Rapid administration of methoxyflurane versus standard care for pain management in the ED
2021-03-02
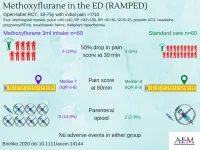
(Press-News.org) Des Plaines, IL - Initial management with inhaled methoxyflurane in the emergency department did not achieve the prespecified substantial reduction in pain, but was associated with clinically significant lower pain scores compared to standard therapy. That is the conclusion of a study titled Rapid Administration of Methoxyflurane to Patients in the Emergency Department (RAMPED) Study: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Methoxyflurane Versus Standard Care that was published recently in the February 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
According to findings of the controlled randomized trial, secondary outcomes included the pain score at multiple time points and the difference in the proportion of patients achieving a >2 point reduction on the pain numerical rating scale. Additionally, methoxyflurane use was not associated with any serious adverse events and was not associated with a significant change in opioid use among emergency department patients.
The lead author of the study is Lisa Brichko, MBBS (Hons), DCH, MHM, of the Emergency and Trauma Centre at Alfred Health in Melbourne, Australia. The findings of the study are discussed with the author in a recent AEM podcast titled The RAMPED Trial - It's a Gas, Gas, Gas.
INFORMATION:
ABOUT ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
Academic Emergency Medicine, the monthly journal of Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, features the best in peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research relevant to the practice and investigation of emergency care. The above study is published open access and can be downloaded by following the DOI link: 10.1111/acem.14144. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Tami Craig at tcraig@saem.org.
ABOUT THE SOCIETY FOR ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
SAEM is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit organization dedicated to the improvement of care of the acutely ill and injured patient by leading the advancement of academic emergency medicine through education and research, advocacy, and professional development. To learn more, visit saem.org.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-02
Northwestern Engineering researchers have developed a theoretical model to design soft materials that demonstrate autonomous oscillating properties that mimic biological functions. The work could advance the design of responsive materials used to deliver therapeutics as well as for robot-like soft materials that operate autonomously.
The design and synthesis of materials with biological functions require a delicate balance between structural form and physiological function. During embryonic development, for instance, flat sheets of embryonic cells morph through a series of folds into intricate three-dimensional structures such as branches, tubes, and furrows. These, in turn, become dynamic, three-dimensional building blocks for organs performing vital functions ...
2021-03-02
Washington, March 2, 2021--A first-of-its-kind analysis of parents' reviews of U.S. public K-12 schools, posted primarily from 2009 to 2019 on the popular school information site GreatSchools.org, found that most reviews were written by parents at schools in affluent neighborhoods and provided information that correlated strongly with test scores, a measure that closely tracks race and family income. Language associated with school effectiveness, which measures how much students improve in their test scores over time and is less correlated with demographics, was ...
2021-03-02
Eighty percent of Americans over 50 say their primary care doctor hasn't asked about their hearing in the past two years, and nearly as many - 77% -- haven't had their hearing checked by a professional in that same time, according to a new national poll report.
That's despite a growing body of evidence about the importance of hearing to other aspects of life, from dementia and risk of falls to the ability to stay connected to friends and family.
Men were more likely than women to say they'd had a recent hearing screening or test, and so were people ages 65 to 80 compared with those in ...
2021-03-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Black players in the NBA have 30% greater odds of leaving the league in any given season than white players who have equivalent performance on the court, a new study finds.
The results were driven mostly by bench players, who are the majority of those in the league, but who average less than 20 minutes of action per game.
These findings suggest that even in the NBA - a league in which Black players make up 70-75% of those on the court - African Americans face discrimination, said Davon Norris, lead author of the study and a doctoral student in sociology at The Ohio State University.
"If there is going to be anywhere in America where you would expect there wouldn't be racial ...
2021-03-02
TROY, N.Y. -- Envisioning an animal-free drug supply, scientists have -- for the first time -- reprogrammed a common bacterium to make a designer polysaccharide molecule used in pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. Published today in Nature Communications, the researchers modified E. coli to produce chondroitin sulfate, a drug best known as a dietary supplement to treat arthritis that is currently sourced from cow trachea.
Genetically engineered E. coli is used to make a long list of medicinal proteins, but it took years to coax the bacteria into producing even ...
2021-03-02
Tokyo, Japan - Humans are largely omnivores, and meat in various forms has always featured in the diet of most cultures. However, with the increasing population and pressure on the environment, traditional methods of meeting this fundamental food requirement are likely to fall short. Now, researchers at the University of Tokyo report innovative biofabrication of bovine muscle tissue in the laboratory that may help meet escalating future demands for dietary meat.
With global urbanization, the economics of animal husbandry are becoming unsustainable. From an environmental viewpoint, the land and water costs of modern mega-scale ...
2021-03-02
In a world first, an international team of researchers has read an unopened letter from Renaissance Europe - without breaking its seal or damaging it in any way.
The research, published in Nature Communications, describes how an X-ray scanner used in dental research and 'virtual unfolding' allowed the interdisciplinary team to read the contents of a securely and intricately folded letter which has remained unopened for 300 years, while preserving its valuable physical evidence.
A highly sensitive X-ray microtomography scanner, developed at ...
2021-03-02
A volcanic eruption in the Galápagos Islands has given scientists a fresh insight into how volcanoes behave and provided vital information that will help to predict future hazards on the islands.
Irish scientists, based at Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies (DIAS) and Trinity College Dublin respectively, were members of an international research team from Ireland, United Kingdom, United States, France and Ecuador that made the discovery.
The research published today (02.03.21) in Nature Communications reveals the first ever detailed description of a volcanic eruption from Sierra Negra - one ...
2021-03-02
Hours before the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra, the Galápagos Islands' largest volcano, an earthquake rumbled and raised the ground more than 6 feet in an instant. The event, which triggered the eruption, was captured in rare detail by an international team of scientists, who said it offers new insights into one of the world's most active volcanoes.
"The power of this study is that it's one of the first times we've been able to see a full eruptive cycle in this detail at almost any volcano," said Peter La Femina, associate professor of geosciences ...
2021-03-02
A large proportion of the benefit that a person gets from taking a real drug or receiving a treatment to alleviate pain is due to an individual's mindset, not to the drug itself. Understanding the neural mechanisms driving this placebo effect has been a longstanding question. A meta-analysis published in Nature Communications finds that placebo treatments to reduce pain, known as placebo analgesia, reduce pain-related activity in multiple areas of the brain.
Previous studies of this kind have relied on small-scale studies, so until now, researchers did not know if the neural mechanisms underlying ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Rapid administration of methoxyflurane versus standard care for pain management in the ED