(Press-News.org) BLOOMINGTON, Ind. - Automotive recalls are occurring at record levels, but seem to be announced after inexplicable delays. A research study of 48 years of auto recalls announced in the United States finds carmakers frequently wait to make their announcements until after a competitor issues a recall - even if it is unrelated to similar defects.
This suggests that recall announcements may not be triggered solely by individual firms' product quality defect awareness or concern for the public interest, but may also be influenced by competitor recalls, a phenomenon that no prior research had investigated.
Researchers analyzed 3,117 auto recalls over a 48-year period -- from 1966 to 2013 -- using a model to investigate recall clustering and categorized recalls as leading or following within a cluster. They found that 73 percent of recalls occurred in clusters that lasted 34 days and had 7.6 following recalls on average.
On average, a cluster formed after a 16-day gap in which no recalls were announced. They found 266 such clusters over the period studied.
"The implication is that auto firms are either consciously or unconsciously delaying recall announcements until they are able to hide in the herd," said George Ball, assistant professor of operations and decision technologies and Weimer Faculty Fellow at the Indiana University Kelley School of Business. "By doing this, they experience a significantly reduced stock penalty from their recall."
Ball is co-author of the study, "Hiding in the Herd: The Product Recall Clustering Phenomenon," recently published online in Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, along with faculty at the University of Illinois, the University of Notre Dame, the University of Minnesota and Michigan State University.
Researchers found as much as a 67 percent stock market penalty difference between leading recalls, which initiate the cluster, and following recalls, who follow recalls and hide in the herd to experience a lower stock penalty.
This indicates a "meaningful financial incentive for auto firms to cluster following recalls behind a leading recall announcement," researchers said. "This stock market penalty difference dissipates over time within a cluster. Additionally, across clusters, the stock market penalty faced by the leading recall amplifies as the time since the last cluster increases."
The authors also found that firms with the highest quality reputation, in particular Toyota, triggered the most recall followers.
"Even though Toyota announces some of the fewest recalls, when they do announce a recall, 31 percent of their recalls trigger a cluster and leads to many other following recalls," Ball said. "This number is between 5 and 9 percent for all other firms. This means that firms are likely to hide in the herd when the leading recall is announced by a firm with a stellar quality reputation such as Toyota.
"A key recommendation of the study is for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) to require auto firms to report the specific defect awareness date for each recall, and to make this defect awareness date a searchable and publicly available data field in the auto recall dataset NHTSA provides online," Ball added. "This defect awareness date is required and made available by other federal regulators that oversee recalls in the U.S., such as the Food and Drug Administration. Making this defect awareness date a transparent, searchable and publicly available data field may discourage firms from hiding in the herd and prompt them to make more timely and transparent recall decisions."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the study were Ujjal Mukherjee, assistant professor of business administration at the Gies College of Business at the University of Illinois who was the lead author; Kaitlin Wowak, assistant professor of IT, analytics, and operations at the Mendoza College of Business at the University of Notre Dame; Karthik Natarajan, assistant professor of supply chain and operations at the Carlson School of Management at the University of Minnesota; and Jason Miller, associate professor of supply chain management at the Broad College of Business at Michigan State University.
In a world as diverse as our own, the journey towards a sustainable future will look different depending on where in the world we live, according to a recent paper published in One Earth and led by McGill University, with researchers from the Stockholm Resilience Centre.
"There are many regional pathways to a more sustainable future, but our lack of understanding about how these complex and sometimes contradictory pathways interact (and in particular when they synergize or compete with one another) limits our ability to choose the 'best' ones," says Elena Bennett, a professor in the Department of Natural ...
Eating a low quality diet, high in foods and food components associated with chronic inflammation, during pregnancy may be associated with an increased risk of obesity and excess body fat in children, especially during late-childhood. The findings are published the open access journal BMC Medicine.
Researchers from University College Dublin, Ireland found that children of mothers who ate a higher quality diet, low in inflammation-associated foods, during pregnancy had a lower risk of obesity and lower body fat levels in late-childhood than children whose mothers ate a lower quality diet, ...
Researchers have mapped an underlying "psychological signature" for people who are predisposed to holding extreme social, political or religious attitudes, and support violence in the name of ideology.
A new study suggests that a particular mix of personality traits and unconscious cognition - the ways our brains take in basic information - is a strong predictor for extremist views across a range of beliefs, including nationalism and religious fervour.
These mental characteristics include poorer working memory and slower "perceptual strategies" - the unconscious processing of changing stimuli, such as shape and colour - as well as tendencies towards impulsivity and sensation seeking.
This combination of cognitive and ...
Researchers have called on European policymakers to make adequate resources available to tackle pancreatic cancer, a disease that is almost invariably fatal and where little progress has been made over the past 40 years.
In the latest predictions for cancer deaths in the EU and UK for 2021, published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday), researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), a professor at the University of Milan (Italy), say that pancreatic death rates are predicted to remain approximately stable for men, but continue to rise in women in most EU countries.
The researchers predict that ...
Home gardens are by far the biggest source of food for pollinating insects, including bees and wasps, in cities and towns, according to new research.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and published today in the Journal of Ecology, measured for the first time how much nectar is produced in urban areas and discovered residential gardens accounted for the vast majority - some 85 per cent on average.
Results showed three gardens generated daily on average around a teaspoon of Nature's ambrosia, the unique sugar-rich liquid found in flowers which pollinators drink for energy. While a teaspoon ...
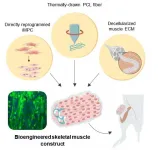
Muscle is the largest organ that accounts for 40% of body mass and plays an essential role in maintaining our lives. Muscle tissue is notable for its unique ability for spontaneous regeneration. However, in serious injuries such as those sustained in car accidents or tumor resection which results in a volumetric muscle loss (VML), the muscle's ability to recover is greatly diminished. Currently, VML treatments comprise surgical interventions with autologous muscle flaps or grafts accompanied by physical therapy. However, surgical procedures often lead to a reduced muscular function, and in some cases result in a complete graft failure. Thus, there is a demand for additional therapeutic options to improve muscle loss recovery.
A promising strategy to improve ...
Coral within the family Acropora are fast growers and thus important for reef growth, island formation, and coastal protection but, due to global environmental pressures, are in decline
A species within this family has three different color morphs - brown, yellow-green, and purple, which appear to respond differently to high temperatures
Researchers looked at the different proteins expressed by the different color morphs, to see whether these were related to their resilience to a changing environment
The green variant was found to maintain high levels of green fluorescent proteins during summer heatwaves and was less likely to bleach than the other two morphs
This suggest that resistance to thermal stress is influenced by a coral's underlying genetics, ...
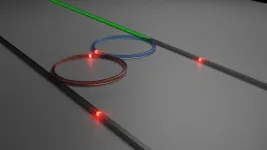
Periodic pulses of light forming a comb in the frequency domain are
widely used for sensing and ranging. The key to the miniaturisation of
this technology towards chip-integrated solutions is the generation of
dissipative solitons in ring-shaped microresonators. Dissipative solitons
are stable pulses circulating around the circumference of a nonlinear
resonator.
Since their first demonstration, the process of dissipative soliton
formation has been extensively studied and today it is rather
considered as textbook knowledge. Several directions of further
development are ...
A survey by a Boston University researcher of nearly 33,000 college students across the country reveals the prevalence of depression and anxiety in young people continues to increase, now reaching its highest levels, a sign of the mounting stress factors due to the coronavirus pandemic, political unrest, and systemic racism and inequality.
"Half of students in fall 2020 screened positive for depression and/or anxiety," says END ...
Microorganisms possess natural product biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) that may harbor unique bioactivities for use in drug development and agricultural applications. However, many uncharacterized microbial BGCs remain inaccessible. Researchers at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign previously demonstrated a technique using transcription factor decoys to activate large, silent BGCs in bacteria to aid in natural product discovery.
Now, they have developed a direct cloning method that aims to accelerate large-scale discovery of novel natural products. Their findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications.
Named Cas12a assisted precise targeted cloning using in vivo Cre-lox recombination (CAPTURE), ...