Antibiotic resistance from random DNA sequences
2021-01-08
(Press-News.org) An important and still unanswered question is how new genes that cause antibiotic resistance arise. In a new study, Swedish and American researchers have shown how new genes that produce resistance can arise from completely random DNA sequences. The results have been published in the journal PLOS Genetics.
Antibiotic resistance is a major global problem and the spread of resistant bacteria causes disease and death, and constitutes a major cost to society. The most common way for bacteria to develop resistance is by taking up various types of resistance genes from other bacteria. These genes encode proteins (peptides) that can lead to resistance by: (i) deactivating the antibiotic, (ii) reducing its concentration, or (iii) altering the antibiotic's target so that the antibiotic can no longer bind to that target and hence halt the growth of the bacterium. Once resistance genes have arisen, they can quickly spread between different pathogenic bacteria and reduce the effectiveness of our antibiotics. It is therefore important to detect and characterise new resistance genes as quickly as possible - in order to monitor the spread of resistance and also to facilitate treatment and the development of new antibiotics.
To study the emergence of resistance genes, the researchers used laboratory experiments to investigate whether it was possible to generate a gene from random DNA sequences that would give rise to antibiotic resistance. This was done by first designing nearly one billion random DNA sequences that were then placed on a plasmid in the intestinal bacterium Escherichia coli. (Plasmids are DNA molecules that replicate independently and can be transferred from one organism to another.)
These random DNA sequences were then expressed in the bacterium as short peptides. While most of these peptides had no effect on the bacterium at all, six different peptides did, causing the bacterium to become resistant to the antibiotic Colistin, an important antibiotic medication of last resort that is used in severe infections to kill the bacteria by binding to and destroying the bacterium's cell membrane. These peptides caused resistance by increasing the expression of genes that are involved in the modification of the bacterium's cell membrane. This modification of the cell membrane resulted in the antibiotic not being able to bind to cell membrane, and thus not being able to reduce the survival of the bacterium.
"We have now shown in two different studies that random sequences of amino acids can give rise to new functions that are beneficial to the bacterium such as antibiotic resistance. This suggests that the evolution of new functions from random DNA sequences is not as unusual as previously thought," says Dan I. Andersson, Professor in Medical Bacteriology and responsible for the study.
"An important question that remains unanswered and requires further study is whether these new genes are naturally present in bacteria or can only be observed in laboratory experiments," says Michael Knopp, post-doctoral researcher at the Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology and the study's first author.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-08
PITTSBURGH--Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University report findings on an advanced nanomaterial-based biosensing platform that detects, within seconds, antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition to testing, the platform will help to quantify patient immunological response to the new vaccines with precision.
The results were published this week in the journal Advanced Materials. Carnegie Mellon's collaborators included the University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) and the UPMC.
The testing platform identifies the presence of two of the virus' antibodies, spike S1 protein and receptor binding domain (RBD), in a ...
2021-01-08
Leg amputees are often not satisfied with their prosthesis, even though the sophisticated prostheses are becoming available. One important reason for this is that they perceive the weight of the prosthesis as too high, despite the fact that prosthetic legs are usually less than half the weight of a natural limb. Researchers led by Stanisa Raspopovic, a professor at the Department of Health Sciences and Technology, have now been able to show that connecting the prostheses to the nervous system helps amputees to perceive the prosthesis weight as lower, which ...
2021-01-08
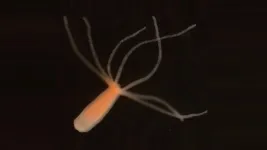
Stay awake too long, and thinking straight can become extremely difficult. Thankfully, a few winks of sleep is often enough to get our brains functioning up to speed again. But just when and why did animals start to require sleep? And is having a brain even a prerequisite?
In a study that could help to understand the evolutional origin of sleep in animals, an international team of researchers has shown that tiny, water-dwelling hydras not only show signs of a sleep-like state despite lacking central nervous systems but also respond to molecules associated ...
2021-01-08
Since 2006, a fungal disease called white-nose syndrome has caused sharp declines in bat populations across the eastern United States. The fungus that causes the disease, Pseudogymnoascus destructans, thrives in subterranean habitats where bats hibernate over the winter months.
Bats roosting in the warmest sites have been hit particularly hard, since more fungus grows on their skin, and they are more likely to die from white-nose syndrome, according to a new study by researchers at Virginia Tech.
But instead of avoiding these warm and deadly sites, bats continue to use them year after year. The reason? Bats are mistakenly preferring sites where fungal growth is ...
2021-01-08
An invisible flow of groundwater seeps into the ocean along coastlines all over the world. Scientists have tended to disregard its contributions to ocean chemistry, focusing on the far greater volumes of water and dissolved material entering the sea from rivers and streams, but a new study finds groundwater discharge plays a more significant role than had been thought.
The new findings, published January 8 in Nature Communications, have implications for global models of biogeochemical cycles and for the interpretation of isotope records of Earth's climate history.
"It's really hard to characterize groundwater discharge, so it has been a source of uncertainty in the modeling of global cycles," said first author Kimberley Mayfield, who led the study as ...
2021-01-08
Pleiotropy analysis, which provides insight on how individual genes result in multiple characteristics, has become increasingly valuable as medicine continues to lean into mining genetics to inform disease treatments. Privacy stipulations, though, make it difficult to perform comprehensive pleiotropy analysis because individual patient data often can't be easily and regularly shared between sites. However, a statistical method called Sum-Share, developed at Penn Medicine, can pull summary information from many different sites to generate significant insights. In a test of the method, published in Nature Communications, Sum-Share's developers were able to detect more than 1,700 DNA-level variations that ...
2021-01-08
A joint group of scientists from Finland, Russia, China and the USA have demonstrated that temperature difference can be used to entangle pairs of electrons in superconducting structures. The experimental discovery, published in Nature Communications, promises powerful applications in quantum devices, bringing us one step closer towards applications of the second quantum revolution.
The team, led by Professor Pertti Hakonen from Aalto University, has shown that the thermoelectric effect provides a new method for producing entangled electrons in a new device. "Quantum entanglement is the cornerstone of the novel quantum technologies. This concept, however, has puzzled many physicists over the years, including Albert Einstein who worried a lot about the ...
2021-01-08
Reactive molecules, such as free radicals, can be produced in the body after exposure to certain environments or substances and go on to cause cell damage. Antioxidants can minimize this damage by interacting with the radicals before they affect cells.
Led by Enrique Gomez, professor of chemical engineering and materials science and engineering, Penn State researchers have applied this concept to prevent imaging damage to conducting polymers that comprise soft electronic devices, such as organic solar cells, organic transistors, bioelectronic devices and flexible electronics. The researchers ...
2021-01-08
Jan. 8, 2021 - A new study published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society examines the recovery of lung function and overall wellness in individuals who had varying degrees of COVID-19 severity. Little is known about lung health following infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and whether later respiratory problems, fatigue and ill health are associated with the disease's initial severity.
In " END ...
2021-01-08
Researchers from Oklahoma State University, University of Missouri, Iowa State University, and University of Georgia published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that investigates the question of how salespeople should balance advocacy for the seller with advocacy for the customer.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Salesperson Dual Agency in Price Negotiations" and is authored by Justin Lawrence, Lisa Scheer, Andrew Crecelius, and Son Lam.
How should salespeople represent both the seller and the customer when their interests diverge, as in pricing negotiations? The research team extends a dual agency framework to the sales domain and examines the salesperson's role throughout the three stages of the discount process: (a) the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Antibiotic resistance from random DNA sequences