New discovery sheds light on human history of symbols
A recent discovery by archeologists has uncovered evidence of what may be the earliest-known use of symbols
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) While scientists and historians have long surmised that etchings on stones and bones have been used as a form of symbolism dating back as early as the Middle Paleolithic period (250,000-45,000 BCE), findings to support that theory are extremely rare.
A recent discovery by archeologists from the Hebrew University and the University of Haifa alongside a team from the Le Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique in France have uncovered evidence of what may be the earliest-known use of symbols. The symbols were found on a bone fragment in the Ramle region in central Israel and are believed to be approximately 120,000 years old.
Remarkably the fragment remained largely intact and the researchers were able to detect six similar etchings on one side of the bone, leading them to believe that they were in the possession of something which held symbolic or spiritual significance. The find which was recently published in the scientific journal 'Quaternary International' was discovered in a trove of flint tools and animal bones exposed at a site during archaeological excavations.
Dr. Yossi Zaidner of the Institute of Archeology at Hebrew University says that the site was likely used as a camp or a meeting place for Paleolithic hunters who would then slaughter the animals they caught at that location. The identified bone is believed to have come from an extinct large wild cattle, a species which was very common in the Middle East at that time.
Using three-dimensional imaging, microscopic methods of analysis and experimental reproduction of engravings in the laboratory, the team was able to identify six different engravings ranging from 38 to 42 millimeters in length. Dr. Iris Groman-Yaroslavski from the University of Haifa explained, "Based on our laboratory analysis and discovery of microscopic elements, we were able to surmise that people in prehistoric times used a sharp tool fashioned from flint rock to make the engravings."
The paper's authors stress that their analysis makes it very clear that the engravings were definitely intentionally man made and could not have been the result of animal butchering activities or natural processes over the millennia. They pointed to the fact that the grooves of the engravings discovered are in a clear U-shape and wide and deep enough that they could not have been made by anything other than humans intent on carving lines into the bone.
The analysis was also able to determine that the work was performed by a right-handed craftsman in a single working session.
Ms. Marion Prévost from the Institute of Archeology at Hebrew University says that every indication was that there was a definite message behind what was carved into the bone. "We reject any assumption that these grooves were some sort of inadvertent doodling. That type of artwork wouldn't have seen this level of attention to detail."
So then what was the message behind the six lines in the bone? The authors write, "This engraving is very likely an example of symbolic activity and is the oldest known example of this form of messaging that was used in the Levant. We hypothesize that the choice of this particular bone was related to the status of that animal in that hunting community and is indicative of the spiritual connection that the hunters had with the animals they killed."
Dr. Zaidner said, "It is fair to say that we have discovered one of the oldest symbolic engraving ever found on earth- and certainly the oldest in the Levant. This discovery has very important implications for understanding of how symbolic expression developed in humans. At the same time, while it is still not possible to determine the exact meaning of these symbols we hope that continued research will unveil those key details."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-04
A City of Hope-led research team found that the same gene that increases the risk for Alzheimer's disease, ApoE4, can increase the susceptibility to and severity of COVID-19.
"Our study provides a causal link between the Alzheimer's disease risk factor ApoE4 and COVID-19 and explains why some (e.g., ApoE4 carriers) but not all COVID-19 patients exhibit neurological manifestations" said Yanhong Shi, Ph.D., director of the Division of Stem Cell Biology at City of Hope and co-corresponding author of the new study. "Understanding how risk factors for neurodegenerative diseases ...
2021-02-04
The distinctive gut microbiome profile of a person with liver cancer linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) could be the key to predicting someone's risk of developing the cancer, say researchers from the UNSW Microbiome Research Centre (MRC).
Their new study, published in Nature Communications recently, found the gut microbiome - the kingdom of microorganisms living in our digestive tracts - can modulate the immune response in liver cancer patients with NAFLD, in a way that promotes the cancer's survival.
While the research is still in its early stages, this finding could lead to more effective preventative and therapeutic treatments for people at risk of developing NAFLD-related liver ...
2021-02-04
The intestine harbors the largest number of immune cells in our body. Since the intestine is constantly exposed to various antigens like bacteria and food, appropriate induction of gut immune cells plays a pivotal role in gut homeostasis.
A POSTECH research team - led by Professor Seung-Woo Lee, Ph.D. candidate Sookjin Moon and research assistant professor Yunji Park of the Department of Life Sciences - has uncovered for the first the mechanism for regulating the differentiation of T cells (intraepithelial lymphocyte, IEL) via intestinal epithelial cells (IEC). These findings were recently published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine ...
2021-02-04
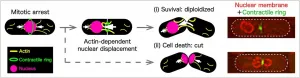
Cells replicate their genetic material and divide into two identical clones, perpetuating life -- until they don't. Some cells pause -- or are intentionally made to pause -- in the process. When the cell resumes division after such a pause, a displaced nucleus -- an essential part of cell survival -- can become caught in the fissure, splitting violently and killing both cells. But that is not always the case; some mutant cells can recover by pushing their nucleus to safety. Researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan are starting to understand how in the first step toward potential cell death rescue applications.
The results were published on Jan. 22 in iScience, a Cell Press journal.
The researchers examined fission yeast, a common model organism ...
2021-02-04
This is the finding of an 18-year-study of over 300,000 people with diabetes in England, from scientists from Imperial College London and published in the journal The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Thursday Feb 4th is World Cancer Day.
The research, funded by the Wellcome Trust, reveals that between 2001-2018 heart disease and stroke were no longer the leading causes of death among people with diabetes, as they were 18 years ago.
Diabetes affects 4.7 million people in the UK, and is caused by the body being unable to regulate blood sugar levels. Around 90 per cent have type ...
2021-02-04
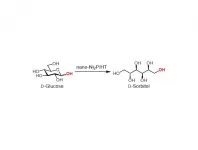
Osaka - Many different catalysts that promote the conversion of glucose to sorbitol have been studied; however, most offer certain properties while requiring compromises on others. Now, researchers from Osaka University have reported a hydrotalcite-supported nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst (nano-Ni2P/HT) that ticks all the boxes. Their findings are published in Green Chemistry.
Sorbitol is a versatile molecule that is widely used in the food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals industries. There is therefore a pressing need to produce sorbitol in a sustainable, low-cost, and green manner.
The nickel catalysts that are commonly used in the industrial hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol are unstable in air and require hash reaction conditions. Rare metal alternatives--despite being ...
2021-02-04
Remember the first rule of fight club? That's right: You don't talk about fight club. Luckily, the rules of Hollywood don't apply to science. In new published research, University of Arizona researchers report what they learned when they started their own "fight club" - an exclusive version where only insects qualify as members, with a mission to shed light on the evolution of weapons in the animal kingdom.
In many animal species, fighting is a common occurrence. Individuals may fight over food, shelter or territory, but especially common are fights between males over access to females for mating. Many of the most striking and unusual features of animals are associated with these mating-related fights, including the horns of beetles and the antlers of deer. What is less clear ...
2021-02-04
PHILADELPHA--Inflammation in the blood could serve as a new biomarker to help identify patients with advanced pancreatic cancer who won't respond to the immune-stimulating drugs known as CD40 agonists, suggests a new study from researchers in the Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania published in JCI Insight
It is known that pancreatic cancer can cause systemic inflammation, which is readily detectable in the blood. The team found that patients with systemic inflammation had worse overall survival rates than patients without inflammation when treated with both a CD40 agonist and the chemotherapy gemcitabine.
The ...
2021-02-04
This study is the first randomised control trial to rigorously test a sequential approach to treating comorbid PTSD and major depressive disorder.
Findings from a trial of 52 patients undergoing three types of treatment regime - using only Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), using Behavioural Activation Therapy (BA) with some CPT, or CPT with some BA - found that a combined treatment protocol resulted in meaningful reductions in PTSD and depression severity, with improvements maintained at six-month follow-up investigations.
"We sought to examine whether a protocol that specifically targeted both PTSD and comorbid ...
2021-02-04
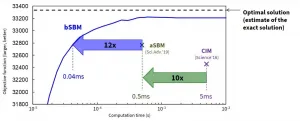
TOKYO --Toshiba Corporation (TOKYO: 6502) and Toshiba Digital Solutions Corporation (collectively Toshiba), industry leaders in solutions for large-scale optimization problems, today announced the Ballistic Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (bSB) and the Discrete Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (dSB), new algorithms that far surpass the performance of Toshiba's previous Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (SB). The new algorithms will be applied to finding solutions to highly complex problems in areas as diverse as portfolio management, drug development and logistics management. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New discovery sheds light on human history of symbols
A recent discovery by archeologists has uncovered evidence of what may be the earliest-known use of symbols