(Press-News.org) WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- Doppler radar improves lives by peeking inside air masses to predict the weather. A Purdue University team is using similar technology to look inside living cells, introducing a method to detect pathogens and treat infections in ways that scientists never have before.
In a new study, the team used Doppler to sneak a peek inside cells and track their metabolic activity in real time, without having to wait for cultures to grow. Using this ability, the researchers can test microbes found in food, water, and other environments to see if they are pathogens, or help them identify the right medicine to treat antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
David Nolte, Purdue's Edward M. Purcell Distinguished Professor of Physics and Astronomy; John Turek, professor of basic medical sciences; Eduardo Ximenes, research scientist in the Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering; and Michael Ladisch, Distinguished Professor of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, adapted this technique from their previous study on cancer cells in a paper released this month in Communications Biology.
Using funding from the National Science Foundation as well as Purdue's Discovery Park Big Idea Challenge, the team worked with immortalized cell lines -- cells that will live forever unless you kill them. They exposed the cells to different known pathogens, in this case salmonella and E. coli. They then used the Doppler effect to spy out how the cells reacted. These living cells are called "sentinels," and observing their reactions is called a biodynamic assay.
"First we did biodynamic imaging applied to cancer, and now we're applying it to other kinds cells," Nolte said. "This research is unique. No one else is doing anything like it. That's why it's so intriguing."
This strategy is broadly applicable when scientists have isolated an unknown microbe and want to know if it is pathogenic -- harmful to living tissues -- or not. Such cells may show up in food supply, water sources or even in recently melted glaciers.
"This directly measures whether a cell is pathogenic," Ladisch said. "If the cells are not pathogenic, the Doppler signal doesn't change. If they are, the Doppler signal changes quite significantly. Then you can use other methods to identify what the pathogen is. This is a quick way to tell friend from foe."
Being able to quickly discern whether a cell is harmful is incredibly helpful in situations where people encounter a living unknown microorganism, allowing scientists to know what precautions to take. Once it is known that a microbe is harmful, they can begin established protocols that allow them to determine the specific identity of the cell and determine an effective antibiotic against the microorganism.
Another benefit is the ability to quickly and directly diagnose which bacteria respond to which antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance can be a devastating problem in hospitals and other environments where individuals with already compromised bodies and immune systems may be exposed to and infected by increasingly high amounts of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Sometimes this results in a potentially fatal condition called bacterial sepsis, or septicemia. This is different from the viral sepsis that has been discussed in connection with COVID-19, though the scientists say their next steps will include investigating viral sepsis.
Treating sepsis is challenging. Giving the patient broad-spectrum antibiotics, which sounds like a good idea, might not help and could make the situation worse for the next patient. Letting bacteria come into close contact with antibiotics that do not kill them only makes them more resistant to that antibiotic and more difficult to fight next time.
Culturing the patient's tissues and homing in on the correct antibiotic to use can take time the patient does not have, usually eight to 10 hours. This new biodynamic process allows scientists to put the patient's bacterial samples in an array of tiny petri dishes containing the tissue sentinels and treat each sample with a different antibiotic. Using Doppler, they can quickly notice which bacterial samples have dramatic metabolic changes. The samples that do are the ones that have reacted to the antibiotic -- the bacteria are dying, being defeated and beaten back by antibiotics.
"When we treat with antibiotics, the bacteria don't have to multiply much before they start to affect the tissue sentinels," Nolte explained. "There are still too few bacteria to see or to measure directly, but they start to affect how the tissues behaves, which we can detect with Doppler."
In less than half the time a traditional culture and diagnosis takes, doctors could tell which antibiotic to administer, bolstering the patient's chances for recovery. The researchers worked closely with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization to patent and license their technologies. They plan to further explore whether this method would work for tissue samples exposed to nonliving pathogenic cells or dried spores, and to test for and treat viral sepsis.
INFORMATION:
About Purdue University
Purdue University is a top public research institution developing practical solutions to today's toughest challenges. Ranked the No. 5 Most Innovative University in the United States by U.S. News & World Report, Purdue delivers world-changing research and out-of-this-world discovery. Committed to hands-on and online, real-world learning, Purdue offers a transformative education to all. Committed to affordability and accessibility, Purdue has frozen tuition and most fees at 2012-13 levels, enabling more students than ever to graduate debt-free. See how Purdue never stops in the persistent pursuit of the next giant leap at https://purdue.edu/.
ABSTRACT
Doppler imaging detects bacterial infection of living tissue
Honggu Choi, Zhe Li, Zhen Hua, Jessica Zuponcic, Eduardo Ximenes, John J. Turek, Michael R. Ladisch and David D. Nolte
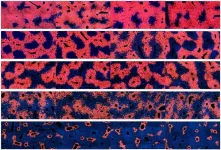
Living 3D in vitro tissue cultures, grown from immortalized cell lines, act as living sentinels as pathogenic bacteria invade the tissue. The infection is reported through changes in the intracellular dynamics of the sentinel cells caused by the disruption of normal cellular function by the infecting bacteria. Here, the Doppler imaging of infected sentinels shows the dynamic characteristics of infections. Invasive Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis and Listeria monocytogenes penetrate through multicellular tumor spheroids, while non-invasive strains of Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua remain isolated outside the cells, generating different Doppler signatures. Phase distributions caused by intracellular transport display Lévy statistics, introducing a Lévy-alpha spectroscopy of bacterial invasion. Antibiotic treatment of infected spheroids, monitored through time-dependent Doppler shifts, can distinguish drug-resistant relative to non-resistant strains. This use of intracellular Doppler spectroscopy of living tissue sentinels opens a new class of microbial assay with potential importance for studying the emergence of antibiotic resistance.
HOUSTON - (Feb. 25, 2021) - Low-income livestock farmers in developing countries are often faced with a difficult dilemma: protect their animals from endangered predators, or spare the threatened species at the expense of their livestock and livelihood.
A new paper by Rice University economist Ted Loch-Temzelides examines such circumstances faced by farmers in Pakistan. "Conservation, risk aversion, and livestock insurance: The case of the snow leopard" outlines a plan under which farmers can protect themselves from crippling financial losses while ...
While the amazing regenerative power of the liver has been known since ancient times, the cells responsible for maintaining and replenishing the liver have remained a mystery. Now, research from the Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) has identified the cells responsible for liver maintenance and regeneration while also pinpointing where they reside in the liver.
These findings, reported today in Science, could help scientists answer important questions about liver maintenance, liver damage (such as from fatty liver or alcoholic liver disease), and liver cancer.
The liver performs vital functions, including chemical detoxification, blood protein production, bile excretion, and regulation of energy metabolism. Structurally, the liver ...
Paleo-ecologists from The University of New Mexico and at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln have demonstrated that the offspring of enormous carnivorous dinosaurs, such as Tyrannosaurus rex may have fundamentally re-shaped their communities by out-competing smaller rival species.
The study, released this week in the journal Science, is the first to examine community-scale dinosaur diversity while treating juveniles as their own ecological entity.
"Dinosaur communities were like shopping malls on a Saturday afternoon ? jam-packed with teenagers" explained Kat Schroeder, a graduate student in the UNM Department of Biology who led the study. "They made up a significant portion of the individuals in a species and would have had a very real impact ...
An international team of scientists has developed a system that can generate random numbers over a hundred times faster than current technologies, paving the way towards faster, cheaper, and more secure data encryption in today's digitally connected world.
The random generator system was jointly developed by researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Yale University, and Trinity College Dublin, and made in NTU.
Random numbers are used for a variety of purposes, such as generating data encryption keys and one-time ...
As Covid-19 impacts lives around the world- a new skeleton study is reconstructing ancient pandemics to assess human's evolutionary ability to fight off leprosy, tuberculosis and treponematoses with help from declining rates of transmission when the germs became widespread.
The researchers state the germs mutated to infect ancient humans so they could replicate- hopping across to as many new hosts as possible- but the severity of the diseases reduced as a result.
The analysis by Adjunct Professor in Archaeology Maciej Henneberg and Dr Teghan Lucas at Flinders ...
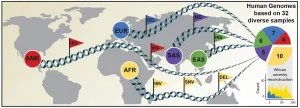
In 2001, the International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium announced the first draft of the human genome reference sequence. The Human Genome Project, as it was called, had taken more than eleven years of work and involved more than 1000 scientists from 40 countries. This reference, however, did not represent a single individual but instead is a composite of humans that could not accurately capture the complexity of human genetic variation.
Building on this, scientists have carried out many sequencing projects over the last 20 years to identify and catalog genetic differences between an individual and the reference genome. Those differences usually ...
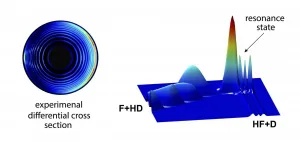
A chemical reaction can be understood in detail at the quantum state-resolved level, through a combined study of molecular crossed beam experiments and theoretical quantum molecular reaction dynamics simulations.
At a single collision condition, the molecular crossed beam apparatus is able to detect the scattering angle-resolved product with rotational state-resolution. Whereas, with accurate global potential energy surface, quantum reactive scattering theory is able to predict the corresponding reactive scattering information.
In previous studies, the chemical reaction dynamics was revealed only with the product rotational state-resolution. And the investigation of a reaction ...
Although the value of vaccines for COVID-19 may seem obvious, government action and investment in vaccines have not been commensurate with the enormous scale of benefits they offer, argue Juan Camilo Castillo and colleagues in this Policy Forum. Since even one extra month of exposure to COVID-19 kills hundreds of thousands, reduces global gross domestic product (GDP) by hundreds of billions of dollars, and generates large losses to human capital by harming education and health, expanding vaccine capacity even further would generate substantial global benefits. Castillo et al. report results of two related exercises: estimating the global benefits from vaccine capacity already in place, and estimating the benefits ...
The pandemic has made clear the threat that some viruses pose to people. But viruses can also infect life-sustaining bacteria and a Johns Hopkins University-led team has developed a test to determine if bacteria are sick, similar to the one used to test humans for COVID-19.
"If there was a COVID-like pandemic occurring in important bacterial populations it would be difficult to tell, because before this study, we lacked the affordable and accurate tools necessary to study viral infections in uncultured bacterial populations," said study corresponding author Sarah ...
Bladder cancer is more aggressive and more advanced in South Texas residents than in many parts of the country, a study by the Mays Cancer Center, home to UT Health San Antonio MD Anderson, indicates.
The disease is also deadlier in Latinos and women, regardless of where they live nationwide, according to the research.
The team from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio), which includes the Mays Cancer Center, compared bladder cancer cases in the Texas Cancer Registry with cases in the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program. SEER, which collects data on cancer cases from various locations and sources across the U.S., does not include Texas statistics.
Cases covered the years ...