INFORMATION:
Even in same desert location, species experience differences in exposure to climate warming
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) Despite living in the same part of the Mojave Desert, and experiencing similar conditions, mammals and birds native to this region experienced fundamentally different exposures to climate warming over the last 100 years, a new study shows; small mammal communities there remained much more stable than birds, in the face of local climate change, it reports. The study presents an integrative approach to understanding the climate vulnerability of biodiversity in rapidly warming regions. Exposure to rising temperature extremes threatens species worldwide. It is expected to push many ever closer toward extinction. Thus, understanding how species respond to increased warming is crucial to predicting risks and conserving biodiversity. Predictions of climate vulnerability assume that those species within a shared environment experience similar magnitudes and rates of exposure to extreme heat and respond in similar ways. However, species are complex and exhibit a diverse array of distinct behavioral and physiological adaptive strategies to buffer against environmental change, which could translate into different exposure risks, even across co-located species. Leveraging a century-old historical dataset on species richness, animal surveys of the same locations surveyed now, and detailed ecological modeling, Eric Riddell and colleagues compared the responses of bird and small mammal communities to climate warming in the Mojave Desert. The authors found that, despite sharing a similar location and comparable physiological and ecological requirements, mammals and birds experienced fundamentally different exposures and responses to climate warming and drying over the last 100 years. While small mammal communities have remained remarkably stable in the face of change, bird occupancy and species richness have suffered dramatic declines. Riddell et al. attribute these differences to variations in each groups' ability to exploit microclimate opportunities. While small mammals can mitigate rising temperatures by burrowing into the cool earth, birds are generally far more exposed, and thus likely more vulnerable to climate warming. Modeling approaches that combine physiology and behavior are needed to more accurately predict a species' persistence in the face of climate change, suggest the authors.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Human-generated noise pollution dominates the ocean's soundscape
2021-02-04
The soundscapes of the Anthropocene ocean are fundamentally different from those of pre-industrial times, becoming more and more a raucous cacophony as the noise from human activity has grown louder and more prevalent. In a Review, Carlos Duarte and colleagues show how the rapidly changing soundscape of modern oceans impacts marine life worldwide. According to the authors, mitigating these impacts is key to achieving a healthier ocean. From the plangent songs of cetaceans to grinding arctic sea ice, the world's oceans' natural chorus is performed by a vast ensemble of geological (geophony) and biological (biophony) sounds. However, for more than a century, ...
Special Issue: Human genome at 20
2021-02-04
In February 2001, the first drafts of the human genome were published. In this Special Issue of Science, "Human Genome at 20," an Editorial, a Policy Forum, a series of NextGen Voices Letters and a Perspective explore the complicated legacy of the Human Genome Project (HGP). "Millions of people today have access to their personal genomic information, with direct-to-consumer services and integration with other 'big-data' increasingly commoditizing what was rightly celebrated as a singular achievement in February 2001," writes Science Senior Editor Brad Wible.
An Editorial by Claire Frasier, director of the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University ...
Iodine oxoacids drive rapid aerosol formation in pristine atmospheric areas
2021-02-04
Iodine plays a bigger role than thought in rapid new particle formation (NPF) in relatively pristine regions of the atmosphere, such as along marine coasts, in the Arctic boundary layer or in the upper free troposphere, according to a new study. The authors say their measurements indicate that iodine oxoacid particle formation can compete with sulfuric acid - another vapor that can form new particles under atmospheric conditions - in pristine atmospheric regions. Tiny particles suspended high in the atmosphere - aerosols - play an essential role in Earth's climate system. Clouds require airborne particles, or cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), ...
Fecal microbiota transplants help patients with advanced melanoma respond to immunotherapy
2021-02-04
For patients with cancers that do not respond to immunotherapy drugs, adjusting the composition of microorganisms in the intestines--known as the gut microbiome--through the use of stool, or fecal, transplants may help some of these individuals respond to the immunotherapy drugs, a new study suggests. Researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Center for Cancer Research, part of the National Institutes of Health, conducted the study in collaboration with investigators from UPMC Hillman Cancer Center at the University of Pittsburgh.
In the study, some patients with advanced melanoma who initially did not respond to treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor, a type of immunotherapy, did respond to the drug after receiving a transplant ...
Some sperms poison their competitors
2021-02-04
Competition among sperm cells is fierce - they all want to reach the egg cell first to fertilize it. A research team from Berlin now shows in mice that the ability of sperm to move progressively depends on the protein RAC1. Optimal amounts of active protein improve the competitiveness of individual sperm, whereas aberrant activity can cause male infertility.
It is literally a race for life when millions of sperm swim towards the egg cells to fertilize them. But does pure luck decide which sperm succeeds? As it turns out, there are differences in competitiveness between individual sperm. ...
In a desert seared by climate change, burrowers fare better than birds
2021-02-04
Berkeley -- In the arid Mojave Desert, small burrowing mammals like the cactus mouse, the kangaroo rat and the white-tailed antelope squirrel are weathering the hotter, drier conditions triggered by climate change much better than their winged counterparts, finds a new study published today in Science.
Over the past century, climate change has continuously nudged the Mojave's searing summer temperatures ever higher, and the blazing heat has taken its toll on the desert's birds. Researchers have documented a collapse in the region's bird populations, likely resulting ...
Human immune cells have natural alarm system against HIV
2021-02-04
Treatment for HIV has improved tremendously over the past 30 years; once a death sentence, the disease is now a manageable lifelong condition in many parts of the world. Life expectancy is about the same as that of individuals without HIV, though patients must adhere to a strict regimen of daily antiretroviral therapy, or the virus will come out of hiding and reactivate. Antiretroviral therapy prevents existing virus from replicating, but it can't eliminate the infection. Many ongoing clinical trials are investigating possible ways to clear HIV infection.
In a study published Feb. 4 in the journal Science, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a potential way to eradicate ...
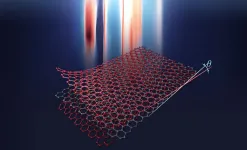
Harvard scientists use trilayer graphene to observe more robust superconductivity
2021-02-04
In 2018, the physics world was set ablaze with the discovery that when an ultrathin layer of carbon, called graphene, is stacked and twisted to a "magic angle," that new double layered structure converts into a superconductor, allowing electricity to flow without resistance or energy waste. Now, in a literal twist, Harvard scientists have expanded on that superconducting system by adding a third layer and rotating it, opening the door for continued advancements in graphene-based superconductivity.
The work is described in a new paper in Science and can one day help lead toward superconductors that operate at higher or even close to room temperature. These superconductors are considered the holy grail of condensed matter physics ...
Food allergies are more common among Black children
2021-02-04
Black children have significantly higher rates of shellfish and fish allergies than White children, in addition to having higher odds of wheat allergy, suggesting that race may play an important role in how children are affected by food allergies, researchers at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, Rush University Medical Center and two other hospitals have found.
Results of the study were published in the February issue of the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
"Food allergy is a common condition in the U.S., and we know from our previous research that there are important differences between Black and White children with food allergy, but there is so much we need to know to be able to help our patients ...
Pharmacologist offers plan to solve disparities in designing medicine
2021-02-04
In a new perspective piece published in the Feb. 5 issue of Science, pharmacologist Namandje Bumpus, Ph.D. -- who recently became the first African American woman to head a Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine department, and is the only African American woman leading a pharmacology department in the country -- outlines the molecular origins for differences in how well certain drugs work among distinct populations. She also lays out a four-part plan to improve the equity of drug development.
"Human beings are more similar than we are different," says Bumpus. "Yet, the slightest variations in our genetic material ...