The research, published in Nature Communications, describes how an X-ray scanner used in dental research and 'virtual unfolding' allowed the interdisciplinary team to read the contents of a securely and intricately folded letter which has remained unopened for 300 years, while preserving its valuable physical evidence.
A highly sensitive X-ray microtomography scanner, developed at Queen Mary University of London's dental research labs, was used to scan a batch of unopened letters from a 17th-century postal trunk full of undelivered mail.
The senders of these letters had closed them using 'letterlocking' - the historical process of intricately folding and securing a flat sheet of paper to become its own envelope. Letterlocking was common practice for secure communication before modern envelopes came into use, and is considered to be the missing link between ancient physical communications security techniques and modern digital cryptography.
Until now these letterpackets could only be studied and read by cutting them open, often damaging the historical documents. Now the team have been able to examine the letters' contents without irrevocably damaging the systems that secured them.
Professor Graham Davis from Queen Mary University of London said: "We designed our X-ray scanner to have unprecedented sensitivity for mapping the mineral content of teeth, which is invaluable in dental research. But this high sensitivity has also made it possible to resolve certain types of ink in paper and parchment. It's incredible to think that a scanner designed to look at teeth has taken us this far."
Dr David Mills from Queen Mary University of London said: "We've been able to use our scanners to X-ray history. The scanning technology is similar to medical CT scanners, but using much more intense X-rays which allow us to see the minute traces of metal in the ink used to write these letters. The rest of the team were then able to take our scan images and turn them into letters they could open virtually and read for the first time in over 300 years."
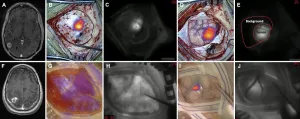
This process revealed the contents of a letter dated July 31, 1697. It contains a request from Jacques Sennacques to his cousin Pierre Le Pers, a French merchant in The Hague, for a certified copy of a death notice of one Daniel Le Pers (full transcript and images available). The letter gives a fascinating insight into the lives and concerns of ordinary people in a tumultuous period of European history, when correspondence networks held families, communities, and commerce together over vast distances.
Following the X-ray microtomography scanning of the letter packets, the international team then applied computational algorithms to the scan images to identify and separate the different layers of the folded letter and 'virtually unfold' it.
The authors suggest that the virtual unfolding method, and categorisation of folding techniques, could help researchers to understand this historical version of physical cryptography, while at the same time conserving their cultural heritage.
"This algorithm takes us right into the heart of a locked letter," the research team explains. "Sometimes the past resists scrutiny. We could simply have cut these letters open, but instead we took the time to study them for their hidden, secret, and inaccessible qualities. We've learned that letters can be a lot more revealing when they are left unopened. Using virtual unfolding to read an intimate story that has never seen the light of day - and never even reached its recipient - is truly extraordinary."
INFORMATION:
The research team includes Jana Dambrogio, Thomas F. Peterson (1957) Conservator, MIT Libraries; Amanda Ghassaei, research engineer, Adobe Research; Daniel Starza Smith, lecturer in Early Modern English Literature, King's College London; Holly Jackson, MIT undergraduate class of 2022; Erik Demaine, professor, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), MIT; Martin Demaine, robotics engineer, CSAIL, and Angelika and Barton Weller Artist-in-Residence in EECS, MIT; Graham Davis and David Mills, Queen Mary University of London, Institute of Dentistry; Rebekah Ahrendt, associate professor in the Department of Media and Culture Studies, Utrecht University; Nadine Akkerman, reader in early modern English literature, Leiden University; and David van der Linden, assistant professor in early modern history, Radboud University Nijmegen.
ENDS
For more information, please contact:
Joel Winston
Communications Manager (School of Medicine and Dentistry)
Queen Mary University of London
j.winston@qmul.ac.uk
Tel: +44 (0)7968 267 064
Notes to the editor
Dropbox links to images and animations of the scanned letter and unfolding are available here:
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1MpFB65UgUAat6pgnUgrUBDte8b4wSrgn2BBzynTzlF0/edit
A video about Queen Mary University of London and King's College London's contributions to the project is available here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?app=desktop&v=a4XLyMcNXT8&feature=youtu.be
Research paper: 'Unlocking history through automated virtual unfolding of sealed documents imaged by X-ray microtomography'. Jana Dambrogio, Amanda Ghassaei, Daniel Starza Smith, Holly Jackson, Martin L. Demaine, Graham Davis, David Mills, Rebekah Ahrendt, Nadine Akkerman, David van der Linden & Erik D. Demaine. Nature Communications. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21326-w
Available here after the embargo lifts:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21326-w
Signed, Sealed, and Undelivered, featuring an online exhibition:
http://brienne.org/.
More about letterlocking:
http://letterlocking.org/.
Letterlocking YouTube channel:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCNPZ-f_IWDLz2S1hO027hRQ.
About Queen Mary University of London
At Queen Mary University of London, we believe that a diversity of ideas helps us achieve the previously unthinkable.
In 1785, Sir William Blizard established England's first medical school, The London Hospital Medical College, to improve the health of east London's inhabitants. Together with St Bartholomew's Medical College, founded by John Abernethy in 1843 to help those living in the City of London, these two historic institutions are the bedrock of Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry.
Today, Barts and The London continues to uphold this commitment to pioneering medical education and research. Being firmly embedded within our east London community, and with an approach that is driven by the specific health needs of our diverse population, is what makes Barts and The London truly distinctive.
Our local community offer to us a window to the world, ensuring that our ground-breaking research in cancer, cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases, and population health not only dramatically improves the outcomes for patients in London, but also has a far-reaching global impact.
This is just one of the many ways in which Queen Mary is continuing to push the boundaries of teaching, research and clinical practice, and helping us to achieve the previously unthinkable.