(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH--Babies whose births were depicted in Bollywood films from the 1950s and 60s were more often than not boys; in today's films, boy and girl newborns are about evenly split. In the 50s and 60s, dowries were socially acceptable; today, not so much. And Bollywood's conception of beauty has remained consistent through the years: beautiful women have fair skin.
Fans and critics of Bollywood -- the popular name for a $2.1 billion film industry centered in Mumbai, India -- might have some inkling of all this, particularly as movies often reflect changes in the culture. But these insights came via an automated computer analysis designed by Carnegie Mellon University computer scientists.
The researchers, led by Kunal Khadilkar and Ashiqur R. KhudaBukhsh of CMU's Language Technologies Institute (LTI), gathered 100 Bollywood movies from each of the past seven decades along with 100 of the top-grossing Hollywood moves from the same periods. They then used statistical language models to analyze subtitles of those 1,400 films for gender and social biases, looking for such factors as what words are closely associated with each other.
"Most cultural studies of movies might consider five or 10 movies," said Khadilkar, a master's student in LTI. "Our method can look at 2,000 movies in a matter of days."
It's a method that enables people to study cultural issues with much more precision, said
Tom Mitchell, Founders University Professor in the School of Computer Science and a co-author of the study.
"We're talking about statistical, automated analysis of movies at scale and across time," Mitchell said. "It gives us a finer probe for understanding the cultural themes implicit in these films." The same natural language processing tools might be used to rapidly analyze hundreds or thousands of books, magazine articles, radio transcripts or social media posts, he added.
For instance, the researchers assessed beauty conventions in movies by using a so-called cloze test. Essentially, it's a fill-in-the-blank exercise: "A beautiful woman should have BLANK skin." A language model normally would predict "soft" as the answer, they noted. But when the model was trained with the Bollywood subtitles, the consistent prediction became "fair." The same thing happened when Hollywood subtitles were used, though the bias was less pronounced.
To assess the prevalence of male characters, the researchers used a metric called Male Pronoun Ratio (MPR), which compares the occurrence of male pronouns such as "he" and "him" with the total occurrences of male and female pronouns. From 1950 through today, the MPR for Bollywood and Hollywood movies ranged from roughly 60 to 65 MPR. By contrast, the MPR for a selection of Google Books dropped from near 75 in the 1950s to parity, about 50, in the 2020s.
Dowries -- monetary or property gifts from a bride's family to the groom's -- were common in India before they were outlawed in the early 1960s. Looking at words associated with dowry over the years, the researchers found such words as "loan," "debt" and "jewelry" in Bollywood films of the 50s, which suggested compliance. By the 1970s, other words, such as "consent" and "responsibility," began to appear. Finally, in the 2000s, the words most closely associated with dowry -- including "trouble," "divorce" and "refused" -- indicate noncompliance or its consequences.
"All of these things we kind of knew," said KhudaBukhsh, an LTI project scientist, "but now we have numbers to quantify them. And we can also see the progress over the last 70 years as these biases have been reduced."
A research paper by Khadilkar, KhudaBukhsh and Mitchell was presented at the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence virtual conference earlier this month.
INFORMATION:
Sea turtles are witnesses and victims of the high level of plastic pollution of the Adriatic Sea. A group of researchers at the University of Bologna analysed 45 turtles hospitalised at Fondazione Cetacea in Riccione and found plastic debris in their faeces. Besides confirming the role of turtles as ideal sentinels to monitor plastic pollution in the sea, the results of their analysis - published in the journal Frontiers of Marine Medicine - crucially show how the plastic debris in their intestines can dangerously alter their microbiota, eventually compromising their health.
"The results ...
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Research shows that Soldiers exposed to shockwaves from military explosives are at a higher risk for developing Alzheimer's disease -- even those that don't have traumatic brain injuries from those blasts. A new Army-funded study identifies how those blasts affect the brain.
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Pembroke in collaboration with the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, now known as DEVCOM, the Army Research Laboratory, and the National Institutes of Health found that the mystery behind blast-induced neurological ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The optimal timeframe for donating convalescent plasma for use in COVID-19 immunotherapy, which was given emergency use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in August 2020, is within 60 days of the onset of symptoms, according to a new Penn State-led study. The research also reveals that the ideal convalescent plasma donor is a recovered COVID-19 patient who is older than 30 and whose illness had been severe.
"Millions of individuals worldwide have recovered from COVID-19 and may be eligible for participation in convalescent plasma donor programs," said Vivek Kapur, professor of microbiology and infectious diseases, Penn State. "Our findings enable identification ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. --Many climate models focus on scenarios decades into the future, making their outcomes seem unreliable and problematic for decision-making in the immediate future. In a proactive move, researchers are using short-term forecasts to stress the urgency of drought risk in the United States and inform policymakers' actions now.
A new study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign civil and environmental engineering professor Ximing Cai examines how drought propagates through climate, hydrological, ecological and social systems throughout different U.S. regions. The results are published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
"The same amount of precipitation, or the lack of thereof, in one region could have very different impacts on the hydrologic ...
Black men and women, as well as adolescent boys and girls, may react differently to perceived racial discrimination, with Black women and girls engaging in more exercise and better eating habits than Black men and boys when faced with discrimination, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
"In this study, Black women and girls didn't just survive in the face of racism, they actually responded in a positive manner, in terms of their health behavior," said lead researcher Frederick Gibbons, PhD, with the University of Connecticut. "This gives us some hope that despite the spike in racism across the country, some people are finding healthy ways to cope." ...
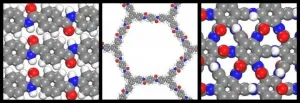
ADELPHI, Md. -- Army researchers reached a breakthrough in the nascent science of two-dimensional polymers thanks to a collaborative program that enlists the help of lead scientists and engineers across academia known as joint faculty appointments.
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, now known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory partnered with Prof. Steve Lustig, a joint faculty appointment at Northeastern University, to accelerate the development of 2D polymers for military applications.
The collaboration with ARL Northeast led to a groundbreaking study published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Macromolecules. Editors featured the research in a cover article.
"2D polymers have been studied very seriously from a synthetic ...
Researchers have developed a tool to identify security and privacy risks associated with Covid-19 contact tracing apps.
COVIDGuardian, the first automated security and privacy assessment tool, tests contact tracing apps for potential threats such as malware, embedded trackers and private information leakage.
Using the COVIDGuardian tool, cybersecurity experts assessed 40 Covid-19 contact tracing apps that have been employed worldwide for potential privacy and security threats. Their findings include that:
72.5 per cent of the apps use at least one insecure cryptographic ...
Medical researchers have long understood that a pregnant mother's diet has a profound impact on her developing fetus's immune system and that babies -- especially those born prematurely -- who are fed breast milk have a more robust ability to fight disease, suggesting that even after childbirth, a mother's diet matters. However, the biological mechanisms underlying these connections have remained unclear.
Now, in a study published Feb. 15, 2021, in the journal Nature Communications, a Johns Hopkins Medicine research team reports that pregnant mice fed a diet rich in a molecule found abundantly in cruciferous vegetables -- such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower -- gave birth to pups with stronger protection against necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). ...
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as various forms of senile dementia or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), have one thing in common: large amounts of certain RNA-protein complexes (snRNPs) are produced and deposited in the nerve cells of those affected - and this hinders the function of the cells. The overproduction is possibly caused by a malfunction in the assembly of the protein complexes.
How the production of these protein complexes is regulated was unknown until now. Researchers from Martinsried and Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, have solved the puzzle and now report on it in the open access journal Nature Communications. They describe in detail a signaling pathway that prevents the overproduction of snRNPs when they are not needed. The results should ...
A diet rich in human food may be wreaking havoc on the health of urban coyotes, according to a new study by University of Alberta biologists.
The research team from the Faculty of Science examined the stomach contents, gut microbiome and overall health of nearly 100 coyotes in Edmonton's capital region. Their results also show coyotes that consume more human food have more human-like gut bacteria--with potential impact on their nutrition, immune function and, based on similar findings in dogs, even behaviour.
"If eating human food disturbs the 'natural' coyote gut bacteria, it is possible that eating human food has the potential to affect all ...