(Press-News.org) New research affirms a unique peptide found in an Australian plant can destroy the No. 1 killer of citrus trees worldwide and help prevent infection.
Huanglongbing, HLB, or citrus greening has multiple names, but one ultimate result: bitter and worthless citrus fruits. It has wiped out citrus orchards across the globe, causing billions in annual production losses.
All commercially important citrus varieties are susceptible to it, and there is no effective tool to treat HLB-positive trees, or to prevent new infections.
However, new UC Riverside research shows that a naturally occurring peptide found in HLB-tolerant citrus relatives, such as Australian finger lime, can not only kill the bacteria that causes the disease, it can also activate the plant's own immune system to inhibit new HLB infection. Few treatments can do both.
Research demonstrating the effectiveness of the peptide in greenhouse experiments has just been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The disease is caused by a bacterium called CLas that is transmitted to trees by a flying insect. One of the most effective ways to treat it may be through the use of this antimicrobial peptide found in Australian finger lime, a fruit that is a close relative of citrus plants.
"The peptide's corkscrew-like helix structure can quickly puncture the bacterium, causing it to leak fluid and die within half an hour, much faster than antibiotics," explained Hailing Jin, the UCR geneticist who led the research.
When the research team injected the peptide into plants already sick with HLB, the plants survived and grew healthy new shoots. Infected plants that went untreated became sicker and some eventually died.
"The treated trees had very low bacteria counts, and one had no detectable bacteria anymore," Jin said. "This shows the peptide can rescue infected plants, which is important as so many trees are already positive."
The team also tested applying the peptide by spraying it. For this experiment, researchers took healthy sweet orange trees and infected them with HLB-positive citrus psyllids -- the insect that transmits CLas.
After spraying at regular intervals, only three of 10 treated trees tested positive for the disease, and none of them died. By comparison, nine of 10 untreated trees became positive, and four of them died.
In addition to its efficacy against the bacterium, the stable anti-microbial peptide, or SAMP, offers a number of benefits over current control methods. For one, as the name implies, it remains stable and active even when used in 130-degree heat, unlike most antibiotic sprays that are heat sensitive -- an important attribute for citrus orchards in hot climates like Florida and parts of California.
In addition, the peptide is much safer for the environment than other synthetic treatments. "Because it's in the finger lime fruit, people have eaten this peptide for hundreds of years," Jin said.
Researchers also identified that one half of the peptide's helix structure is responsible for most of its antimicrobial activity. Since it is only necessary to synthesize half the peptide, this is likely to reduce the cost of large-scale manufacturing.
The SAMP technology has already been licensed by Invaio Sciences, whose proprietary injection technology will further enhance the treatment.
Following the successful greenhouse experiments, the researchers have started field tests of the peptides in Florida. They are also studying whether the peptide can inhibit diseases caused by the same family of bacteria that affect other crops, such as potato and tomato.
"The potential for this discovery to solve such devastating problems with our food supply is extremely exciting," Jin said.
INFORMATION:
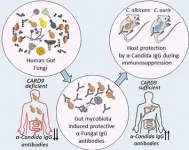
Common fungi, often present in the gut, teach the immune system how to respond to their more dangerous relatives, according to new research from scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine. Breakdowns in this process can leave people susceptible to deadly fungal infections.
The study, published Feb. 5 in Cell, reveals a new twist in the complex relationship between humans and their associated microbes, and points the way toward novel therapies that could help combat a rising tide of drug-resistant pathogens.
The new discovery stemmed from work on inflammatory bowel disease, which often causes patients to carry larger than normal populations of fungi in their guts. ...
To arrive at Nunavut, turn left at the Dakotas and head north. You can't miss it--the vast tundra territory covers almost a million square miles of northern Canada. Relatively few people call this lake-scattered landscape home, but the region plays a crucial role in understanding global climate change. New research from Soren Brothers, assistant professor in the Department of Watershed Sciences and Ecology Center, details how lakes in Nunavut could have a big impact on carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, and it's not all bad news--at least for now. Brothers examined 23 years of data from lakes near Rankin Inlet. He noted a peculiarity--as the lakes warmed, their carbon dioxide concentrations fell. ...
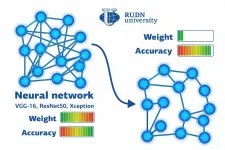
A team of mathematicians from RUDN University found a way to reduce the size of a trained neural network six times without spending additional resources on re-training it. The approach is based on finding a correlation between the weights of neural connections in the initial system and its simplified version. The results of the work were published in the Optical Memory and Neural Networks journal.
The structures of artificial neural networks and neurons in a living organism are based on the same principles. Nodes in a network are interconnected; some of them receive a signal, and some transmit it by activating or suppressing the next element in the chain. The processing of any signal (for ...
The discovery of an "Achilles heel" in a type of gut bacteria that causes intestinal inflammation in patients with Crohn's disease may lead to more targeted therapies for the difficult to treat disease, according to Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators.
In a study published Feb. 3 in Cell Host and Microbe, the investigators showed that patients with Crohn's disease have an overabundance of a type of gut bacteria called adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC), which promotes inflammation in the intestine. Their experiments revealed ...
Progressive vision loss, and eventually blindness, are the hallmarks of juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (JNCL) or CLN3-Batten disease. New research shows how the mutation associated with the disease could potentially lead to degeneration of light sensing photoreceptor cells in the retina, and subsequent vision loss.
"The prominence and early onset of retinal degeneration in JNCL makes it likely that cellular processes that are compromised in JNCL are critical for health and function of the retina," said Ruchira Signh, Ph.D., an associate professor in the Department of Ophthalmology and Center for Visual Science and lead author of the study which appears in the journal Communications Biology. "It is important to understand how vision loss is triggered in this disease, ...
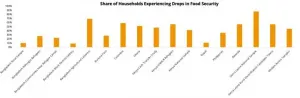
Washington, D.C.. -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sharp decline in living standards and rising food insecurity in developing countries across the globe, according to a new study by an international team of economists.
The study, published Feb. 5 in the journal Science Advances, provides an in-depth view of the health crisis's initial socioeconomic effects in low- and middle-income countries, using detailed micro data collected from tens of thousands of households across nine countries. The phone surveys were conducted from April through July 2020 of nationally and sub-nationally representative samples in Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Colombia, Ghana, Kenya, Nepal, Philippines, Rwanda, and Sierra Leone. Across the board, study ...
The largest single cell study to date of the childhood cancer, neuroblastoma, has answered important questions about the genesis of the disease. The researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) and the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology, discovered that all neuroblastomas arise from a single type of embryonic cell called sympathoblasts.
The study, published today (5 February 2021) in Science Advances, sought to understand why neuroblastomas range in severity, with some easy to treat and others having relatively low five-year survival rates. The fact that all neuroblastomas arise from sympathoblasts makes them an attractive ...
Berkeley -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic last year led to a devastating loss of jobs and income across the global south, threatening hundreds of millions of people with hunger and lost savings and raising an array of risks for children, according to new research co-authored at the University of California, Berkeley.
The research, to be published Friday Feb. 5, 2021, in the journal Science Advances, found "staggering" income losses after the pandemic emerged last year, with a median 70% of households across nine countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America reporting financial losses. By April last year, roughly 50% ...
Scientists led by Eliza Harris and Michael Bahn from the Institute of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck have succeeded in studying emissions of the greenhouse gas N2O under the influence of environmental impacts in an unprecedented level of detail. The study, which has now been published in Science Advances, is thus also a starting point for the creation of models that could predict future trends in the greenhouse gas emission dynamics of ecosystems under global climate change.
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas whose atmospheric growth rate has accelerated over the past decade. The largest share of anthropogenic N2O emissions results from the fertilization of soils with nitrogen, which is converted into N2O via various abiotic ...
Genes that determine the shape of a person's facial profile have been discovered by a UCL-led research team.
The researchers identified 32 gene regions that influenced facial features such as nose, lip, jaw, and brow shape, nine of which were entirely new discoveries while the others validated genes with prior limited evidence.
The analysis of data from more than 6,000 volunteers across Latin America was published today in Science Advances.
The international research team, led from UCL, Aix-Marseille University and The Open University, found that one of the genes appears ...