(Press-News.org) 3D-printable resins, such as those used in dental applications, are marketed as biocompatible
Clear tooth aligners, a multi-billion-dollar industry, use these resins
Many other consumer products use 3D-printable resins
CHICAGO --- Two commercially available 3D-printable resins, which are marketed as being biocompatible for use in dental applications, readily leach compounds into their surroundings. These compounds can induce severe toxicity in the oocyte, the immature precursor of the egg which can eventually be fertilized, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study in mouse oocytes.
The research team made this unexpected discovery while validating the use of commercially available resins to 3D print materials to culture reproductive cells.
"Our results are important because they demonstrate leachates from commonly used materials in 3D printing slated as 'biocompatible' but may have adverse effects on reproductive health," said Francesca Duncan, co-corresponding author of the study and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. "There is a critical need to better understand the identity and biological impact of compounds that leach from these materials."
The final study was published in the journal Chemosphere on January 26.
While there have been a few previous studies investigating potential toxicities due to exposure to 3D-printed materials, there have been no studies investigating the potential reproductive toxicities induced by these materials in mammalian models.
"Despite the revelations surrounding BPA almost 20 years ago, it is still rare that the potential impact new materials may have on reproductive health are rigorously and systematically studied despite their ubiquitous nature in our day-to-day lives," Duncan said.
The clear tooth aligner market that uses resins such as Dental SG (DSG) and Dental LT (DLT) has become a multi-billion-dollar business in recent years, Duncan said, with some companies utilizing 3D-printing techniques in manufacturing due to their ability to rapidly produce products.
Duncan and colleagues characterized the leachates of the resins using mass spectroscopy and identified Tinuvin-292, a commercial light stabilizer that is commonly used in the production of plastic materials.
The results of this study potentially reach well beyond just the 3D-printing space however, Duncan said, because Tinuvin-292 is a common additive used in the production of many different types of plastic consumer products.
But even beyond dental applications, 3D-printed materials are being used more often due to recent technological advancements that make them easy to produce.
While the results of the study only provide evidence for egg toxicity of these materials in an in vitro setting, whether there are possible in vivo effects need to be further examined, scientists said. This is especially the case for DLT resins, which are intended for making oral retainers that must stay in one's mouth for long periods of time, leading to extended exposure in the body.
"The results demonstrate reproductive toxicity should be a priority when characterizing all materials humans may come into contact with either in a medical setting or in their day-to-day lives," Duncan said.
In terms of next steps, scientists plan to investigate whether in vivo exposures to DSG and DLT resins have egg toxicity similar to what occurs in vitro, examine whether there are sex differences in reproductive toxicity in response to DSG and DLT and examine the human exposure levels to Tinuvin 292.
INFORMATION:
Other Northwestern authors include Hunter B. Rogers, Luhan T. Zhou, Atsuko Kusuhara, Emily Zaniker, Saman Shafaie and Benjamin C. Owen. Co-corresponding author Teresa Woodruff, formerly of Northwestern, is now Michigan State University's provost and executive vice president for academic affairs.
The study was supported by grants UG3 ES029073 and UH3 ES029073 from the National Institutes of Health, the Gates Foundation and the Thomas J.Watkins Memorial Professorship at Northwestern University.
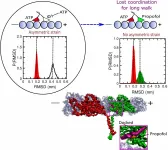
HOUSTON - (Jan. 28, 2021) - Like a wrench that gums up the gears, a common anesthetic keeps the motor proteins in your cells from making their rounds.
This is not necessarily a bad thing, but how it works has been a mystery until now.
Researchers at Rice's Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP) detail the mechanism that allows propofol -- the general anesthetic injected to knock you out before surgery -- to halt the movement of kinesin proteins that deliver cargoes along microtubules to the far reaches of cells.
The drug's effect on kinesin was known, ...
WACO, Texas (Jan. 28, 2021) - An organization that projects an ethical face but whose managers fail to respond to internal ethical situations sends mixed messages to its employees, which can lead to a lack of employees' moral courage and an increase in unethical behavior, according to a study led by a Baylor University researcher.
The study, "Management Without Morals: Construct Development and Initial Testing of Amoral Management," is published in the journal Human Relations. The research comprises three survey-based studies of 1,034 full- and part-time workers to answer the question of, "What happens when leaders do not respond to the ethical components of business situations?".
"I ...
Washington, DC — Research shows that certain segments of the population who contract SARS-CoV-2, the strain of the virus that causes COVID-19, tend to get sicker and are at higher risk for worse outcomes, and that includes pregnant women and infants under two months.
In a new study to be presented today at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine's (SMFM) annual meeting, The Pregnancy Meeting™, researchers will unveil findings that suggest that women who contract COVID-19 during pregnancy are able to make antibodies, but that transfer of these antibodies to their infants is less than expected.
Antibodies are produced by the body's immune ...
Washington, DC — Pregnant women who contract SARS-CoV-2, the strain of the virus that causes COVID-19, are at greater risk of dying and experiencing serious complications compared to nonpregnant women who contract the disease, according to a recent report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Now, in a new study to be presented today at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine's (SMFM) annual meeting, The Pregnancy Meeting™, researchers will unveil findings that suggest that pregnant women who become severely or critically ill due to COVID-19 are at greater risk of dying and experiencing serious pregnancy complications compared to pregnant women who ...
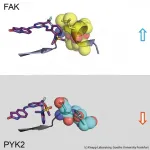
FRANKFURT. Many anti-cancer drugs block signals in cancer cells that help degenerated cells to multiply uncontrollably and detach from tissue. For example, blocking the signalling protein FAK, a so-called kinase, causes breast cancer cells to become less mobile and thus less likely to metastasise. The problem is that when FAK is blocked by an inhibitor, the closely related signalling protein PYK2 becomes much more active and thus takes over some of FAK's tasks. The ideal would therefore be an inhibitor that inhibits both FAK and PYK2 in the same way for as ...
An international team of researchers led by the Universities of Liverpool and Keele, working with Public Health England, has found that the common anticoagulant drug heparin inhibits the SARS-Cov2 virus spike protein, by reducing the virus' ability to attach to human cells and infect them.
The research, published in the journals British Journal of Pharmacology, and Thrombosis and Haemostasis, found that heparin interacts with the spike protein on the surface of coronavirus (SARS-CoV2), destabilising its structure and preventing it from docking with the ACE2 receptor on human ...
The American lobster, which supports the most valuable fishery in North America, may be more susceptible to the effects of climate change than previously thought, according to a new study published in END ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. - For Michigan State University's Felicia Wu, the surprise isn't that people who work with livestock are at higher risk of picking up antibiotic-resistant bacteria, but instead how much higher their risk levels are.
"This is a bit of a wakeup call," said Wu, John. A Hannah Distinguished Professor in the Departments of Food Science and Human Nutrition and Agricultural, Food and Resource Economics. "I don't think there was much awareness that swine workers are at such high risk, for example. Or that large animal vets are also at extremely high risk."
Compared with individuals who don't work with animals, those working on swine farms are more than 15 times more likely to harbor a particular strain of a bacterium known as methicillin-resistant ...
The increased global use of antiviral and antiretroviral medication could have a detrimental impact on crops and potentially heighten resistance to their effects, new research has suggested.
Scientists from the UK and Kenya found that lettuce plants exposed to a higher concentration of four commonly-used drugs could be more than a third smaller in biomass than those grown in a drug-free environment.
They also examined how the chemicals transferred throughout the crop and found that, in some cases, concentrations were as strong in the leaves as they were in the roots.
The study - published in Science of the Total Environment - was conducted by environmental chemists from the University of Plymouth (UK), Kisii University (Kenya) and ...
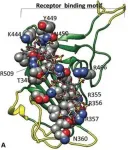
An international team of researchers has characterized the effect and molecular mechanisms of an amino acid change in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein N439K. Viruses with this mutation are both common and rapidly spreading around the globe. The peer reviewed version of the study appears January 25 in the journal Cell.
Investigators found that viruses carrying this mutation are similar to the wild-type virus in their virulence and ability to spread but can bind to the human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor more strongly. Importantly, researchers show that this mutation confers resistance to some individual's serum antibodies and against many neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, including one that is part of a treatment authorized for emergency use by the U.S. ...