INFORMATION:
*- Laurent Godet from the Coastline, Environment, Geomatics, and Teledetection laboratory (CNRS/EPHE/Université de Bretagne occidentale/Université de Caen Normandie/Université d'Angers/Université de Nantes) and Vincent Devictor from the Institute of Evolution Sciences of Montpellier. (CNRS/IRD/EPHE/Université de Montpellier).
Ecology: The scientific literature dominated by men and a handful of countries
2021-03-02
(Press-News.org) Publishing in peer-reviewed scientific journals is crucial for the development of a researcher's career. The scientists that publish the most often in the most prestigious journals generally acquire greater renown, as well as higher responsibilities. However, a team involving two CNRS researchers* has just shown that the vast majority of scientific articles in the fields of ecology and conservation biology are authored by men working in a few Western countries. They represent 90% of the 1,051 authors that have published the most frequently in the 13 major scientific journals in the field since 1945. Three quarters of these men are affiliated with institutions in just five countries (the United States, Canada, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Germany). However, there are signs of improvement, as women are increasingly among the authors that publish the most, representing 18% of the youngest authors, whereas they represent only 3% of the oldest ones. The geographic diversity of the countries in which authors work also increased markedly by 15% since 1980. Published in Conservation Letters on 2 March 2021, this study calls for combating the process of discrimination engendered by the publication system by proposing concrete measures to halt the overrepresentation of men and Western countries.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New report offers detailed analysis of Capitol Hill siege
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON (Mar. 2, 2021) -- A report released today by the George Washington University Program on Extremism reveals new information about the 257 people charged in federal court for playing a role in the Jan. 6 attack on the United States Capitol. The report, "This is Our House!" A Preliminary Assessment of the Capitol Hill Siege Participants," also provides several recommendations aimed at combating domestic extremism.
The GW Program on Extremism tracked and categorized the people charged so far in the attack and the resulting report provides a preliminary assessment of the siege participants.
"The events of Jan. 6 may mark a watershed moment for domestic violent ...
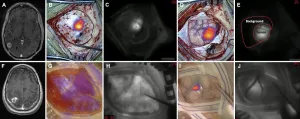
2nd window ICG predicts gross-total resection/progression-free survival in brain metastasis
2021-03-02
Charlottesville, VA (March 2, 2021). Researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania conducted a prospective cohort study utilizing their technique of delayed near-infrared imaging with high-dose indocyanine green (called "second window ICG" or "SWIG") in the identification of brain metastases during surgery. In this study, all metastatic lesions enhanced under near-infrared light with application of SWIG. The researchers compared near-infrared SWIG images obtained at the end of tumor resection with postoperative gadolinium-enhanced MRIs, considered the gold standard for imaging. The comparison demonstrated that SWIG can be used to predict the extent of gross-total resection and, ...
Coffee for the birds: connecting bird-watchers with shade-grown coffee
2021-03-02
Since 1970, bird populations in North America have declined by approximately 2.9 billion birds, a loss of more than one in four birds. Factors in this decline include habitat loss and ecosystem degradation from human actions on the landscape.
At the same time, enthusiasm for bird-watching has grown, with more than 45 million recreational participants in the United States alone. Now, researchers are looking into how to mobilize these bird enthusiasts to help limit bird population declines.
Enter bird-friendly coffee.
Bird-friendly coffee is certified organic, but its impact on the environment goes further than that: it is cultivated specifically to maintain bird habitats instead of clearing vegetation that birds and other animals rely on.
Researchers ...
New study proposes a low cost, high efficiency mask design
2021-03-02
A new paper in Oxford Open Materials Science, published by Oxford University Press, presents low cost modifications to existing N95 masks that prolongs their effectiveness and improves their reusability post disinfectants.
The COVID-19 crisis has increased demand for respiratory masks, with various models of DIY masks becoming popular alongside the commercially available N95. The utility of such masks is primarily based on the size of aerosols that they are capable of filtering out and how long they can do so effectively.
Conventional masks like the N95 use a layered system and have an efficiency ...
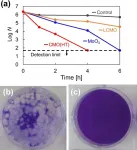
A materials science approach to combating coronavirus
2021-03-02
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology working in collaboration with colleagues at the Kanagawa Institute of Industrial Science and Technology and Nara Medical University in Japan have succeeded in preparing a material called cerium molybdate (γ-Ce2Mo3O13 or CMO), which exhibits high antiviral activity against coronavirus.
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has highlighted the urgency not only of vaccine development and rollout but also of developing innovative materials and technologies with antiviral properties that could play a vital role in helping to contain the spread of the virus.
Conventional inorganic antimicrobial materials are often prepared with metals such as copper or photocatalysts ...
High fat diets may over-activate destructive heart disease protein
2021-03-02
Peer Reviewed
Experimental
Animals
Consumption of a high fat diet may be activating a response in the heart that is causing destructive growth and lead to greater risk of heart attacks, according to new research.
In a paper published in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, researchers looked at the effect of feeding mice a high fat diet on oxidative stress levels on heart cells. The team from the University of Reading found that cells from the mice had twice the amount of oxidative stress, and led to heart cells being up to 1.8 times bigger due to cardiac hypertrophy which is associated with heart disease.
Named first author Dr Sunbal Naureen ...
Tissue, scaffold technologies provide new options for breast cancer, other diseases
2021-03-02
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New technology from Purdue University innovators may help improve tissue restoration outcomes for people with breast cancer and other diseases or traumatic injuries.
Purdue researchers, along with fellowship-trained breast surgeon Carla Fisher of Indiana University School of Medicine, teamed up with Purdue startup GeniPhys to develop and perform preclinical studies on a regenerative tissue filler.
This is a first-of-a-kind, in situ scaffold-forming collagen. When applied as a filler for soft tissue defects and voids, it shows promise for accelerating and improving tissue restoration outcomes. The team's work is published in Scientific Reports.
"It ...
Neanderthal and early modern human stone tool culture co-existed for over 100,000 years
2021-03-02
The Acheulean was estimated to have died out around 200,000 years ago but the new findings suggest it may have persisted for much longer, creating over 100,000 years of overlap with more advanced technologies produced by Neanderthals and early modern humans.
The research team, led by Dr Alastair Key (Kent) alongside Dr David Roberts (Kent) and Dr Ivan Jaric (Biology Centre of the Czech Academy of Sciences), made the discovery whilst studying stone tool records from different regions across the world. Using statistical techniques new to archaeological science, the archaeologists and conservation experts were able to reconstruct the end of the Acheulean period and re-map the archaeological record.
Previously, a more rapid shift between the earlier Acheulean stone ...
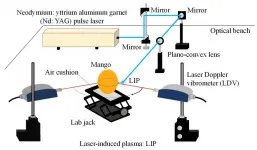
The time is ripe! An innovative contactless method for the timely harvest of soft fruits
2021-03-02
Most people are probably familiar with the unpleasant feeling of eating overripe or underripe fruit. Those who work in agriculture are tasked with ensuring a timely harvest so that ripeness is at an optimal point when the fruit is sold, both to minimize the amount of fruit that goes to waste and maximize the quality of the final product. To this end, a number of techniques to assess fruit ripeness have been developed, each with their respective advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of produce.
Although biochemical and optical methods exist, mechanical techniques are the most widely used. They indirectly assess ripeness based on the fruit's firmness. In turn, firmness ...
Rarest seal breeding site discovered
2021-03-02
Scientists have discovered a previously unknown breeding site used by the world's rarest seal species.
The Mediterranean monk seal is classified as "endangered", with a total population of about 700.
The new study - by the University of Exeter and the Society for the Protection of Turtles (SPOT) - used camera-traps to confirm breeding in caves in northern Cyprus, with at least three pups born from 2016-19 at one cave.
Only certain caves are suitable for monk seal breeding and resting, so - although the numbers are small - the researchers say urgent action is needed to protect these caves.
"This area of coastline in being developed rapidly, especially for ...