Entangling electrons with heat
Quantum entanglement is key for next-generation computing and communications technology, Aalto researchers can now produce it using temperature differences
2021-01-08
(Press-News.org) A joint group of scientists from Finland, Russia, China and the USA have demonstrated that temperature difference can be used to entangle pairs of electrons in superconducting structures. The experimental discovery, published in Nature Communications, promises powerful applications in quantum devices, bringing us one step closer towards applications of the second quantum revolution.
The team, led by Professor Pertti Hakonen from Aalto University, has shown that the thermoelectric effect provides a new method for producing entangled electrons in a new device. "Quantum entanglement is the cornerstone of the novel quantum technologies. This concept, however, has puzzled many physicists over the years, including Albert Einstein who worried a lot about the spooky interaction at a distance that it causes", says Prof. Hakonen.
In quantum computing, entanglement is used to fuse individual quantum systems into one, which exponentially increases their total computational capacity. "Entanglement can also be used in quantum cryptography, enabling the secure exchange of information over long distances", explains Prof. Gordey Lesovik, from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, who has acted several times as a visiting professor at Aalto University School of Science. Given the significance of entanglement to quantum technology, the ability to create entanglement easily and controllably is an important goal for researchers.
The researchers designed a device where a superconductor was layered withed graphene and metal electrodes. "Superconductivity is caused by entangled pairs of electrons called "cooper pairs". Using a temperature difference, we cause them to split, with each electron then moving to different normal metal electrode," explains doctoral candidate Nikita Kirsanov, from Aalto University. "The resulting electrons remain entangled despite being separated for quite long distances."
Along with the practical implications, the work has significant fundamental importance. The experiment has shown that the process of Cooper pair splitting works as a mechanism for turning temperature difference into correlated electrical signals in superconducting structures. The developed experimental scheme may also become a platform for original quantum thermodynamical experiments.
INFORMATION:
The work was carried out using the OtaNano research infrastructure. OtaNano provides state-of-the-art working environment and equipment for nanoscience and -technology, and quantum technologies research in Finland. OtaNano is operated by Aalto University and VTT, and is available for academic and commercial users internationally. To find out more, visit their website. The work was supported by funded from QTF (Academy of Finland CoE). Gordey Lesovik's visiting professorship funding came fro Aalto University School of Science and Zhenbing Tan's post doctoral grant came from the Academy of Finland.
The full paper, Thermoelectric current in a graphene Cooper pair splitter can be read here http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20476-7
Contact
Pertti Hakonen
Professor
Aalto University
pertti.hakonen@aalto.fi
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-08
Reactive molecules, such as free radicals, can be produced in the body after exposure to certain environments or substances and go on to cause cell damage. Antioxidants can minimize this damage by interacting with the radicals before they affect cells.
Led by Enrique Gomez, professor of chemical engineering and materials science and engineering, Penn State researchers have applied this concept to prevent imaging damage to conducting polymers that comprise soft electronic devices, such as organic solar cells, organic transistors, bioelectronic devices and flexible electronics. The researchers ...
2021-01-08
Jan. 8, 2021 - A new study published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society examines the recovery of lung function and overall wellness in individuals who had varying degrees of COVID-19 severity. Little is known about lung health following infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and whether later respiratory problems, fatigue and ill health are associated with the disease's initial severity.
In " END ...
2021-01-08
Researchers from Oklahoma State University, University of Missouri, Iowa State University, and University of Georgia published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that investigates the question of how salespeople should balance advocacy for the seller with advocacy for the customer.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Salesperson Dual Agency in Price Negotiations" and is authored by Justin Lawrence, Lisa Scheer, Andrew Crecelius, and Son Lam.
How should salespeople represent both the seller and the customer when their interests diverge, as in pricing negotiations? The research team extends a dual agency framework to the sales domain and examines the salesperson's role throughout the three stages of the discount process: (a) the ...
2021-01-08
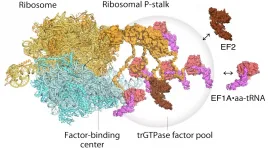
Ribosomes are the complexes of ribonucleoproteins at the heart of protein synthesis in cells. However in the absence of conclusive evidence, how these complexes operate has been open to debate. Now Hirotatsu Imai and Noriyuki Kodera at Kanazawa University, alongside Toshio Uchiumi at Niigata University in Japan, show visualizations of the structural dynamics and factor pooling that take place at ribosome stalk proteins as they build new proteins.
Ribosomes were first discovered in the 1950s and their broad function has been widely understood for some time - they read messenger RNA sequences and from that generate sequences of correctly ordered amino acids into new proteins. The ribosome stalk protein in particular plays an ...
2021-01-08
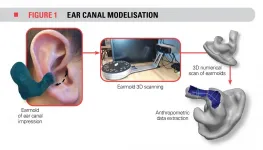
Noise exposure accounts for 22% of worldwide work-related health problems. Excessive noise not only causes hearing loss and tinnitus, but also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. To provide protection, workers normally wear earplugs. However, commonly available earplugs are often uncomfortable, since they don't fit everyone's ears equally well.
How could we improve the comfort and effectiveness of these earplugs? What aspects of the ear canal must be taken into account? To answer these questions, researchers from the École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS University) and the Institut de recherche en santé et sécurité ...
2021-01-08
Non-violent offenders serving time for drug use or possession should be freed immediately and their convictions erased, according to research published in the peer-reviewed The American Journal of Bioethics.
More than 60 international experts including bioethicists, psychologists and drug experts have joined forces to call for an end to the war on drugs which they argue feeds racism.
All drugs currently deemed illicit - even crack cocaine and heroin - should be decriminalized as a matter of urgency, according to this new alliance. Legalisation and regulation should then follow with restrictions on age, advertising and licensing, they say.
They have analysed evidence from over 150 studies and reports, concluding that prohibition unfairly affects Black people, damages communities, ...
2021-01-08
A new study has found that spending time outdoors and switching off our devices is associated with higher levels of happiness during a period of COVID-19 restrictions.
Previous academic studies have indicated how being outdoors, particularly in green spaces, can improve mental health by promoting more positive body image, and lowering levels of depression and anxiety.
Jointly led by academics from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in the UK, the Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences in Austria, and Perdana University in Malaysia, this new research examined how levels ...
2021-01-08
PHILADELPHIA--Medications to treat high blood pressure did not affect outcomes among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, found an international team led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The study, published today in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, is the first randomized controlled trial to show there is no risk for patients continuing these medications while hospitalized for COVID-19.
As part of the REPLACE COVID trial, investigators examined whether ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) or Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) -- two classes of medications to treat high blood pressure -- ...
2021-01-07
Touted by makers as a "healthy" alternative to traditional nicotine cigarettes, new research indicates the chemicals found in e-cigarettes disrupt the gut barrier and trigger inflammation in the body, potentially leading to a variety of health concerns.
In the study, published Jan. 5, 2021 in the journal END ...
2021-01-07
Abu Dhabi, UAE, January 6, 2021: To provide effective aid to children who live in areas of conflict it is necessary to understand precisely how they have been impacted by the crises around them. One area of importance is the effect of conflict and trauma on a child's development and education.
In a new paper, Global TIES for Children researchers J. Lawrence Aber, Carly Tubbs Dolan, Ha Yeon Kim, and Lindsay Brown, present a review of opportunities and challenges they have encountered in designing and conducting rigorous research that advances our understanding of this effect. Global TIES for Children, an international research center based at NYU Abu Dhabi and NYU New York, generates evidence to support the most effective humanitarian and development aid to promote children's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Entangling electrons with heat
Quantum entanglement is key for next-generation computing and communications technology, Aalto researchers can now produce it using temperature differences