High-risk gene for neurodevelopmental disorders linked to sleep problems in flies
Findings may explain how brain dysfunction gives rise to sleep disruptions in children with neurodevelopmental disorders, say Penn Medicine researchers
2021-02-17
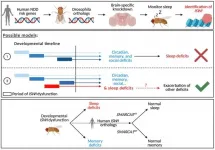
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - The mutation of a gene that has been associated with neurodevelopmental disorders like autism spectrum disorder led to marked sleep disturbances in fruit flies, according to a new study from scientists in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The findings, published Wednesday in Science Advances, provide further evidence that sleep is linked to early neurodevelopmental processes and could guide future treatments for patients.
While sleep disruption is a commonly reported symptom across neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism, it is often treated clinically as a "secondary effect" of other cognitive or behavioral problems, according to senior author Matthew Kayser, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of Psychiatry and Neuroscience at Penn, who led the study with Natalie Gong and Leela Chakravarti Dilley, both MD/PhD students.
"Our paper shows that sleep problems are not arising because of these other issues, but rather, this gene acts in different brain circuits, at different periods of time during development, to independently give rise to each of these symptoms," Kayser said. "Which is to say, we're guessing that the genetic constellation or signaling pathway that leads to disorders like autism or depression can also lead to sleep problems in humans."
To identify a correlation between sleep and neurodevelopment, Kayser and his research team genetically manipulated Drosophila, or fruit flies, by individually "knocking down" each of 218 genes that have been strongly associated with risk for neurodevelopmental disorders in humans. They then observed how the flies -- a remarkably powerful model for biomedical research -- reacted.
After observing the flies' behavioral patterns, they saw that knocking down the gene Imitation SWItch/SNF (ISWI) made the fruit flies almost entirely unable to sleep. ISWI in fruit flies is homologous to SMARCA1 and SMARCA5 genes in humans that have been linked to various neurodevelopmental disorders. In addition to sleep deficits, the researchers found that knocking down ISWI also led to memory problems and social dysfunction. Surprisingly, the ISWI gene was found to act in different cells of the fly brain during distinct developmental times to independently affect each of these behaviors.
Importantly, even though sleep deficits appear to arise directly from dysfunction of a given gene, Kayser said that previous research suggests treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia are still likely to be effective.
"Even if problems like sleep disruption or insomnia arise from really early problems in the brain's wiring, we have every reason to believe that we can use existing treatments," Kayser said.
The findings support the idea that treating sleep problems in children with neurodevelopmental disorders could potentially improve other symptoms. Future work will examine the potential for leveraging sleep as a modifiable risk factor in mitigating the severity of neurodevelopmental disorders.
"Now that we know that sleep deficits are a primary characteristic of early developmental origin in neurodevelopmental disorders, we can start to ask," Kayser said, "whether improving sleep will also improve memory and social function."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (K08 NS09046, DP2 NS111996, and T32 HL07953). Penn researchers Charlette Williams, Emilia Moscato, and Milan Szuperak also contributed to this work.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-17
In ancient European settlements, livestock use was likely primarily determined by political structure and market demands, according to a study published February 17, 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ariadna Nieto-Espinet and colleagues of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Barcelona.
Zooarchaeology - the study of animal remains from archaeological sites - has great potential to provide information on past human communities. Livestock preferences are known to have changed over time in Europe, but little is known about how much these changes are influenced by environmental, economic, or political conditions of ancient settlements.
In ...
2021-02-17
The new method works without extremely high temperatures, is therefore more energy-efficient and has a significantly higher recovery rate (approx. 96 per cent of the starting material) than established processes. These findings will be published on 17 February 2021 in the scientific journal Nature.
Mechanical recycling vs. chemical recycling
"The direct re-utilization of plastics is often hampered by the fact that, in practice, mechanical recycling only functions to a limited degree - because the plastics are contaminated and mixed with additives, which impairs the properties ...
2021-02-17
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have created a four-legged soft robot that doesn't need any electronics to work. The robot only needs a constant source of pressurized air for all its functions, including its controls and locomotion systems.
The team, led by Michael T. Tolley, a professor of mechanical engineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, details its findings in the Feb. 17, 2021 issue of the journal Science Robotics.
"This work represents a fundamental yet significant step towards fully-autonomous, electronics-free walking robots," said Dylan Drotman, a Ph.D. student in Tolley's research group and the paper's first author.
Applications include low-cost robotics for entertainment, such ...
2021-02-17
The unprecedented and deadly blazes that engulfed the American West in 2020 attest to the increasing number, size and severity of wildfires in the region. And while scientists predict the climate crisis will exacerbate this situation, there's still much discussion around its contributing factors.
With this in mind, scientists at five western universities, including UC Santa Barbara, investigated the effects of human-driven climate change and more than a century of fire suppression, which has produced dense forests primed to burn. Their research, published in the journal Environmental ...
2021-02-17
In the search for planets capable of sustaining life, an international research team with members from ETH has taken a significant step forward. As the researchers reported recently in the journal Nature Communications, they found signs of a Neptune-sized planet in the Alpha Centauri star system, a mere 4.4 light years away from Earth. This exoplanet is located in a zone that may offer suitable conditions for life. The team was able to collect data with unprecedented sensitivity, thus registering even very weak signals.
Earth is a disruptive factor
Thanks to the new process, the researchers have advanced one step closer to ...
2021-02-17
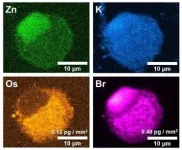
In the paper, 'Tracking Reactions of Asymmetric Organo-Osmium Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts in Cancer Cells', published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, researchers from the University of Warwick have, for the first time, used the new 185 m beamline to track Osmium in a single cancer cell at a scale of 100 nanometers.
They used two techniques to track potential treatments in cancer cells, the first, ICP-MS, which stands for Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry, can quantify a wide range of natural and drug elements in millions of cells. However, to investigate a single cancer cell, researchers used synchrotron X-ray Fluorescence ...
2021-02-17
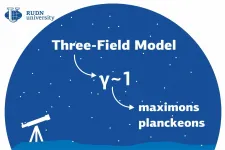
Gravity might play a bigger role in the formation of elementary particles than scientists used to believe. A team of physicists from RUDN University obtained some solutions of semi-classical models that describe particle-like waves. They also calculated the ratio between the gravitational interaction of particles and the interaction of their charges. The results of the study were published in the Universe journal.
Due to their small size, the gravitational interaction between elementary particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons) is weak compared to Coulomb forces--attraction ...
2021-02-17
Experts say English slang and regional dialect should not be banned from classrooms but when you're getting to grips with a second language how helpful is it to learn non-standard lingo?
Very, says Sascha Stollhans, of the Department of Languages and Cultures at Lancaster University, who argues that standardised language norms are artificial and language learners should learn about all aspects of language, even the controversial ones.
In his policy paper, just published in the Languages, Society & Policy Journal, he says:
There are concerns among professionals that introducing learners to 'non-standard' language could lead to ambiguity and confusion and that students might be penalised for using it in assessments.
Linguistic variation is a rich area of study that can appeal to language ...
2021-02-17
Researchers from the University of Granada warn that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck (both the double chin and the deeper deposits, located between muscles and around the cervical vertebrae) is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk, and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
A study conducted by researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) has revealed that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk (heart problems), and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
Traditionally, the accumulation of visceral adipose tissue has been considered one of the factors most strongly ...
2021-02-17
Research teams from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and the University of Copenhagen have therefore developed an approach that can predict the optimal composition and confirm its accuracy with high-throughput experiments. They report in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition of 28. December 2020.
Much less expensive elements than previous catalysts
Many electrochemical reactions go through several steps. Each should be optimized on a catalyst surface if possible, but different requirements apply to each step. "Since previous catalysts usually had only one optimized ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High-risk gene for neurodevelopmental disorders linked to sleep problems in flies
Findings may explain how brain dysfunction gives rise to sleep disruptions in children with neurodevelopmental disorders, say Penn Medicine researchers