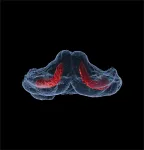
Tropical paper wasps babysit for neighbours
2021-02-15
(Press-News.org) [Images and video available: see notes to editors]
Wasps provide crucial support to their extended families by babysitting at neighbouring nests, according to new research by a team of biologists from the universities of Bristol, Exeter and UCL published today [15 February] in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
The findings suggest that animals should often seek to help more distant relatives if their closest kin are less in need.
Dr Patrick Kennedy, lead author and Marie Curie research fellow in the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Bristol, said: "These wasps can act like rich family members lending a hand to their second cousins. If there's not much more you can do to help your immediate family, you can turn your attention to the extended family."
By closely observing twenty thousand baby wasps and their carers on colonies around the Panama Canal, the research team could determine the usefulness of workers on colonies of different sizes. They showed that workers become less useful as the number of colony members rises, due to a surplus of help.
Andy Radford, Professor of Behavioural Ecology, also from Bristol and co-author, explained: "By helping more distant relatives who are more in need--those living next door with fewer carers--workers can pass on more copies of their genes overall. We believe that similar principles of diminishing returns might explain seemingly paradoxical acts of altruism in many other social animals."
Dr Kennedy added: "The fact that these paper wasps in Central and South America help at other colonies is really bizarre when you consider that most wasps, ants and bees are extremely hostile to outsiders. To solve this puzzling behaviour, we combined mathematical modelling with our detailed field observations."
Dr Kennedy continued: "We ended up being stung a lot. But it was worth it, because our results show that worker wasps can become redundant at home. A wasp on a colony with few larvae but lots of other workers becomes almost useless: the best thing to do is to babysit the larvae of other relatives."
Since Darwin, biologists have been trying to understand how 'altruism' evolves in animals. At first glance, acts of selflessness to help other individuals do not seem to allow individuals to pass on their genes.
Professor Radford said: "In 1964, the legendary biologist W. D. Hamilton figured out the cardinal rule of animal altruism. Lavish help on your family because they share many of your genes. Copies of your genes will triumph in the population."
But the tropical paper wasps studied by the team baffled Hamilton back in 1964. In Brazil, he was surprised to notice that Polistes wasps were leaving their close family on their home nests and flying off to help the neighbours, who are less closely related.
Previous work by co-author Seirian '@WaspWoman' Sumner, Professor of Behavioural Ecology at University College London, showed that over half the workers in a Panamanian population were helping on multiple nests. Wasps usually viciously attack outsiders, so this babysitting suggested something unusual was going on.
Professor Sumner explained: "Wasps offer amazing windows into the evolution of selflessness. There is so much going on in a wasp nest: power struggles, self-sacrifice, groups battling against the odds to survive... If we want to understand how societies evolve, we should look more deeply at wasps."
INFORMATION:
This fieldwork was supported by the National Geographic Society and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Panama.
Paper
'Diminishing returns drive altruists to help extended family' by P. Kennedy, S. Sumner?, P. Botha, N. J. Welton, A. D. Higginson and A. N. Radford in Nature Ecology and Evolution
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-15
Feathers are a sleek, intricate evolutionary innovation that makes flight possible for birds, but in addition to their stiff, aerodynamic feathers used for flight, birds also keep a layer of soft, fluffy down feathers between their bodies and their outermost feathers to regulate body temperature.
Using the Smithsonian's collection of 625,000 bird specimens, Sahas Barve, a Peter Buck Fellow at the Smithsonian's National Museum of Natural History, led a new study to examine feathers across 249 species of Himalayan songbirds, finding that birds living at higher elevations have more of the fluffy down--the type of feathers humans stuff their jackets with--than birds from lower elevations. Published ...
2021-02-15
Ciliopathies are genetic disorders caused by defects in the structure and function of cilia, microtubule-based organelles present on the surface of almost every cell in the human body which play crucial roles in cell signalling. Ciliopathies present a wide range of often severe clinical symptoms, frequently affecting the head and face and leading to conditions such as cleft palate and micrognathia (an underdeveloped lower jaw that can impair feeding and breathing). While we understand many of the genetic causes of human ciliopathies, they are only half the story: the question remains as to why, at a cellular level, defective cilia cause developmental craniofacial abnormalities. Researchers have now discovered that ciliopathic micrognathia in an animal model results from abnormal skeletal ...
2021-02-15
Years of suffering and billions of euro in global health care costs, arising from osteoporosis-related bone fractures, could be eliminated using big data to target vulnerable patients, according to researchers at Lero, the Science Foundation Ireland Research Centre for Software.
A study of 36,590 patients who underwent bone mineral density scans in the West of Ireland between January 2000 and November 2018, found that many fractures are potentially preventable by identifying those at greatest risk before they fracture, and initiating proven, safe, low-cost effective interventions.
The multi-disciplinary study, ...
2021-02-15
Long held in a private collection, the newly analysed tooth of an approximately 9-year-old Neanderthal child marks the hominin's southernmost known range. Analysis of the associated archaeological assemblage suggests Neanderthals used Nubian Levallois technology, previously thought to be restricted to Homo sapiens.
With a high concentration of cave sites harbouring evidence of past populations and their behaviour, the Levant is a major centre for human origins research. For over a century, archaeological excavations in the Levant have produced human ...
2021-02-15
A recent study finds that the invasive spotted wing drosophila (Drosophila suzukii) prefers to lay its eggs in places that no other spotted wing flies have visited. The finding raises questions about how the flies can tell whether a piece of fruit is virgin territory - and what that might mean for pest control.
D. suzukii is a fruit fly that is native to east Asia, but has spread rapidly across North America, South America, Africa and Europe over the past 10-15 years. The pest species prefers to lay its eggs in ripe fruit, which poses problems for fruit growers, since consumers don't want to buy infested fruit.
To avoid consumer rejection, there are extensive measures in place to avoid infestation, and to prevent infested ...
2021-02-15
Aalto researchers have used an IBM quantum computer to explore an overlooked area of physics, and have challenged 100 year old cherished notions about information at the quantum level.
The rules of quantum physics - which govern how very small things behave - use mathematical operators called Hermitian Hamiltonians. Hermitian operators have underpinned quantum physics for nearly 100 years but recently, theorists have realized that it is possible to extend its fundamental equations to making use of Hermitian operators that are not Hermitian. The new equations describe a universe with its own peculiar set of rules: for example, by looking in the ...
2021-02-15
It was tens of miles wide and forever changed history when it crashed into Earth about 66 million years ago.
The Chicxulub impactor, as it's known, left behind a crater off the coast of Mexico that spans 93 miles and goes 12 miles deep. Its devastating impact brought the reign of the dinosaurs to an abrupt and calamitous end by triggering their sudden mass extinction, along with the end of almost three-quarters of the plant and animal species then living on Earth.
The enduring puzzle has always been where the asteroid or comet that set off the destruction originated, and how it came to strike the Earth. And ...
2021-02-15
The UK's commercial fishing industry is currently experiencing a number of serious challenges.
However, a study by the University of Plymouth has found that managing the density of crab and lobster pots at an optimum level increases the quality of catch, benefits the marine environment and makes the industry more sustainable in the long term.
Published today in Scientific Reports, a journal published by the Nature group, the findings are the result of an extensive and unprecedented four-year field study conducted in partnership with local fishermen off the coast of southern England.
Over a sustained period, researchers exposed sections of the seabed to differing densities of pot fishing and monitored any impacts using a combination of underwater videos and catch ...
2021-02-15
It forever changed history when it crashed into Earth about 66 million years ago.
The Chicxulub impactor, as it's known, left behind a crater off the coast of Mexico that spans 93 miles and runs 12 miles deep. Its devastating impact brought the reign of the dinosaurs to an abrupt and calamitous end by triggering their sudden mass extinction, along with the end of almost three-quarters of the plant and animal species living on Earth.
The enduring puzzle: Where did the asteroid or comet originate, and how did it come to strike Earth? Now, a pair of researchers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian believe they have the answer.
In a study published today in Nature's Scientific Reports, Harvard University ...
2021-02-15
When the Covid-19 pandemic struck in early 2020, doctors and researchers rushed to find effective treatments. There was little time to spare. "Making new drugs takes forever," says Caroline Uhler, a computational biologist in MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and the Institute for Data, Systems and Society, and an associate member of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. "Really, the only expedient option is to repurpose existing drugs."
Uhler's team has now developed a machine learning-based approach to identify drugs already on the market that could ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tropical paper wasps babysit for neighbours