of sharing some of their genes across species. This often applies to genes that make the bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
The use and overuse of antibiotics provide an advantage to those bacteria that have acquired resistance genes, thus further promoting the spread of resistance and making it more difficult to treat infections. This development threatens large parts of modern healthcare.
The rapid advances in DNA ...
A subtle change in the DNA may predispose to polyneuropathy after gut infection
2021-01-07
Tokyo, Japan - Guillain-Barré syndrome is an infamous autoimmune neuropathy, yet genetic variants predisposing individuals to this disease have yet to be described. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) discovered two novel genetic variants in a protein made by antibody-forming immune cells, providing a mechanism for the development of the disease.
The body's immune system is supposed to fight off invaders; however, in autoimmune diseases this defense goes rogue and attacks the host instead through the production of autoantibodies. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an acutely developing, autoimmune peripheral neuropathy that leads to muscle ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
[Press-News.org] Vaccine myths on social media can be effectively reduced with credible fact checkingSimple tags can make a difference