(Press-News.org) Hours before the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra, the Galápagos Islands' largest volcano, an earthquake rumbled and raised the ground more than 6 feet in an instant. The event, which triggered the eruption, was captured in rare detail by an international team of scientists, who said it offers new insights into one of the world's most active volcanoes.
"The power of this study is that it's one of the first times we've been able to see a full eruptive cycle in this detail at almost any volcano," said Peter La Femina, associate professor of geosciences at Penn State. "We've monitored Sierra Negra from when it last erupted in 2005 through the 2018 eruption and beyond, and we have this beautiful record that's a rarity in itself."
For nearly two months in 2018, lava erupted from the volcano, covering about 19 square miles of Isabela Island, the largest island in the Galápagos and home to about 2,000 people and endangered animal species like the Galápagos giant tortoise.
"The 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra was a really spectacular volcanic event, occurring in the 'living laboratory' of the Galápagos Islands," said Andrew Bell, a volcanologist at the University of Edinburgh. "Great teamwork, and a bit of luck, allowed us to capture this unique dataset that provide us with important new understanding as to how these volcanoes behave, and how we might be able to better forecast future eruptions."
While Sierra Negra is among the world's most active volcanos, its remote location previously made monitoring difficult. Scientists now use networks of ground-based seismic and GPS monitoring stations and satellite observations to observe the volcano.
"Based on constant monitoring of activity of Galapagos volcanoes, we detected a dramatic increase of seismicity and a steady uplift of crater floor at Sierra Negra," said Mario Ruiz, director of the Ecuador Geophysical Institute, the country's national monitoring agency. "Soon we contacted colleagues from the United Kingdom, United States and Ireland and proposed them to work together to investigate the mechanisms leading to an impending eruption of this volcano. This research is an example of international collaboration and partnership."
The scientists captured data over 13 years as the volcano's magma chamber gradually refilled following the 2005 eruption, stressing the surrounding crust and creating earthquakes. This continued until June 2018, when an earthquake occurred on the calderas fault system and triggered the subsequent eruption, the scientists said.
"We have this story of magma coming in and stressing the system to the point of failure and the whole system draining again through the eruption of lava flows," La Femina said. "This is the first time anyone's seen that in the Galápagos to this detail. This is the first time we've had the data to say, 'okay, this is what happened here.'"
Often during volcanic eruptions, as magma chambers empty the ground above them sinks and forms a bowl-like depression, or a caldera. But Sierra Negra experienced a caldera resurgence, leaving this area higher in elevation than it was before the eruption, the scientists said.
Inside the Sierra Negra caldera is a "trap-door fault," which is hinged at one end while the other can be uplifted by rising magma. The scientists found the fault caused hills inside of the six-mile-wide caldera to lift vertically by more than 6 feet during the earthquake that triggered the eruption.
Caldera resurgence, important to better understanding eruptions, had not been previously observed in such detail, the scientists reported in the journal Nature Communications.
"Resurgence is typical of explosive calderas at volcanoes like Yellowstone, not the kind of shield volcanoes we see in the Galápagos or Hawaii," La Femina said. "This gives us the ability to look at other volcanoes in the Galápagos and say, 'well that's what could have happened to form that caldera or that resurgent ridge.'"
The scientists said the findings could help their counterparts in Ecuador better track unrest and warn of future eruptions.
"There are people who live on Isabella Island, so studying and understanding how these eruptions occur is important to manage the hazards and risks to local populations," La Femina said.
INFORMATION:
Other Penn State researchers on the project were Machel Higgins and Andres Gorki Ruiz, doctoral students, and Nathan Meier, a former undergraduate student.
Scientists from the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Trinity College Dublin, the University of Cambridge, the University of Miami, Tulane University, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory also contributed to the study.
The National Science Foundation, NASA and the Nature Environment Research Council funded this research.
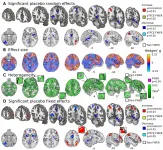
A large proportion of the benefit that a person gets from taking a real drug or receiving a treatment to alleviate pain is due to an individual's mindset, not to the drug itself. Understanding the neural mechanisms driving this placebo effect has been a longstanding question. A meta-analysis published in Nature Communications finds that placebo treatments to reduce pain, known as placebo analgesia, reduce pain-related activity in multiple areas of the brain.
Previous studies of this kind have relied on small-scale studies, so until now, researchers did not know if the neural mechanisms underlying ...
In June 2019, an international team brought the complete skull of the 3.67-million-year-old Little Foot Australopithecus skeleton, from South Africa to the UK and achieved unprecedented imaging resolution of its bony structures and dentition in an X-ray synchrotron-based investigation at the UK's national synchrotron, Diamond Light Source. The X-ray work is highlighted in a new paper in e-Life, published today (2nd March 2021) focusing on the inner craniodental features of Little Foot. The remarkable completeness and great age of the Little Foot skeleton makes it a crucially important ...
Publishing in peer-reviewed scientific journals is crucial for the development of a researcher's career. The scientists that publish the most often in the most prestigious journals generally acquire greater renown, as well as higher responsibilities. However, a team involving two CNRS researchers* has just shown that the vast majority of scientific articles in the fields of ecology and conservation biology are authored by men working in a few Western countries. They represent 90% of the 1,051 authors that have published the most frequently in the 13 major scientific journals in the field since 1945. ...
WASHINGTON (Mar. 2, 2021) -- A report released today by the George Washington University Program on Extremism reveals new information about the 257 people charged in federal court for playing a role in the Jan. 6 attack on the United States Capitol. The report, "This is Our House!" A Preliminary Assessment of the Capitol Hill Siege Participants," also provides several recommendations aimed at combating domestic extremism.
The GW Program on Extremism tracked and categorized the people charged so far in the attack and the resulting report provides a preliminary assessment of the siege participants.
"The events of Jan. 6 may mark a watershed moment for domestic violent ...
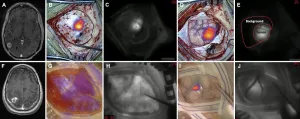
Charlottesville, VA (March 2, 2021). Researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania conducted a prospective cohort study utilizing their technique of delayed near-infrared imaging with high-dose indocyanine green (called "second window ICG" or "SWIG") in the identification of brain metastases during surgery. In this study, all metastatic lesions enhanced under near-infrared light with application of SWIG. The researchers compared near-infrared SWIG images obtained at the end of tumor resection with postoperative gadolinium-enhanced MRIs, considered the gold standard for imaging. The comparison demonstrated that SWIG can be used to predict the extent of gross-total resection and, ...
Since 1970, bird populations in North America have declined by approximately 2.9 billion birds, a loss of more than one in four birds. Factors in this decline include habitat loss and ecosystem degradation from human actions on the landscape.
At the same time, enthusiasm for bird-watching has grown, with more than 45 million recreational participants in the United States alone. Now, researchers are looking into how to mobilize these bird enthusiasts to help limit bird population declines.
Enter bird-friendly coffee.
Bird-friendly coffee is certified organic, but its impact on the environment goes further than that: it is cultivated specifically to maintain bird habitats instead of clearing vegetation that birds and other animals rely on.
Researchers ...
A new paper in Oxford Open Materials Science, published by Oxford University Press, presents low cost modifications to existing N95 masks that prolongs their effectiveness and improves their reusability post disinfectants.
The COVID-19 crisis has increased demand for respiratory masks, with various models of DIY masks becoming popular alongside the commercially available N95. The utility of such masks is primarily based on the size of aerosols that they are capable of filtering out and how long they can do so effectively.
Conventional masks like the N95 use a layered system and have an efficiency ...
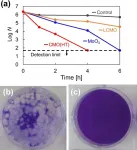
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology working in collaboration with colleagues at the Kanagawa Institute of Industrial Science and Technology and Nara Medical University in Japan have succeeded in preparing a material called cerium molybdate (γ-Ce2Mo3O13 or CMO), which exhibits high antiviral activity against coronavirus.
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has highlighted the urgency not only of vaccine development and rollout but also of developing innovative materials and technologies with antiviral properties that could play a vital role in helping to contain the spread of the virus.
Conventional inorganic antimicrobial materials are often prepared with metals such as copper or photocatalysts ...
Peer Reviewed
Experimental
Animals
Consumption of a high fat diet may be activating a response in the heart that is causing destructive growth and lead to greater risk of heart attacks, according to new research.
In a paper published in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, researchers looked at the effect of feeding mice a high fat diet on oxidative stress levels on heart cells. The team from the University of Reading found that cells from the mice had twice the amount of oxidative stress, and led to heart cells being up to 1.8 times bigger due to cardiac hypertrophy which is associated with heart disease.
Named first author Dr Sunbal Naureen ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New technology from Purdue University innovators may help improve tissue restoration outcomes for people with breast cancer and other diseases or traumatic injuries.
Purdue researchers, along with fellowship-trained breast surgeon Carla Fisher of Indiana University School of Medicine, teamed up with Purdue startup GeniPhys to develop and perform preclinical studies on a regenerative tissue filler.
This is a first-of-a-kind, in situ scaffold-forming collagen. When applied as a filler for soft tissue defects and voids, it shows promise for accelerating and improving tissue restoration outcomes. The team's work is published in Scientific Reports.
"It ...