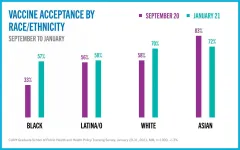(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A new study finds that providing people who have recently given birth access to long-acting reversible methods of contraception, such as intrauterine devices and contraceptive implants, could help prevent them from unintentionally falling pregnant in the following months.
The study -- which analyzed the effects of a 2012 Medicaid policy implemented in South Carolina -- found that expanded access to particular forms of birth control were especially helpful in preventing unintended pregnancies among adolescents who had just given birth, giving them more control over their own futures.
"The ability to control whether and when you become pregnant is a basic human right, since pregnancy and childbirth have enormous implications for social and economic life trajectories," said Maria Steenland, an assistant professor of population studies (research) at Brown University who is affiliated with the Population Studies and Training Center.
Steenland conducted the study, published on Friday, Feb. 5, in Health Affairs, along with three colleagues at Harvard University's medical and public health schools.
Steenland said that in 2012, South Carolina's Medicaid program became the first in the United States to reimburse hospitals for the provision of immediate postpartum long-acting reversible contraception (LARC). LARCs, which prevent pregnancy for extended periods of time without any effort on the patient's part, include intrauterine devices, arm implants and hormonal injections.
Before the state enacted the policy, she said, patients who had just given birth and wanted immediate postpartum contraception had few options; LARCs were only available if they were willing to come back to the hospital for a separate outpatient procedure, and birth control pills are not considered medically safe to use early in the postpartum period. As a result, 59% chose to use no highly or moderately effective method of contraception; 22% chose a short-acting method, such as spermicide; and 13% chose sterilization, which is irreversible.
To examine the impact of the new policy, the study analyzed data on more than 150,000 Medicaid-insured South Carolina women between ages 12 and 50 who gave birth from 2010 to 2014. They found that in the medical facilities that began to offer LARCs after the policy change, use of highly effective contraception among postpartum patients shot up among adolescents, who are particularly vulnerable to closely spaced, higher-risk repeat pregnancies. Among Medicaid patients age 12 to 19, the rate of immediate postpartum LARC use increased by more than 6 percentage points between March 2012 and November 2014. Across all age groups, the total percentage of Medicaid patients who opted for postpartum LARCs nearly quadrupled in two and a half years. In some facilities, medical workers were providing LARCs to up to 20% of all postpartum patients.
"Contraceptive choice is based on many factors, such as side effects, reversibility and effectiveness," Steenland said. "Our study shows that making these new contraceptive methods available can make it easier for patients to find a method that meets their needs and preferences, and ultimately it can give them more agency in deciding whether and when to become pregnant again."
Less encouraging, Steenland said, was the researchers' discovery that as of 2014, fewer than half of South Carolina facilities had begun to offer immediate postpartum LARCs to patients, despite the policy change.
"We found that few hospitals began offering immediate postpartum LARCs after the policy change, indicating that Medicaid reimbursement is only a first step to making these options available," she said.
Steenland and her coauthors recommended that facilities and the state Medicaid program take further policy steps to make long-acting contraception more widely available -- especially given that many studies, including one of their own, show that when LARCs are available and free, more patients opt to use them and rates of unintended pregnancy decrease.
INFORMATION:
The work was funded in part by a grant from the population dynamics branch of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (R03HD099428). Steenland was supported by the National Institutes of Health (training grant #T32 HD007338) and by other NIH support (grant #P2C HD041020). The Eric M. Mindich Research Fund for the Foundations of Human Behavior provided funding to acquire the data used in this study.
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Feb. 9, 2021) -- Scientists have devised a new approach for detecting and potentially heading off the effects of two rare pediatric diseases before birth.
The study, performed in mouse models of the diseases and published today in Cell Reports, represents an important step toward much-needed early interventions for Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome.
Both diseases result in growth-related symptoms in children and often lead to additional problems later in life, such as increased cancer risk from Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome ...
The research team of NUST MISIS has presented an improved structure of perovskite solar cells. Scientists have modified perovskite-based solar cells using MXenes -- thin two-dimensional titanium carbides with high electrical conductivity. The MXenes-based modified cells showed superior performance, with power conversion efficiency exceeding 19% (the reference demonstrated 17%) and improved stabilized power output with respect to reference devices. The results have been published in the Nano energy international scientific journal.
Perovskite solar cells ...
Women whose household drinking water contained nitrate had babies that weighed, on average, 10 grams less than babies born to mothers where household water had no detectible nitrate, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago and Aarhus University.
The study, which is published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, followed pregnant women living in Denmark. The researchers found that even low nitrate levels -- about half of the allowable level set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, or EPA -- caused an adverse effect.
"While ...
Under the Biden Administration, New Yorkers' acceptance of the Covid-19 vaccine has increased significantly. In September, 55% of residents reported they would take the vaccine when it became available and this January, 64% reported they would take it.
Differences in vaccine acceptance persist across racial and ethnic groups. Among Whites and Asians acceptance is 70-72%; among Blacks and Latina/os it is 57-58%. On a positive note, the largest increase in rate of acceptance was seen among Black respondents, up from 33% in September to 57% in January.
These are key findings from the most recent tracking survey of public perceptions and experiences in New York City during the Covid-19 pandemic, conducted January 29-31 by the City University of New York Graduate School of ...
The colors in a flower patch appear completely different to a bear, a honeybee, a butterfly and humans. The ability to see these colors is generated by specific properties of opsins - light-sensitive proteins in the retina of our eyes. The number of opsins expressed and the molecular structure of the receptor proteins determines the colors we see.
In a paper published February 9 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences a team of researchers led by Harvard University develop a novel method to express long wavelength invertebrate opsin proteins in vitro and detail the molecular structure of redshift (long-wavelength) ...
In 2018, a faulty electric transmission line ignited the Camp Fire in Northern California, ultimately consuming 239 square miles and several communities, including the town of Paradise, which was 95 percent destroyed. At least 85 people died.
Structures have been rebuilt, but some things are worse. In a paper published February 2, 2021 in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, scientists at University of California San Diego, with colleagues elsewhere, describe chronic mental health problems among some residents who experienced the Camp Fire in varying degrees.
Direct exposure to large-scale fires significantly ...
Photoionization of water involves the migration and solvation of electrons, with many transient and highly active intermediates. The process results in a large blue shift in the absorption spectrum, from the THz or gigahertz region to the visible range. While the behavior of low-density quasifree electrons excited by small pump power density has been investigated extensively, we still know little about the transient evolution of photoexcited plasma in liquid water. Valuable insights were recently provided by an international research team in a study published in Advanced Photonics.
According to Liangliang Zhang, physics professor at Capital Normal University in Beijing and one of the senior authors on the study, the physical mechanism of plasma evolution on the ...
The structure of organic substances tetrahydroisoquinolines (THIQ) includes a benzene ring fused with a nitrogen-containing cycle. These compounds are in high demand in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of myorelaxants, antidepressants, and drugs against hypertension, cough, and insomnia. Although different variations of THIQ structures can be found in natural sources (for example, as parts of phytotoxins), modern-day pharmaceutical manufacturers are also interested in their rare types, such as spirocyclic THIQs. In their molecules, two adjacent cycles share one common atom, thus creating an unusual and very stable 3D structure. This feature ...
The development of the so-called small molecules is a promising field of the pharmaceutical industry. Small molecules are organic compounds with a small molecular mass. They are often based on heterocycles--carbon rings that also include atoms of nitrogen and other elements. The synthesis of small molecules is much cheaper than the development of drugs based on antibodies or other biological molecules; however, their properties are still understudied. Even the slightest modifications can change the characteristics of a small molecule and open a whole new range of its practical applications. Therefore, many research teams working in the field of chemical pharmacology improve synthesis methods to create libraries of ...
The COVID-19 pandemic that shuttered cities around the world did not just affect the way we work, study and socialize. It also affected our mobility. With millions of workers no longer commuting, vehicle traffic across Canada has plummeted. This has had a significant impact on the quality of air in major Canadian cities, according to a new study by Concordia researchers.
A paper published in the journal Science of the Total Environment looked at downtown air quality monitoring station data from Vancouver, Edmonton, Saskatoon, Winnipeg, Toronto, Montreal, Halifax ...