How the 3-D structure of eye-lens proteins is formed
Researchers from Frankfurt and Grenoble observe disulphide bridge formation in gamma-B crystalline for the first time in the ribosomal exit tunnel
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) FRANKFURT. The lens of the human eye gets its transparency and refractive power from the fact that certain proteins are densely packed in its cells. These are mainly crystallines. If this dense packing cannot be maintained, for example due to hereditary changes in the crystallines, the result is lens opacities, known as cataracts, which are the most common cause of vision loss worldwide.
In order for crystallins to be packed tightly in lens fibre cells, they must be folded stably and correctly. Protein folding already begins during the biosynthesis of proteins in the ribosomes, which are large protein complexes. Ribosomes help translate the genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. In the process, ribosomes form a protective tunnel around the new amino acid chain, which takes on three-dimensional structures with different elements such as helices or folded structures immediately after the tunnel's formation. The gamma-B crystallines studied in Frankfurt and Grenoble also exhibit many bonds between two sulphur-containing amino acids, so-called disulphide bridges.
The production of these disulphide bridges is not easy for the cell, since biochemical conditions prevail in the cell environment that prevent or dissolve such disulphide bridges. In the finished gamma-B crystalline protein, the disulphide bridges are therefore shielded from the outside by other parts of the protein. However, as long as the protein is in the process of formation, this is not yet possible.
But because the ribosomal tunnel was considered too narrow, it was assumed - also on the basis of other studies - that the disulphide bridges of the gamma-B crystallins are formed only after the proteins have been completed. To test this assumption, the researchers from Frankfurt and Grenoble used genetically modified bacterial cells as a model system, stopped the synthesis of the gamma-B crystallins at different points in time and examined the intermediate products with mass spectrometric, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic and electron microscopic methods, and supplemented these with theoretical simulation calculations. The result: The disulphide bridges are already formed on the not yet finished protein during the synthesis of the amino acid chain.
"We were thus able to show that disulphide bridges can already form in the ribosomal tunnel, which offers sufficient space for this and shields the disulphide bridges from the cellular milieu," says Prof. Harald Schwalbe from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Goethe University. "Surprisingly, however, these are not the same disulphide bridges that are later present in the finished gamma-B crystallin. We conclude that at least some of the disulphide bridges are later dissolved again and linked differently. The reason for this probably lies in the optimal timing of protein production: the 'preliminary' disulphide bridges accelerate the formation of the 'final' disulphide bridges when the gamma-B crystallin is released from the ribosome."
In further studies, the researchers now want to test whether the synthesis processes in the slightly different ribosomes of higher cells are similar to those in the bacterial model system.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
Seismic monitoring devices linked to the internet are vulnerable to cyberattacks that could disrupt data collection and processing, say researchers who have probed the devices for weak points.
Common security issues such as non-encrypted data, insecure protocols, and poor user authentication mechanisms are among the biggest culprits that leave seismological networks open to security breaches, Michael Samios of the National Observatory of Athens and colleagues write in a new study published in Seismological Research Letters.
Modern seismic stations are now implemented as an Internet-of-Things (IoT) station, with physical devices that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet. In their test attacks ...
2021-02-10
Human language can be inefficient. Some words are vital. Others, expendable.
Reread the first sentence of this story. Just two words, "language" and "inefficient," convey almost the entire meaning of the sentence. The importance of key words underlies a popular new tool for natural language processing (NLP) by computers: the attention mechanism. When coded into a broader NLP algorithm, the attention mechanism homes in on key words rather than treating every word with equal importance. That yields better results in NLP tasks like detecting positive or negative sentiment or predicting which words should come next in a sentence.
The attention mechanism's ...
2021-02-10
(Philadelphia, PA) - While the COVID-19 pandemic brought most of the country to a standstill in March 2020, Philadelphia trauma surgeons noticed an alarming trend in the incidence of firearm violence. Instead of decreasing with containment measures, firearm-injured patients were presenting at even higher rates to Temple University Hospital and other trauma centers around the city.
A team led by Jessica H. Beard, MD, MPH, FACS, Assistant Professor of Surgery and Director of Trauma Research at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University (LKSOM), sought to determine the magnitude of Philadelphia's increase in firearm violence during the COVID-19 pandemic. They also aimed to understand potential causes ...
2021-02-10
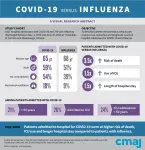
A new study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) found that the risk of death from COVID-19 was 3.5 times higher than from influenza.
"We can now say definitively that COVID-19 is much more severe than seasonal influenza," says Dr. Amol Verma, St. Michael's Hospital, Unity Health Toronto, and the University of Toronto. "Patients admitted to hospital in Ontario with COVID-19 had a 3.5 times greater risk of death, 1.5 times greater use of the ICU, and 1.5 times longer hospital stays than patients admitted with influenza."
These ...
2021-02-10
Dramatic decreases in traffic caused by COVID-19 shutdowns improved air quality in car-dependent states but didn't offset additional forms of pollution in other parts of the country.
Those findings by a University of South Florida researcher suggest that while decreasing the number of vehicles on the road is a good first step toward creating cleaner air, additional measures aimed at reducing other sources of air pollution, such as coal plants or industrial factories, must also be considered.
The study, led by Yasin Elshorbany, an assistant professor of atmospheric chemistry and climate change at USF's St. Petersburg campus, was published ...
2021-02-10
CLEVELAND--A team of Case Western Reserve University researchers has found a way to measure key characteristics of proteins that bind to RNA in cells--a discovery that could improve our understanding of how gene function is disturbed in cancer, neurodegenerative disorders or infections.
RNA--short for ribonucleic acid--carries genetic instructions within the body. RNA-binding proteins play an important role in the regulation of gene expression. Scientists already knew that the way these proteins function depends on their "binding kinetics," a term that describes how frequently they latch on to a site in an RNA, and how long they ...
2021-02-10
A team of researchers, led by a Texas A&M University professor, has found that some energy drinks have adverse effects on the muscle cells of the heart.
The study, led by Dr. Ivan Rusyn, a professor in the Veterinary Integrative Biosciences (VIBS) Department at the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences (CVMBS), was published in Food and Chemical Toxicology. In it, researchers observed cardiomyocytes - human heart cells grown in a laboratory - exposed to some energy drinks showed an increased beat rate and other factors affecting cardiac function.
When placed in the context of the human body, ...
2021-02-10
A team at the University of Colorado Boulder has designed new kinds of liquid crystals that mirror the complex structures of some solid crystals--a major step forward in building flowing materials that can match the colorful diversity of forms seen in minerals and gems, from lazulite to topaz.
The group's findings, published today in the journal Nature, may one day lead to new types of smart windows and television or computer displays that can bend and control light like never before.
The results come down to a property of solid crystals that will be familiar to many chemists and gemologists: Symmetry.
Ivan Smalyukh, ...
2021-02-10
Israelis across the political spectrum prefer the status quo to the two-state solution, and Palestinians are only willing to accept a two-state solution that Israelis will be unable to accept, according to a new RAND Corporation report that assesses whether there are any alternative solutions to the conflict that average Israelis and Palestinians would support.
Derived from a series of innovative, structured focus group discussions, the report suggests that the Biden Administration's recent reaffirmation of U.S. policy to support a "mutually agreed two-state solution, one in which Israel lives in peace ...
2021-02-10
The number of people who own electric vehicles (EVs) is increasing, but they face a conundrum: Unlike those who own gasoline-burning cars, EV owners can't just pop down to the corner gas station for a fill-up. Particularly in rural areas, charging stations can be few and far between.
Joshua Pearce, Richard Witte Endowed Professor of Materials Science and Engineering and professor of electrical and computer engineering at Michigan Technological University, hopes to change that.
In a model outlined in a paper in the journal Renewable Energy, Pearce and his co-author, graduate student Swaraj Sanjay Deshmukh, note the untapped potential of retail parking lot solar photovoltaic awnings.
The study investigates the energy-related benefits ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How the 3-D structure of eye-lens proteins is formed
Researchers from Frankfurt and Grenoble observe disulphide bridge formation in gamma-B crystalline for the first time in the ribosomal exit tunnel