INFORMATION:
Cells use concentration gradients as a compass
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) Biophysicists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munch have developed a new theory, which accounts for the observation that cells can perceive their own shapes, and use this information to direct the distribution of proteins inside the cell.
Many cellular processes are critically dependent on the precise distribution and patterning of proteins on the cell membrane. Diverse studies have shown that, in addition to protein-protein interactions and transport processes, cell shape can also have a considerable impact on intracellular pattern formation. Conversely, there are patterning processes in which any dependence on cell form would be deleterious. Using starfish oocytes as a model system, LMU physicists led by Professor Erwin Frey have now explained how robust protein patterns can emerge in the face of drastic changes in cell shape. As Frey and colleagues report a new study that appears in the journal Nature Physics, a concentration gradient formed within the cell itself encodes the shape information of the cell and gets decoded by self-organized protein patterns.
Starfish oocytes are relatively large and transparent, and are therefore well suited for biochemical investigations. Just before meiotic cell division, a wave of membrane contraction passes along the cell membrane towards the position where the cell divides asymmetrically. This contraction wave is triggered by the membrane-bound enzyme called Rho, which's activity propagates as a pulse over the membrane. The wave progresses from what is known as the vegetal pole of the oocyte to the animal pole, where the nucleus is located, and divides asymmetrically as the wave arrives. To study the influence of changes in cell shape on this process, the researchers placed single oocytes in differently shaped microchambers, thus forcing the cells to adopt the geometry imposed by the boundary of each container. "We found that, although the pulse of Rho activation propagates in a correspondingly altered manner in the deformed cells, it always reaches the position at which the nucleus lies," says Frey. "This fascinating observation proves that the Rho pulse recognizes the shape of the cell and adapts to it."
Self-organized protein patterns can decode information about the cell shape
To understand the mechanism behind this remarkable adaptability, the team went on to develop a biophysical theory that accounts for this finding. The model is based on the earlier discovery that the cell-cycle regulator Cdk1 is asymmetrically distributed in the oocyte cytoplasm, where it forms a concentration gradient that extends from the nucleus into the cytoplasm and decays with time. This gradient enables the proteins on the membrane to adapt to the cell shape. "The key insight is that the protein that activates Rho measures the gradient close to the membrane and marks a threshold concentration of the gradient: It forms a front-like concentration profile on the membrane, such that the front is positioned exactly at the threshold concentration. At this front position, the Rho activator, in turn, locally triggers an activity pulse of Rho." says Wigbers, one of the first-authors of the article. As the gradient decays, the position of this threshold value moves at varying speed along the membrane, depending on the cell shape. Thus, via this hierarchy of protein concentration profiles, the shape information that is encoded in the gradient gets transformed into a mechanochemical response - the contraction wave that passes over the membrane.
"Our results underline the significance of the self-organization of hierarchical protein patterns for the understanding of biological functions," says Frey. In effect, the authors have integrated two major paradigms in the field of protein pattern formation - self-organization based on reaction-diffusion mechanisms and the exploitation of positional information. "We believe that such a mechanism, which utilizes a hierarchy of protein patterns to encode information that reflects cell shape, could represent a general physical principle for the recognition and regulation of cell shape," Frey concludes.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Observations at a shed light on how hard coral survives without light
2021-02-16
In shallow water, less than 30 metres, the survival of hard corals depends on photosynthetic unicellular algae (zooxanthellae) living in their tissues. But how does the coral adapt at depth when the light disappears? French researchers from the CNRS, EPHE-PSL and their international collaborators, associated with Under the Pole (Expedition III), have studied for the first time the distribution of these so-called mesophotic corals in the French Polynesian archipelago, from the surface to 120 metres deep (with a record descent of 172 metres). As the amount of light decreases, the coral associates ...
CPAP treatment increases physical activity in adults with sleep apnea, heart disease
2021-02-16
DARIEN, IL - A new study found that treating obstructive sleep apnea with CPAP therapy increased self-reported physical activity in adults with a history of heart disease.
During a mean follow-up period of 3.7 years, the group treated with CPAP therapy reported approximately 20% higher levels of moderate physical activity compared with the control group. The study also found the CPAP group was more likely to report activity levels consistent with expert recommendations.
"We were pleased to find that our CPAP users reported that they were better able to maintain their levels of activity over the four years of the study, and that they reported fewer limitations in moderate and vigorous activities including those that are important for independent aging, like walking up the stairs," ...
Finding coronavirus's helper proteins
2021-02-16
The researchers used a biophysical method called thermal proteome profiling (TPP) to gain a comprehensive overview of which human proteins are functionally altered during SARS-CoV-2 infection. TPP monitors protein amounts and denaturation temperatures - the points at which proteins heat up so much that they lose their 3D structure. A shift in denaturation temperature indicates that a particular protein has undergone a functional change upon infection, possibly due to the virus hijacking the protein for use in its own replication.
The scientists observed that infection with SARS-CoV-2 changed the abundance and thermal stability of hundreds of cellular proteins. This included ...
Predicting words' grammatical properties helps us read faster
2021-02-16
Psycholinguists from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain found that when reading, people are not only able to predict specific words, but also words' grammatical properties, which helps them to read faster. Researchers have also discovered that predictability of words and grammatical features can be successfully modelled with the use of neural networks. The study was published in the journal PLOS ONE.
The ability to predict the next word in another person's speech or in reading has been described by many psycho- and neurolinguistic studies over the last 40 years. It is assumed that this ability allows us to process the information faster. Some recent publications on the English language have demonstrated evidence that while reading, people can ...
Differences in walking patterns could predict type of cognitive decline in older adults
2021-02-16
Canadian researchers are the first to study how different patterns in the way older adults walk could more accurately diagnose different types of dementia and identify Alzheimer's disease.
A new study by a Canadian research team, led by London researchers from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, evaluated the walking patterns and brain function of 500 participants currently enrolled in clinical trials. Their findings are published today in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
"We have longstanding evidence showing that cognitive problems, such as poor memory and executive dysfunction, can ...
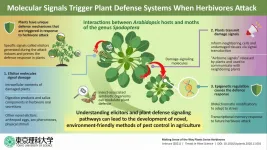
Perceiving predators: Understanding how plants 'sense' herbivore attack
2021-02-16
Nature has its way of maintaining balance. This statement rightly holds true for plants that are eaten by herbivores--insects or even mammals. Interestingly, these plants do not just silently allow themselves to be consumed and destroyed; in fact, they have evolved a defense system to warn them of predator attacks and potentially even ward them off. The defense systems arise as a result of inner and outer cellular signaling in the plants, as well as ecological cues. Plants have developed several ways of sensing damage; a lot of these involve the sensing of various "elicitor" molecules produced by either the predator ...
A boost for plant research
2021-02-16
It is almost ten years since the scientific journal Science called optogenetics the "breakthrough of the decade". Put simply, the technique makes it possible to control the electrical activity of cells with pulses of light. With its help, scientists can gain new insights into the functioning of nerve cells, for example, and thus better understand neurological and psychiatric diseases such as depression and schizophrenia.
Established procedure on animal cells
In research on animal cells, optogenetics is now an established technique used in many fields. The picture is different in plant research: transferring the principle to plant cells and applying it widely has not been possible until now.
However, this has now changed: Scientists ...
Individual differences in Achilles tendon shape can affect susceptibility to injury
2021-02-16
Individual variation in the shape and structure of the Achilles tendon may influence our susceptibility to injury later in life, says a study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that studying individual Achilles tendon shape (or 'morphology') could help with identifying patients at risk of injury and designing new, potentially personalised approaches for treating and preventing Achilles tendinopathy and similar conditions.
The Achilles tendon is the tissue that links the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is fundamental to our movement and athletic ability. Its unique structure, which combines three smaller sub-tendons, increases the efficiency of our movement by allowing individual control from connected muscles. For this control to occur, the ...
The body produces new satiety factor during prolonged exercise
2021-02-16
A drug that helps us to eat less could help the more than 650 million people around the world who live with obesity. One of the emerging drug candidates that interest researchers is the hormone GDF15 that, when given to rodents, lowers their appetite and body weight. New research from the University of Copenhagen finds that the body produces large amounts GDF15 during extended bouts of vigorous exercise, presumably as a physiological stress signal.
This finding highlights central differences between GDF15 given as a drug (pharmacology), and GDF15 released naturally in response to vigorous exercise (physiology). This is an important distinction ...
Internet access spending in public schools increases test scores, but also disciplinary problems
2021-02-16
From 2015 to 2019, public school districts in the United States invested nearly $5 billion to upgrade their Wi-Fi networks, according to EducationSuperHighway. However, in the age of COVID-19-mandated virtual learning, millions of K-12 students still lack the minimal connectivity at home for digital learning.
In a new study from the University of Notre Dame, researchers quantify how school district connectivity increases test scores, but underscore the dark side of technology -- increased behavior problems.
A $600,000 increase in annual internet access spending produces a financial gain of approximately $820,000 to $1.8 million, alongside losses from disciplinary problems totaling $25,800 to $53,440, according to new research from Yixing Chen, an ...