(Press-News.org) The use of online messaging and social media apps among Singapore residents has spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic, a Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) study has found.
Three in four respondents (75%) said that their use of WhatsApp during the pandemic increased. This was followed by Telegram (60.3%), Facebook (60.2%) and Instagram (59.7%).
Accompanying this spike is videoconferencing fatigue, found the NTU Singapore study, which surveyed 1,606 Singapore residents from 17 to 31 December last year. Nearly one in two Singapore residents (44%) said they felt drained from videoconferencing activities, which became more frequent during the COVID-19 outbreak.
Some 86% of the respondents reported that their use of videoconferencing tools increased during the pandemic.
The increased use of online communication tools could in part be driven by feelings of isolation, said the researchers. When asked how often they felt they lacked companionship, 35% of the respondents indicated they have felt this way sometimes, while 19% felt this way often or very often. Some 32% also reported feeling left out sometimes, while 18% said they felt left out often or very often.
The nationwide online study looking at the new normal following the COVID-19 outbreak is commissioned by the Centre for Information Integrity and the Internet (IN-cube), a new research centre at NTU's Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information (WKWSCI) and conducted by a local polling company.
Associate Professor Edson C. Tandoc Jr., the Director at IN-cube, said: "The significant correlation between the use of online communication tools and feelings of isolation from the survey results may help explain why most of our respondents reported an increase in their use of online communication tools in the past few months, as they turn to these tools to feel connected to others even when physical interactions have to be limited.
"Social interaction through these online communication tools definitely brings about new challenges. Some may feel as if they are always on call at work or among their friends. Others may be uncomfortable with turning their cameras on during a video call or may not have a stable internet connection. With these difficulties and limitations in mind, we need to be mindful of our expectations of others when we are using these tools or when we ask others to use them."
Cautious optimism about the COVID-19 situation
The IN-cube survey also found that nearly two in three (63.1%) Singapore residents think that the COVID-19 situation will improve this year, with six in 10 (60.6%) looking forward to travel out of Singapore.
One in four respondents also indicated plans to make high-value purchases after the pandemic, such as buying luxury bags, cars or property.
However, this optimism about the COVID-19 situation improving comes with a tinge of caution. Some 68.7% said they would likely or very likely continue to avoid places with large public gatherings while 68.5% said they would continue to engage in social distancing even after the pandemic is over.
Face masks may also remain commonplace, as 64% said they would continue to wear face masks outdoors even after COVID-19, while 62% said they are likely or very likely to continue to work from home whenever possible, even after the pandemic.
NTU Assistant Professor Edmund Lee, Assistant Director at IN-cube, said: "The intention of Singaporeans to avoid large public gatherings - even though they believe that COVID-19 situation will improve - is a positive indication that people are still remaining vigilant as they adapt to the new normal.
"The challenge is how we can avoid becoming victims of our own success, ensuring that people do not get 'COVID-19 fatigue' and let their guard down as Singapore gradually opens up to the world."
Launched today, IN-cube aims to contribute to promoting information integrity - the creation and sharing of accurate, reliable, and relevant information - in online spaces, especially in an era of misinformation and disinformation, through timely, rigorous, and relevant research that links academics, policymakers, industry players, and the public.
Professor Joseph Liow, Dean of NTU's College of Humanities, Arts, & Social Sciences said: "In this age of fake news, understanding why people seek information, how they do it, and how they use the information is therefore important. For instance, it is important to track an increase in the use of social media and messaging apps, since these spaces are also breeding grounds for fake news. Through IN-cube, we hope to keep track of information behaviour in Singapore on a regular basis and understand their implications, such as on our well-being, and also tackle the issues that arise in a timely and relevant manner. This study by IN-cube about the new normal, looking into public sentiments, is just the first step."
Assoc Prof Tandoc, who is also from NTU WKWSCI, said: "Our collective experience of this pandemic as a community will have long-term effects on our social behaviour and interactions. This is something we are interested to find out and hope to keep track of at our new research centre, especially as health experts warn of future pandemics if we keep up with the same human activities that drive climate change and biodiversity loss. We believe that documenting long-term behavioural changes due to COVID-19 can inform policy and industry, such as how we respond as a community to accelerating shifts to online shopping and e-learning as well as to increased reliance on online tools for information."
INFORMATION:
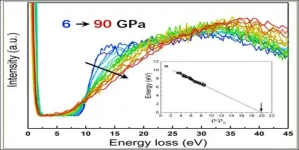
Utilizing a newly developed state-of-the-art synchrotron technique, a group of scientists led by Dr. Ho-kwang Mao, Director of HPSTAR, conducted the first-ever high-pressure study of the electronic band and gap information of solid hydrogen up to 90 GPa. Their innovative high pressure inelastic X-ray scattering result serves as a test for direct measurement of the process of hydrogen metallization and opens a possibility to resolve the electronic dispersions of dense hydrogen. This work is published in the recent issue of Physical Review Letters.
The pressure-induced evolution of hydrogen's electronic band from a wide gap insulator to a closed gap metal, or metallic ...
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted ...
The prevalence of inflammatory bowel diseases has significantly increased both in Finland and globally. These disorders cannot be entirely cured. Instead, they are treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and, at times, through surgery.
If conventional drug therapies based on anti-inflammatory drugs are ineffective, the diseases can be treated using infliximab, a biological TNF-α blocker that is administered intravenously. Infliximab is an antibody that prevents TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory factor, from binding with inflammatory cells in the intestine. It is effective in reducing inflammation and improving the patient's condition, while also controlling the disease well.
Although infliximab therapy is often effective, roughly 30-40% of patients either do not respond ...
An international research team succeeded in gaining new insights into the artificially produced superheavy element flerovium, element 114, at the accelerator facilities of the GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung in Darmstadt, Germany. Under the leadership of Lund University in Sweden and with significant participation of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) as well as the Helmholtz Institute Mainz (HIM) in Germany and other partners, flerovium was produced and investigated to determine whether it has a closed proton shell. The results suggest that, contrary to expectations, flerovium is not a so-called "magic nucleus". The results were published in ...
Two family members test positive for COVID-19 -- how do we know who infected whom? In a perfect world, network science could provide a probable answer to such questions. It could also tell archaeologists how a shard of Greek pottery came to be found in Egypt, or help evolutionary biologists understand how a long-extinct ancestor metabolized proteins.
As the world is, scientists rarely have the historical data they need to see exactly how nodes in a network became connected. But a new paper published in Physical Review Letters offers hope for reconstructing the missing information, using a new method to evaluate the rules that generate network models.
"Network models are like impressionistic ...
A new paper from UC Santa Cruz researchers, published in END ...
Overview:
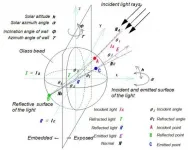
Jihui Yuan (Assistant Professor, Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology) proposed a numerical bead model to predict the upward-to-downward reflection ratio of glass bead retro-reflective (RR) material purposed for urban heat island (UHI) mitigation and reducing energy consumption. It revealed that the retro-reflectivity of glass bead RR material gradually increases from morning to noon, at which time it begins to gradually decrease. These results will contribute to existing research on the absorption or reflection of solar radiation to improve urban thermal and lighting ...
WASHINGTON--Poor social conditions caused by systemic racism contribute to health disparities in people with diabetes, according to a paper published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Minorities are disproportionately affected by diabetes because of poor social conditions that contribute to negative health outcomes such as poverty, unsafe housing, lack of access to healthy food and safe physical activity, and inadequate employment and educational opportunities. These are known as the social determinants of health and are the result of residential ...
PITTSBURGH, 26 January 2021 - A vaginal ring containing the antiretroviral drug dapivirine and the contraceptive hormone levonorgestrel delivered sustained levels of each drug when used continuously for 90 days - levels likely sufficient to serve its dual purpose for protecting against both HIV and unwanted pregnancy, according to findings of a new study.
Results of the Phase I study of the 90-day dual-purpose ring are being presented at the HIV Research for Prevention (HIVR4P) Virtual Conference, or HIVR4P // Virtual, which is taking place over the course of ...
"Shell-crushing" - exactly what it sounds like - is a predatory mode used by numerous marine life from crabs to octopuses to large fishes and mammals when they eat hard-shelled mollusks like clams, oysters and conchs. These predators have to break apart the shell using robust claws or fortified jaws to access the prey's soft tissues.
Despite its prevalence in the marine environment, this feeding behavior has remained elusive to study remotely, particularly for larger marine animals that destroy shells almost completely, leaving behind little trace. Moreover, because they are highly mobile, scientists have difficulty in directly observing their foraging habits, which is why the ecology of shell-crushing (durophagy) remains ...