(Press-News.org) Pleiotropy analysis, which provides insight on how individual genes result in multiple characteristics, has become increasingly valuable as medicine continues to lean into mining genetics to inform disease treatments. Privacy stipulations, though, make it difficult to perform comprehensive pleiotropy analysis because individual patient data often can't be easily and regularly shared between sites. However, a statistical method called Sum-Share, developed at Penn Medicine, can pull summary information from many different sites to generate significant insights. In a test of the method, published in Nature Communications, Sum-Share's developers were able to detect more than 1,700 DNA-level variations that could be associated with five different cardiovascular conditions. If patient-specific information from just one site had been used, as is the norm now, only one variation would have been determined.
"Full research of pleiotropy has been difficult to accomplish because of restrictions on merging patient data from electronic health records at different sites, but we were able to figure out a method that turns summary-level data into results that are exponentially greater than what we could accomplish with individual-level data currently available," said the one of the study's senior authors, Jason Moore, PhD, director of the Institute for Biomedical Informatics and a professor of Biostatistics, Epidemiology and Informatics. "With Sum-Share, we greatly increase our abilities to unveil the genetic factors behind health conditions that range from those dealing with heart health, as was the case in this study, to mental health, with many different applications in between."
Sum-Share is powered by bio-banks that pool de-identified patient data, including genetic information, from electronic health records (EHRs) for research purposes. For their study, Moore, co-senior author Yong Chen, PhD, an associate professor of Biostatistics, lead author Ruowang Li, PhD, a post-doc fellow at Penn, and their colleagues used eMERGE to pull seven different sets of EHRs to run through Sum-Share in an attempt to detect the genetic effects between five cardiovascular-related conditions: obesity, hypothyroidism, type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and hyperlipidemia.
With Sum-Share, the researchers found 1,734 different single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs, which are differences in the building blocks of DNA) that could be tied to the five conditions. Then, using results from just one site's EHR, only one SNP was identified that could be tied to the conditions.
Additionally, they determined that their findings were identical whether they used summary-level data or individual-level data in Sum-Share, making it a "lossless" system.
To determine the effectiveness of Sum-Share, the team then compared their method's results with the previous leading method, PheWAS. This method operates best when it pulls what individual-level data has been made available from different EHRs. But when putting the two on a level playing field, allowing both to use individual-level data, Sum-Share was statistically determined to be more powerful in its findings than PheWAS. So, since Sum-Share's summary-level data findings have been determined to be as insightful as when it uses individual-level data, it appears to be the best method for determining genetic characteristics.
"This was notable because Sum-Share enables loss-less data integration, while PheWAS loses some information when integrating information from multiple sites," Li explained. "Sum-Share can also reduce the multiple hypothesis testing penalties by jointly modeling different characteristics at once."
Currently, Sum-Share is mainly designed to be used as a research tool, but there are possibilities for using its insights to improve clinical operations. And, moving forward, there is a chance to use it for some of the most pressing needs facing health care today.
"Sum-Share could be used for COVID-19 with research consortia, such as the Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR (4CE)," Yong said. "These efforts use a federated approach where the data stay local to preserve privacy."
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant number NIH LM010098).
Co-authors on the study include Rui Duan, Xinyuan Zhang, Thomas Lumley, Sarah Pendergrass, Christopher Bauer, Hakon Hakonarson, David S. Carrell, Jordan W. Smoller, Wei-Qi Wei, Robert Carroll, Digna R. Velez Edwards, Georgia Wiesner, Patrick Sleiman, Josh C. Denny, Jonathan D. Mosley, and Marylyn D. Ritchie.
A joint group of scientists from Finland, Russia, China and the USA have demonstrated that temperature difference can be used to entangle pairs of electrons in superconducting structures. The experimental discovery, published in Nature Communications, promises powerful applications in quantum devices, bringing us one step closer towards applications of the second quantum revolution.
The team, led by Professor Pertti Hakonen from Aalto University, has shown that the thermoelectric effect provides a new method for producing entangled electrons in a new device. "Quantum entanglement is the cornerstone of the novel quantum technologies. This concept, however, has puzzled many physicists over the years, including Albert Einstein who worried a lot about the ...
Reactive molecules, such as free radicals, can be produced in the body after exposure to certain environments or substances and go on to cause cell damage. Antioxidants can minimize this damage by interacting with the radicals before they affect cells.
Led by Enrique Gomez, professor of chemical engineering and materials science and engineering, Penn State researchers have applied this concept to prevent imaging damage to conducting polymers that comprise soft electronic devices, such as organic solar cells, organic transistors, bioelectronic devices and flexible electronics. The researchers ...
Jan. 8, 2021 - A new study published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society examines the recovery of lung function and overall wellness in individuals who had varying degrees of COVID-19 severity. Little is known about lung health following infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and whether later respiratory problems, fatigue and ill health are associated with the disease's initial severity.
In " END ...
Researchers from Oklahoma State University, University of Missouri, Iowa State University, and University of Georgia published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that investigates the question of how salespeople should balance advocacy for the seller with advocacy for the customer.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Salesperson Dual Agency in Price Negotiations" and is authored by Justin Lawrence, Lisa Scheer, Andrew Crecelius, and Son Lam.
How should salespeople represent both the seller and the customer when their interests diverge, as in pricing negotiations? The research team extends a dual agency framework to the sales domain and examines the salesperson's role throughout the three stages of the discount process: (a) the ...
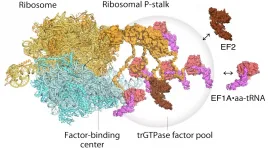
Ribosomes are the complexes of ribonucleoproteins at the heart of protein synthesis in cells. However in the absence of conclusive evidence, how these complexes operate has been open to debate. Now Hirotatsu Imai and Noriyuki Kodera at Kanazawa University, alongside Toshio Uchiumi at Niigata University in Japan, show visualizations of the structural dynamics and factor pooling that take place at ribosome stalk proteins as they build new proteins.
Ribosomes were first discovered in the 1950s and their broad function has been widely understood for some time - they read messenger RNA sequences and from that generate sequences of correctly ordered amino acids into new proteins. The ribosome stalk protein in particular plays an ...
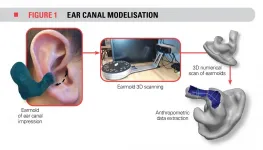
Noise exposure accounts for 22% of worldwide work-related health problems. Excessive noise not only causes hearing loss and tinnitus, but also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. To provide protection, workers normally wear earplugs. However, commonly available earplugs are often uncomfortable, since they don't fit everyone's ears equally well.
How could we improve the comfort and effectiveness of these earplugs? What aspects of the ear canal must be taken into account? To answer these questions, researchers from the École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS University) and the Institut de recherche en santé et sécurité ...
Non-violent offenders serving time for drug use or possession should be freed immediately and their convictions erased, according to research published in the peer-reviewed The American Journal of Bioethics.
More than 60 international experts including bioethicists, psychologists and drug experts have joined forces to call for an end to the war on drugs which they argue feeds racism.
All drugs currently deemed illicit - even crack cocaine and heroin - should be decriminalized as a matter of urgency, according to this new alliance. Legalisation and regulation should then follow with restrictions on age, advertising and licensing, they say.
They have analysed evidence from over 150 studies and reports, concluding that prohibition unfairly affects Black people, damages communities, ...
A new study has found that spending time outdoors and switching off our devices is associated with higher levels of happiness during a period of COVID-19 restrictions.
Previous academic studies have indicated how being outdoors, particularly in green spaces, can improve mental health by promoting more positive body image, and lowering levels of depression and anxiety.
Jointly led by academics from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in the UK, the Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences in Austria, and Perdana University in Malaysia, this new research examined how levels ...
PHILADELPHIA--Medications to treat high blood pressure did not affect outcomes among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, found an international team led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The study, published today in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, is the first randomized controlled trial to show there is no risk for patients continuing these medications while hospitalized for COVID-19.
As part of the REPLACE COVID trial, investigators examined whether ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) or Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) -- two classes of medications to treat high blood pressure -- ...
Touted by makers as a "healthy" alternative to traditional nicotine cigarettes, new research indicates the chemicals found in e-cigarettes disrupt the gut barrier and trigger inflammation in the body, potentially leading to a variety of health concerns.
In the study, published Jan. 5, 2021 in the journal END ...